UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 22nd February 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Tamil-Brahmi script

Why in News?
Artefacts with Tamil-Brahmi script unearthed at Keeladi to find a special place in the museum.
About River Vaigai:
- Vaigai is a river in Tamil Nadu.
- The river is also referred to as Shiva Ganga in many places.
- The river originates in the Varusanadu Hills, the Periyar Plateau of the Western Ghats range.
- The river finally empties into the Palk Strait
- Its main tributaries are Suruliyaru, Mullaiyaru, Varaaga Nadhi, Manjalaru, Kottagudi, Kridhumaal and Upparu.
- The Vattaparai Falls are located on this river.
About Tamil-Brahmi script:
- Tamil-Brahmi, was a variant of the Brahmi script in southern India.
- It was used to write inscriptions in the early form of old Tamil.
- The Tamil-Brahmi script has been paleographically and stratigraphically dated between the third century BCE and the first century CE.
- It constitutes the earliest known writing system evidenced in many parts of Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh, and Sri Lanka.
- It is also known as Tamizhi or Damili.
About Brahmi script:
- Brahmi was the main script used in India since the 3rd century.
- The Ashokan inscriptions dating to the third century BCE used the Brahmi script, and are the earliest evidence of the use of Brahmi.
- It is the ancestor of the Brahmic family of scripts, which includes all Indian scripts, like Devanagari, Odia, Gujarati, Tamil, Telugu, etc from India, and some of the ancient scripts of Sri Lanka, Burma, and south-east Asian countries of Java, Sumatra, and Cambodia.
- James Prinsep was responsible for deciphering Brahmi in 1838.
About Sangam Age:
- The period roughly between the 3rd century B.C. and 3rd century A.D. in South India (the area lying to the south of river Krishna and Tungabhadra) is known as Sangam Period.
- The Sangam literature includes Tolkappiyam, Ettutogai, Pattuppattu, Pathinenkilkanakku, and two epics named – Silappathikaram and Manimegalai.
- The first Sangam, held at then Madurai, was attended by gods and legendary sages but no literary work of this Sangam is available.
- The second Sangam was held at Kapadapuram, but all the literary works had perished except Tolkappiyam.
- The third Sangam at Madurai was founded by Mudathirumaran. It was attended by a large number of poets who produced voluminous literature, but only a few survived.
Source: The Hindu
GS-II
NAVDEX 23 and IDEX 23

Why in News?
Indian Naval Ship Sumedha reached Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates to participate in Naval Defence Exhibition – NAVDEX 23 and International Defence Exhibition – IDEX 23
About INS SUMEDHA:
- INS Sumedha is the third ship of the indigenously built Saryu class Naval Offshore Patrol Vessels (NOPV)which was commissioned into the Indian Navy in 2014.
- The ship has been designed and built by Goa Shipyard Limited.
- The first INS SUMEDHA was built in Goa and was commissioned in the Indian Navy in 2011.
About NAVDEX 23 and IDEX 23:
- IDEX and NAVDEX, and the International Defense Conference are organized by the Abu Dhabi National Exhibitions Company (ADNEC), in cooperation with the Ministry of Defense and the General Command of the UAE Armed Forces.
- IDEX/NAVDEX takes place biennially.
- The exhibitions showcase the latest technologies and innovations in the global defense sector, support the growth of UAE’s defense industry, and forge new relationships between major international companies.
- IDEX is the only international defense exhibition and conference in the MENA (Middle East and North Africa region) region which includes countries like Algeria, Bahrain, Egypt, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Libya, Morocco, Oman, Palestine, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Tunisia, United Arab Emirates, and Yemen.
About India and UAE Defense Relations:
- Desert Eagle II, a ten-day air combat exercise, was held between the air forces of India and UAE.
- The inaugural edition of the Indian & UAE Navy bilateral exercise GULF STAR-1 was conducted in March 2018.
Source: All India Radio
Deputy Speaker Is An Officer of Parliament
Why in News?
The present Lok Sabha has not elected a Deputy Speaker even after three years and seven months of its term, and the non-election has reached the Supreme Court, which has reportedly sent notice to the Union government; historically, a Deputy Speaker is as important as the Speaker for the House.
What is the practice?
- Two presiding officers in Lok Sabha: There are two presiding officers for the Lok Sabha, namely the Speaker and the Deputy Speaker, who are elected by the members of the House.
- Article 93 of the constitution: Under Article 93 of the Constitution, as soon as the House meets after the election these two presiding officers are elected one after the other.
- Practice of electing speaker and deputy speaker: The practice followed so far has been to elect the Speaker after the oath-taking. Thereafter, within a few days, the Deputy Speaker is also elected.
Office of Deputy Speake Speaker of the Lok Sabha
- The Deputy Speaker of the Lok Sabha is not subordinate to the speaker of Lok Sabha; is responsible for the Lok Sabha. and
- He/she is the second-highest-ranking legislative officer of the Lok Sabha.
- He/ She acts as the presiding officer in case of leave of absence caused by death or illness of the Speaker of the Lok Sabha.
Pin this Note
- It is by convention that the position of Deputy Speaker is offered to the opposition party in India.
- But if a government does not favour an Opposition member for political reasons, it is free to choose a member from its own party.
The Historical Significance of the office
- Government of India Act of 1919: The history of the office of Deputy Speaker goes back to the government of India Act of 1919 when he was called Deputy President as the Speaker was known as the president of the central legislative assembly.
- Role is necessary to share the responsibility of running the House: Although the main functions of a Deputy Speaker were to preside over the sittings of the assembly in the absence of the Speaker and chair the select committees etc., the position was considered necessary to share the responsibility of running the House with the Speaker and guide the nascent committees.
Did you know?
- The first Speaker was G V Mavalankar and the first Deputy Speaker was M Ananthasayanam Ayyangar who was elected by the Constituent Assembly (Legislative) on September 3, 1948.
- Later under the new Constitution, M Ananthasayanam Ayyangar was elected the first Deputy Speaker of the House of the people on May 28, 1952.
Importance of the Office
- Powers Under Article 95(1) of the Constitution: The Deputy Speaker gets all the powers of the Speaker when the office of the Speaker is vacant, so the Deputy Speaker can also determine the petitions relating to disqualification under the 10th Schedule of the Constitution.
- Speaker is powerless in matters of revising: The Speaker is powerless in the matter of revising or overruling a decision of the Deputy Speaker. No appeal lies to the Speaker against a ruling given by the Deputy Speaker.
Conclusion
Although the Deputy Speaker gets to exercise these powers only in the absence of the Speaker his decisions are final and binding when he gives a ruling. In the eventuality of the Speaker remaining absent for a longer time due to illness or otherwise the government will have to grapple with the unpredictability of a ruling or an adverse decision by a Deputy Speaker who comes from the Opposition ranks. Article 93 contains a mandatory provision which needs to be carried out by the House.
Source: Indian Express
Children have a Right to protect their Genetic Information from DNA tests: SC

Why in News?
The Supreme Court of India has ruled that children have the right to protect their genetic information from being revealed in DNA tests without their consent.
Right to protect Genetic Information
- The right to protect genetic information is a fundamental right that recognizes an individual’s autonomy and control over their own personal and intimate genetic data.
- It allows individuals to make informed decisions about their health, privacy, and identity.
- In India, the Supreme Court has also held that children have the right to protect their genetic information from DNA testing in divorce proceedings, as it is part of their fundamental right to privacy.
- This is guaranteed under Article 21 of Indian Constitution.
- This right is recognized under various international human rights instruments, including the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights.
Key takeaways from the Judgment
The court ruled that-
- Genetic information is personal and intimate
- Children have the right to privacy and bodily integrity
- Children are not to be regarded like material objects and should not become the focal point of the battle between spouses
- Allowing DNA tests would also harm the reputation and dignity of the mother
Basis of this judgment
- The court drew attention to the rights of privacy, autonomy and identity recognised under the United Nations’ Convention on the Rights of the Child.
- It acknowledged the control that individuals, including children, have over their own personal boundaries and the means by which they define who they are in relation to other people.
- Children are not to be deprived of this entitlement to influence and understand their sense of self simply by virtue of being children.
How can one get the tests done?
- Family courts should direct for a DNA test only in expedient situations and in the interest of justice, as a last resort, said the judgment.
- This should be practised as the option of last resort.
Source: PIB
GS-III
Oder river
Why in News?
A new report by the European Union (EU), has confirmed that the ecological disaster that killed hundreds of tonnes of fish in the Oder river in 2022 was caused by toxic algal bloom .
About River Oder:
- Oder River, is a river in east-central Europe.
- It is one of the most significant rivers in the catchment basin of the Baltic Sea, second only to the Vistula in discharge and length.
- It is Poland’s second-longest river.
- The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows through western Poland, later forming the border between Poland and Germany.
About Algal Blooms:
- An algal bloom is a rapid increase in the population of algae in an aquatic system. These are also called ‘red tides
- They may occur in freshwater as well as marine environments.
- Algal Blooms deprive aquatic organisms of Sunlight and oxygen and negatively impact a variety of species that live below the water surface.
- Harmful Algal Blooms( HABs)- colonies of algae that grow out of control and produce toxic or harmful effects on people, fish, shellfish, marine mammals, and birds.
- Algal blooms in freshwater lakes and reservoirs are most commonly caused by blue-green algae (also known as cyanobacteria) whose growth is supported by Eutrophication (nutrient enrichment).
- Another type of bloom that occurs nearly every summer along Florida’s Gulf Coast is caused by a species of dinoflagellate known as Karenia brevis.
- Algal Bloom Information Service: ABIS provides timely information on harmful algal blooms, which are detrimental to coastal fisheries, and water quality and also tend to induce respiratory problems within the coastal population from time to time.
- ISRO’s Oceansat-2 satellite launched in 2009 can cover larger areas and provide global ocean color.
SOURCE: The Hindu
India, Singapore launch UPI-PayNow Linkage

Why in News?
India’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI) and Singapore’s PayNow were officially connected to allow a “real-time payment linkage”.
What are UPI and PayNow?
- Unified Payments Interface (UPI)
- UPI is India’s mobile-based fast payment system, which facilitates customers to make round-the-clock payments instantly, using a Virtual Payment Address (VPA) created by the customer.
- It eliminates the risk of sharing bank account details by the remitter.
- UPI supports both Person-to-Person (P2P) and Person-to-Merchant (P2M) payments and it also enables a user to send or receive money.
- PayNow
- It is a fast payment system in Singapore.
- It enables peer-to-peer funds transfer service, available to retail customers through participating banks and Non-Bank Financial Institutions (NFIs) in Singapore.
- It allows users to send and receive instant funds from one bank or e-wallet account to another in Singapore by using just their mobile number, Singapore National Registration Identity Card (NRIC)/Foreign Identification Number (FIN), or VPA.
What is the UPI-PayNow linkage?
- Cross-border retail payments are generally less transparent and more expensive than domestic transactions.
- The project to link both the fast payment systems was initiated in September 2021 to facilitate faster, more efficient and transparent cross-border transactions relating to trade, travel and remittances between the two countries.
Significance of the integration
- Enhanced cross-border transactions: The integration will enable easier cross-border transactions between India and Singapore, reducing the need for intermediaries and associated costs.
- Easier remittances: The integration will make it easier for Indian workers in Singapore to send money back home to their families.
- Boost to trade and investment: The integration will facilitate smoother transactions between businesses in the two countries, potentially increasing trade and investment.
- Strengthening of diplomatic ties: The integration is expected to improve diplomatic ties between India and Singapore.
How the integration works?
- The integration is made possible through the use of standardized QR codes.
- The QR codes will allow users to transfer funds between the two systems in real-time, without the need for intermediaries.
Implications for the future
- More integrations: The success of the UPI-PayNow integration could pave the way for similar integrations between other countries.
- Increased use of digital payments: The integration is expected to encourage the adoption of digital payments in both India and Singapore, potentially reducing the use of cash.
Source: The Hindu
Services trade restrictiveness index (STRI)
Why in News?
India’s rank in the Services trade restrictiveness index (STRI) improved a notch to 47 from 48 among 50 countries surveyed by the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
About STRI:
- The STRI provides a snapshot of services regulatory regimes to help policymakers to assess reform options.
- The index takes into consideration different sectors like road freight cover, air transport, government regulations, etc.
- It is a unique, evidence-based tool that provides information on regulations affecting trade in services in 22 sectors across all OECD member countries and Brazil, the People’s Republic of China, India, Indonesia, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Peru, Singapore, South Africa, Thailand, and Vietnam.
India’s performance on STRI:
- lowest scoring sectors (least restricted): computer services, engineering services, sound recording, and road freight transport.
- highest scoring sectors (most restrictive): architecture service, rail freight transport, accounting services, and legal services.
- Government dominance: The railway sector in India is highly restrictive due to the dominance of the Indian government in it.
- Market access for foreigners: Market access to certain key service sectors remains prohibited for foreigners or is subjected to stringent conditions.
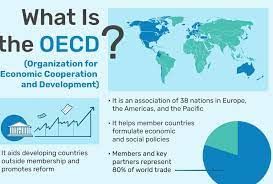
About OECD:
- It is an inter-governmental economic organization, founded to stimulate the economic progress of the world.
- It was founded in 1961.
- Its Headquarters are in Paris.
- It has 36 members. India is not a member but a key economic partner.
- Reports and Indices by OECD: International migration outlook, OECD better life index.
Source: Business Standard
|
44 videos|5271 docs|1113 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 22nd February 2023 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are the three General Studies papers in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of GS-II in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of current affairs in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 4. Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs for the UPSC exam? |  |
| 5. How can one effectively prepare for the General Studies papers in the UPSC exam? |  |


















