HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 4- The Forces- 1 | HC Verma Solutions - JEE PDF Download
Short Answers
Q.1. A body of mass m is placed on a table. The earth is pulling the body with a force mg. Taking this force to be the action what is the reaction?
The Earth is pulling the body with an action force mg. This force is exerted by the body on the table. In turn, the table exerts equal and opposite reaction force (-mg) on the body in the upwards direction which balances the weight of the body.
Q.2. A boy is sitting on a chair placed on the floor of a room. Write as many action-reaction pairs of forces as you can.
The given situation involves two action-reaction pairs of forces. They are :
(a) The action force (F = mg) with which the boy pushes the chair in the downward direction and the reaction force (F' = −mg) with which the chair exerts on the boy in the upward direction.
(b) The action force (F = (M + m)g) with which the boy and the chair push the ground in the downward direction and the reaction force (F' = (M + m)g) with which the ground exerts on the boy and the chair in the upward direction.
Q.3. A lawyer alleges in court that the police had forced his client to issue a statement of confession. What kind of force is this ?
The police may beat the lawyer's client until he issues a statement of confession. This force does not have any physical significance in physics. Hence, it is not a force of physics.
Q.4. When you hold a pen and write on your notebook, what kind of force is exerted by you on the pen? By the pen on the notebook? By you on the notebook?
When we hold a pen and write on our notebook, we are exerting electromagnetic force on the pen. The pen is also exerting the same force on the notebook. We are also exerting gravitational force on the notebook.
Q.5. Is it true that the reaction of a gravitational force is always gravitational, of an electromagnetic force is always electromagnetic and so on?
Yes, it is true that the reaction of a gravitational force is always gravitational and that of an electromagnetic force is always electromagnetic and so on. For example, if the Earth exerts a gravitational action force on the Moon, then the Moon will also exert the same gravitational reaction force on it. Similarly, when a comb, just after being used, is brought near a piece of paper, it exerts an electromagnetic action force on the paper and the paper will also exert an electromagnetic reaction force on it.
Q.6. Suppose the magnitude of Nuclear force between two protons varies with the distance between them as shown in figure. Estimate the ratio "Nuclear force/Coulomb force" for
(a) x = 8 fm
(b) x = 4 fm
(c) x = 2 fm
(d) x = 1 fm (1 fm = 10 −15m).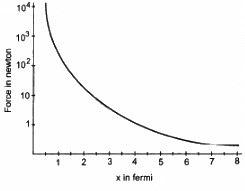
First let us calculate the coulomb force between 2 protons for distance = 8 fm
Q.7. List all the forces acting on the block B in figure.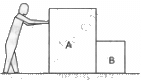
Forces acting on block B :
- A pair of electromagnetic forces between the blocks A and B.
- A pair of electromagnetic forces between the blocks B and the Earth.
- A pair of gravitational forces between the blocks B and the Earth.
- A pair of gravitational forces between the blocks A and B.
- A pair of action-reaction forces between the man and block A.
- Weight of the man, block A and block B as action forces on the ground in the downward direction.
- Reaction of the ground on the man, block A and block B in the upward direction to balance their weights.
Q.8. List all the forces acting on (a) the pulley A, (b) the boy and (c) the block C in figure.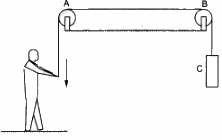
Forces acting on the pulley A :
- A tension exerts electromagnetic force between the string and pulley A.
- A pair of gravitational force between the Earth and pulley.
Forces acting on the boy :
- A tension exerts electromagnetic force between the string and the boy.
- A pair of gravitational force between the Earth and the boy.
Forces acting on the block C :
- A tension exerts electromagnetic force between the string and block C.
- A pair gravitational force between block C and the Earth.
Q.9. Figure shows a boy pulling a wagon on a road. List as many forces as you can which are relevant with this figure. Find the pairs of forces connected by Newton's third law of motion.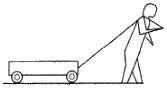
List of forces :
(a) A pair of gravitational force between the wagon and the Earth.
(b) A frictional force exerted by the road on the wagon.
(c) A tension exerts electromagnetic force between the wagon and string.
(d) A pair of gravitational force between the man and the Earth.
(e) A frictional force exerted by the road on the man.
(f) A tension exerts electromagnetic force between the man and string.
Here, (a), (c), (d) and (f) are pairs of forces associated with Newton's third law of motion.
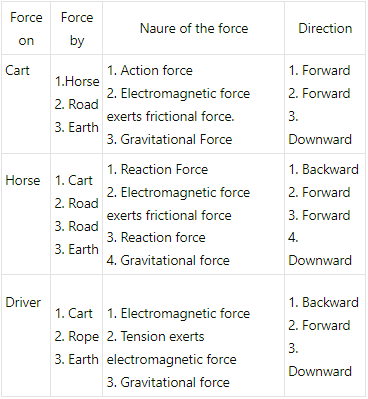
Q.10. Figure shows a cart. Complete the table shown below.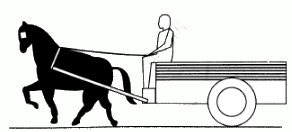
Multiple Choice Questions
|
134 docs
|
FAQs on HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 4- The Forces- 1 - HC Verma Solutions - JEE
| 1. What are the different types of forces? |  |
| 2. How is the net force calculated? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between mass and weight? |  |
| 4. How does friction affect motion? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of Newton's laws of motion? |  |

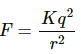
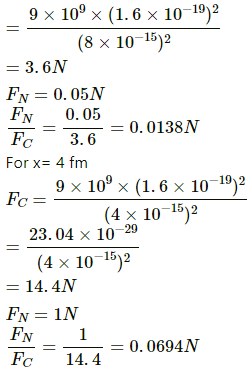
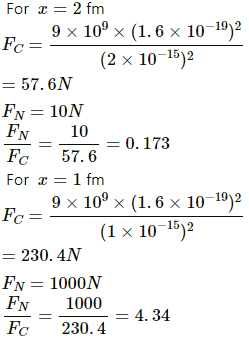
 connected by Newton's third law are known as action-reaction pair.
connected by Newton's third law are known as action-reaction pair.














