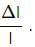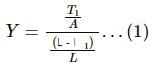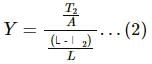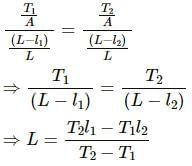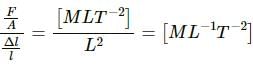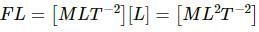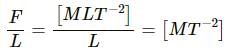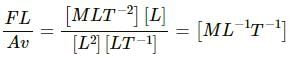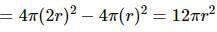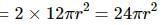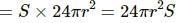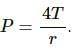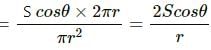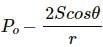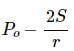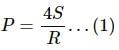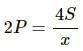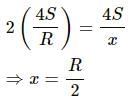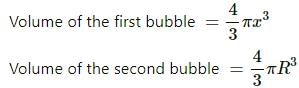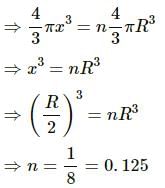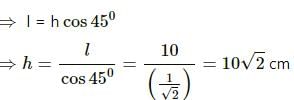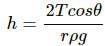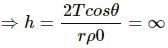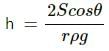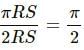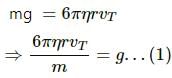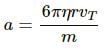Short Answers
Q.1. The ratio stress/strain remain constant for small deformation of a metal wire. When the deformation is made larger, will this ratio increase or decrease?
The ratio of stress to strain will decrease.
Beyond the elastic limit, the body loses its ability to restore completely when subjected to stress. Thus, there occurs more strain for a given stress. At some points, however, the body undergoes strain without the application of stress. So, the ratio of stress to strain decreases.
Q.2. When a block a mass M is suspended by a long wire of length L, the elastic potential potential energy stored in the wire is (1/2) × stress × strain × volume. Show that it is equal to (1/2) Mgl, where l is the extension. The loss in gravitational potential energy of the mass earth system is Mgl. Where does the remaining (1/2) Mgl energy go?
Let the CSA of the wire be A.
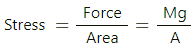
Strain = I/L
Volume = AL
We need to calculate the elastic potential energy stored in the wire which is given to be equal to (1/2) x Stress x Strain x Volume.
Elastic potential energy = (1/2) x Stress x Strain x Volume
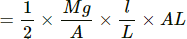
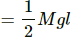
The other 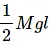 is converted into kinetic energy of the mass.
is converted into kinetic energy of the mass.
When the mass leaves its initial point on the spring, it acquires a velocity as it moves down. The velocity reaches its maximum at the end point. The spring oscillates. Finally, when the kinetic energy is dissipated into heat, the spring comes to rest.
Q.3. When the skeleton of an elephant and the skeleton of a mouse are prepared in the same size, the bones of the elephant are shown thicker than those of the mouse. Explain why the bones of an elephant are thicker than proportionate. The bones are expected to withstand the stress due to the weight of the animal.
The elephant has a greater weight than a mouse, but the material that makes their bones is the same. This means that in order to sustain an elephant's weight, one's bones need to suffer less stress. Stress = Force/area. A greater cross-sectional area reduces stress on the bones. This is why an elephant's bones are thicker.
Q.4. The yield point of a typical solid is about 1%. Suppose you are lying horizontally and two persons are pulling your hands and two persons are pulling your legs along your own length. How much will be the increase in your length if the strain is 1% ? Do you think your yield point is 1% or much less than that?
Let my length = L
Let the increase in length = l
Strain
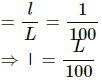
So, the increase in length will be L/100.
Yes, the yield point is much less than the 1% strain because the human body consists of joints and not one uniform solid structure.
Q.5. When rubber sheets are used in a shock absorber, what happens to the energy of vibration?
The energy of vibration dissipates as heat from the shock absorber.
Q.6. If a compressed spring is dissolved in acid, what happened to the elastic potential energy of the spring?
When a compressed spring dissolves in an acid, the acid molecules leave the sold lattice of the spring faster than the uncompressed spring. This in turn increases the kinetic energy of the solution. As a result, the temperature of the acid also increases. However, this temperature increase will be very small because the mechanical energy content in the spring is lesser than its chemical energy content.
Q.7. A steel blade placed gently on the surface of water floats on it. If the same blade is kept well inside the water, it sinks. Explain.
It floats because of the surface tension of water. The surface of water behaves like a stretched membrane. When a blade is placed on the water surface, it's unable to pierce the stretched membrane of water due to its low weight and remains floating.
However, if the blade is placed below the surface of water, it no longer experiences the surface tension and sinks to the bottom as the density of the blade is greater than that of water.
Q.8. When some wax is rubbed on a cloth, it becomes waterproof. Explain.
A liquid wets a surface when the angle of contact of the liquid with the surface is small or zero. Due to its fibrous nature, cloth produces capillary action when in contact with water. This makes clothes have very small contact angles with water. When wax is rubbed over cloth, the water does not wet the cloth because wax has a high contact angle with water.
Q.9. The contact angle between pure water and pure silver is 90°. If a capillary tube made of silver is dipped at one end in pure water, will the water rise in the capillary?
No, the water will neither rise nor fall in the silver capillary.
According to Jurin's law, the level of water inside a capillary tube is given by
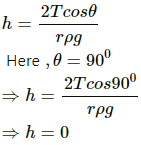
Thus, the water level neither rises nor falls.
Q.10. It is said that a liquid rises or is depressed in capillary due to the surface tension. If a liquid neither rises nor depresses in a capillary, can we conclude that the surface tension of the liquid is zero?
No, we cannot conclude the surface tension to be zero solely by the fact that the liquid neither rises nor falls in a capillary.
The height of the liquid inside a capillary tube is given by 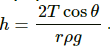 From the equation, we see that the height (h) of the liquid may also be zero if the contact angle θ between the liquid and the capillary tube is 90° or 270°.
From the equation, we see that the height (h) of the liquid may also be zero if the contact angle θ between the liquid and the capillary tube is 90° or 270°.
Q.11. The contact angle between water and glass is 0°. When water is poured in a glass to the maximum of its capacity, the water surface is convex upward. The angle of contact in such a situation is more than 90°. Explain.
When water is poured in a glass, it reaches the brim and rises further. The edge of the glass lies below the water level. In this case, the force of attraction due to molecules of the glass surface is not perpendicular to the solid. Here, the contact angle can be greater than the standard contact angle for a pair of substances.
Q.12. A uniform vertical tube of circular cross section contains a liquid. The contact angle is 90°. Consider a diameter of the tube lying in the surface of the liquid. The surface to the right of this diameter pulls the surface on the left of it. What keeps the surface on the left in equilibrium?
As the angle of contact is 0, there is no force between the surface of the tube and the liquid. The diameter of the liquid surface is pulled on both sides by equal and opposite forces of surface tension. This results in no net force remaining on the surface of the liquid. Hence, the liquid stays in equilibrium.
Q.13. When a glass capillary tube is dipped at one end in water, water rises in the tube. The gravitational potential energy is thus increased. Is it a violation of conservation of energy?
No, it does not violate the principle of conservation of energy.
There is a force of attraction between glass and water, which is why the liquid rises in the tube. However, when water and glass are not in contact, there exists a potential energy in the system. When they are brought into contact, this potential energy is first converted into kinetic energy, which lets the liquid rush upwards in the tube, and then into gravitational potential energy. Therefore, energy is not created in the process.
Q.14. If a mosquito is dipped into water and released, it is not able to fly till it is dry again. Explain?
A mosquito thrown into water has its wings wetted. Now, wet wing surfaces tend to stick together because of the surface tension of water. This does not let the mosquito fly.
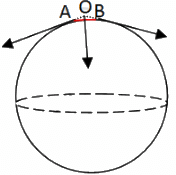
Q.15. The force of surface tension acts tangentially to the surface whereas the force due to air pressure acts perpendicularly on the surface. How is then the force due to excess pressure inside a bubble balanced by the force due to the surface tension?
The forces act tangentially to the bubble surface on both sides of a given line but they have one component normal to the bubble surface. This component balances the force due to excess pressure inside the bubble.
In the figure, let us consider a small length AB on the surface of the spherical bubble. Let the surface forces act tangentially along A and B. On producing the forces backwards, they meet at a point O. By the parallelogram law of forces, we see that the resultant force acts opposite to the normal. This balances the internal forces due to excess pressure.
Q.16. When the size of a soap bubble is increased by pushing more air in it, the surface area increases. Does it mean that the average separation between the surface molecules is increased?
No. The average intermolecular distances do not increase with an increase in the surface area.
A soap bubble's layer consists of several thousand layers of molecules. An increase in the surface area causes the surface energy to also increase. This in turn allows more and more molecules from the inner liquid layers of the bubble to attain potential energy, enabling them to enter the outer surface of the bubble. Hence, the surface area increases.
Q.17. Frictional force between solids operates even when they do not move with respect to each other. Do we have viscous force acting between two layers even if there is no relative motion?
No. For a liquid at rest, no viscous forces exist.
Viscous forces oppose relative motion between the layers of a liquid. These layers do not exist in a liquid that is at rest. Therefore, it is obvious that viscous forces are non-existent in a static liquid.
Q.18. Water near the bed of a deep river is quiet while that near the surface flows. Give reasons.
The motion of any liquid is dependent upon the amount of stress acting on it. The motion of one layer of liquid is resisted by the other due to the property of viscosity. A river bed remains in a static state. Therefore, any immediate layer of liquid in contact with the river bed will also remain static due to the frictional force. However, the next layer of liquid above this static layer will have a greater velocity due to lesser resistance offered by the static layer. Moving upwards, subsequent layers provide lesser and lesser resistance to the movement of the layers above it. Finally, the topmost layer acquires the maximum velocity. Therefore, for a river, the surface waters flow the fastest.
Q.19. If water in one flask and castor oil in other are violently shaken and kept on a table, which will come to rest earlier?
Castor oil will come to rest more quickly because it has a greater coefficient of viscosity than water. Castor oil has a higher viscosity than water. It will therefore, lose kinetic energy and come to rest faster than water.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:A rope 1 cm in diameter breaks if the tension in it exceeds 500 N. The maximum tension that may be given to a similar rope of diameter 2 cm is
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:The breaking stress of a wire depends on
Explanation
Breaking stress depends upon the intermolecular/ inter-atomic forces of attraction within materials. In other words, it depends upon the material of the wire.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:A wire can sustain the weight of 20 kg before breaking. If the wire is cut into two equal parts, each part can sustain a weight of
Explanation
As the wire is cut into two equal parts, both have equal cross-sectional areas. Therefore, a weight of 20 kg exerts a force of 20g on both the pieces. Breaking stress depends upon the material of the wire. Since 20g of force is exerted on wires with equal cross-sectional areas, both the wires can sustain a weight of 20 kg.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:Two wires A and B are made of same material. The wire A has a length l and diameter rwhile the wire B has a length 2l and diameter r/2. If the two wires are stretched by the same force, the elongation in A divided by the elongation in B is
Explanation
Let the Young's modulus of the wire's material be Y.
Here:
Force = F
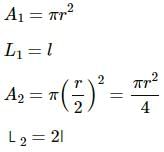
Let the elongation in A be x and that in B be y.
Since the Young's modulus for both the wires is the same:
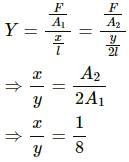
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:A wire elongates by 1.0 mm when a load W is hung from it. If this wire goes over a a pulley and two weights W each are hung at the two ends, he elongation of he wire will be
Explanation
Let the Young's modulus of the material of the wire be Y.
Force = Weight = W (given)
Let C . S . A . = A
x = 1 mm = Elongation in the first case
Length = L
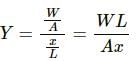
Let y be the elongation on one side of the wire when put in a pulley.
When put in a pulley, the length of the wire on each side = L/2
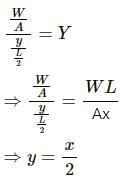
Total elongation in the wire = 2y = 2(x/2) = x = 1 mm
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:A heave uniform rod is hanging vertically form a fixed support. It is stretched by its won weight. The diameter of the rod is
Explanation
As the rod is of uniform mass distribution and stretched by its own weight, the topmost part of the rod experiences maximum stress due to the weight of the entire rod. This stress leads to lateral strain and the rod becomes thinner. Moving down along the length of the rod, the stress decreases because the lower parts bear lesser weight of the rod. With reduced stress, the lateral strain also reduces. Hence, the diameter of the rod gradually increases from top to bottom.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:When a metal wire is stretched by a load, the fractional change in its volume ∆V/V is proportional to
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:The length of a metal wire is l1 when the tension in it T1 and is l2 when the tension is T2. The natural length of the wire is
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:A heavy mass is attached to a thin wire and is whirled in a vertical circle. The wire is most likely to break
Explanation
If the velocity of the mass is a maximum at the bottom, then the string experiences tension due to both the weight of the mass and the high centrifugal force. Both these factors weigh the mass downwards. The tension is therefore, maximum at the lowest point, causing the string to most likely break at the bottom.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:When a metal wire elongates by hanging a load on it, the gravitational potential energy is decreased.
Explanation
None of these is the correct option. The decreased gravitational potential energy transforms partly as elastic energy, partly as kinetic energy and also in the form of dissipated heat energy.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:By a surface of a liquid we mean
Explanation
The surface of a liquid refers to the layer of molecules that have higher potential energy than the bulk of the liquid. This layer is typically 10 to 15 times the diameter of the molecule. Now, the size of an average molecule is around 1 nm = 10-9m, so a diameter of 10 to 15 times would be of order 10 x 10-9 = 10-8m.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:An ice cube is suspended in vacuum in a gravity free hall. As the ice melts it
Explanation
As the ice cube melts completely, the water thus formed will have minimum surface area due to its surface tension. Any state of matter that has a minimum surface area to its volume takes the shape of a sphere. Therefore, as the ice melts, it will take the shape of a sphere.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:When water droplets merge to form a bigger drop
Explanation
As the water droplets merge to form a single droplet, the surface area decreases. With this decrease in surface area, the surface energy of the resulting drop also decreases. Therefore, extra energy must be liberated from the drop in accordance with the conservation of energy.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:The dimension ML−1T−2 can correspond to
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:Air is pushed into a soap bubble of radius r to double its radius. If the surface tension of the soap solution in S, the work done in the process is
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:If more air is pushed in a soap bubble, the pressure in it
Explanation
Excess pressure inside a bubble is given by: 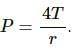
When air is pushed into the bubble, it grows in size. Therefore, its radius increases. An increase in size causes the pressure inside the soap bubble to decrease as pressure is inversely proportional to the radius.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:If two soap bubbles of different radii are connected by a tube,
Explanation
The smaller bubble has a greater inner pressure than the bigger bubble. Air moves from a region of high pressure to a region of low pressure. Therefore, air moves from the smaller to the bigger bubble.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
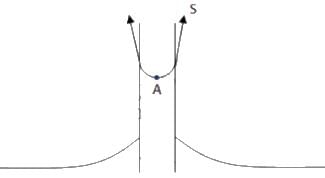
Try yourself:Figure shows a capillary tube of radius r dipped into water. If the atmospheric pressure is P0, the pressure at point A is
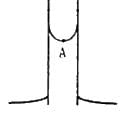
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:The excess pressure inside a soap bubble is twice the excess pressure inside a second soap bubble. The volume of the first bubble is n times the volume of the second where n is
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
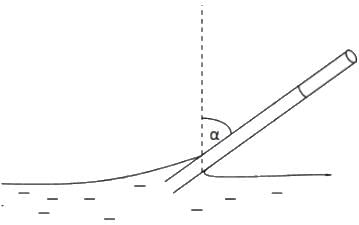
Try yourself:Water rises in a vertical capillary tube up to a length of 10 cm. If the tube is inclined at 45°, the length of water risen in the tube will be
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:A 20 cm long capillary tube is dipped in water. The water rises up to 8 cm. If the entire arrangement is put in a freely falling elevator, the length of water column in the capillary tube will be
Explanation
Height of water column in capillary tube is given by:
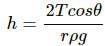
A free falling elevator experiences zero gravity.
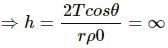
But, h = 20 cm (given)
Therefore, the height of the water column will remain at a maximum of 20 cm.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:Viscosity is a property of
Explanation
Viscosity is one property of fluids. Fluids include both liquids and gases.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:The force of viscosity is
Explanation
The force of viscosity arises from molecular interaction between different layers of fluids that are in motion. Molecular forces are electromagnetic in nature. Therefore, viscosity must also be electromagnetic.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:The viscous force acting between two layers of a liquid is given by 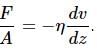 This F/A may be called
This F/A may be called
Explanation
The viscous force acts tangentially between two parallel layers of a liquid. In terms of force on a material, it is analogous to a shearing force.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:A raindrop falls near the surface of the earth with almost uniform velocity because
Explanation
Air has viscosity. During rainfall, the raindrops acquire acceleration due to gravity. However, the increase in velocity is hindered by the viscous force acting upwards. A gradual balance between the two opposing forces causes the raindrops to attain a terminal velocity, thus, falling with a uniform velocity.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:A piece of wood is taken deep inside a long column of water and released. It will move up
Explanation
The density of wood is less than that of water.When a piece of wood is immersed deep inside a long column of water and released, it experiences a buoyant force that gives it an upward acceleration. The velocity of wood increases as its motion is accelerated by the buoyant force. However, the viscous drag force acts simultaneously to oppose its upward motion. As a result, the initial acceleration decreases and the wood rises with a decreasing upward acceleration.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:A solid sphere falls with a terminal velocity of 20 m s−1 in air. If it is allowed to fall in vacuum,
Explanation
In vacuum, no viscous force exists. The sphere therefore, will have constant acceleration because of gravity. An accelerated motion implies that it won't have uniform velocity throughout its motion. In other words, there will be no terminal velocity.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:A spherical ball is dropped in a long column of a viscous liquid. The speed of the ball as a function of time may be best represented by the graph
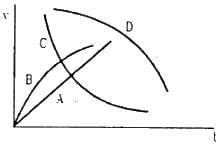
Explanation
Initially, when the ball starts moving, its velocity is small. Gradually, the velocity of the ball increases due to acceleration caused by gravity. However, as the velocity increases, the viscous force acting on the ball also increases. This force tends to decelerate the ball. Therefore, after reaching a certain maximum velocity, the ball slows down.
Report a problem
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:A student plots a graph from his reading on the determination of Young modulus of a metal wire but forgets to put the labels. the quantities on X and Y-axes may be respectively
Explanation
All options are correct.
(a) When a weight is loaded on a wire, the length of the wire increases. The relationship between weight and length is linear.
(b) When a weight is loaded, it produces stress on the wire. The relationship between stress and increase in length is also linear.
(c) When stress is applied, strain develops. Therefore, both are linearly related.
(d) Since the value of Y for the wire is unknown, X may also be the increase in its length. Nevertheless, they still show the same linear relationship.
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:The properties of a surface are different from those of the bulk liquid because the surface molecules
Explanation
(c) The surface molecules acquire air and liquid molecules in their sphere of influence.
(d) The surface molecules have different magnitudes of forces pulling them from the top and the bulk. So, they are affected by a net finite force in one direction.
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:The rise of a liquid in a capillary tube depends on
Explanation
Height of the liquid in the capillary tube is given by:
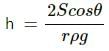
h = Height
S = Surface tension
r = Inner radius of the tube
ρ = Density of the liquid
g = Acceleration due to gravity
(a) θ and ρdepend upon the material of the capillary tube and the liquid.
(b) h is dependent on the length of the tube . If the length is insufficient, then h will be low.
(d) r is the inner radius of the tube.
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:The contact angle between a solid and a liquid is a property of
Explanation
The angle of contact between a solid and a liquid depends upon the molecular forces of both the substances. Therefore, it depends upon the material of the solid and the liquid.
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
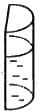
Try yourself:A liquid is contained in a vertical tube of semicircular cross section. The contact angle is zero. The force of surface tension on the curved part and on the flat part are in ratio
Explanation
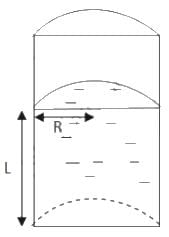
Let the height of the liquid-filled column be L.
Let the radius be denoted by R.
Total perimeter of the curved part = semi - circumference of upper area = πr
Total surface tension force = πRS
Total perimeter of the flat part = 2R
Total surface tension force = 2RS
Ratio of curved surface force to flat surface force = 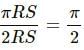
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:When a capillary tube is dipped into a liquid, the liquid neither rises nor falls in the capillary.
Explanation
If the liquid level does not rise, it may be assumed that the surface tension is zero or the contact angle is 90°, or both. However, we cannot tell for sure whether the surface tension of the liquid is zero or the contact angle is 0°.
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 1
Try yourself:A solid sphere moves at a terminal velocity of 20 m s−1 in air at a place where g = 9.8 m s−2. The sphere is taken in a gravity-free hall having air at the same pressure and pushed down at a speed of 20 m s−1.
Explanation
(b) There is no gravitational force acting downwards. However, when the starting velocity is 20 m/s, the viscous force, which is directly proportional to velocity, becomes maximum and tends to accelerate the ball upwards.
When the ball falls under gravity,
neglecting the density of air:
Mass of the sphere = m
Radius = r
Viscous drag coeff. =η
Terminal velocity is given by
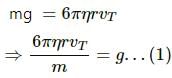
Now, at terminal velocity, the acceleration of the ball due to the viscous force is given by:
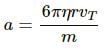
Comparing equations (1) and (2), we find that :
a = g
Thus, we see that the initial acceleration of the ball will be 9.8 ms- 2 .
(c) The velocity of the ball will decrease with time because of the upward viscous drag. As the force of viscosity is directly proportional to the velocity of the ball, the acceleration due to the viscous force will also decrease.
(d) When all the kinetic energy of the ball is radiated as heat due to the viscous force, the ball comes to rest.
is converted into kinetic energy of the mass.
From the equation, we see that the height (h) of the liquid may also be zero if the contact angle θ between the liquid and the capillary tube is 90° or 270°.

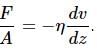 This F/A may be called
This F/A may be called









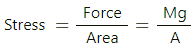
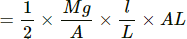
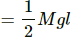
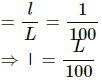
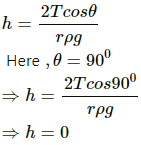


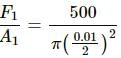
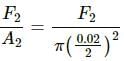
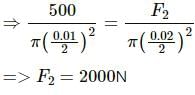
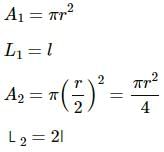
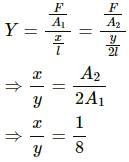
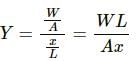
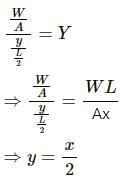
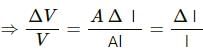
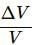 is directly proportional to
is directly proportional to