IAS Salary and Facilities in India - UPSC PDF Download
In India, there are countless young people who aspire to become IAS officers, as they are regarded as being in a class apart from other professionals, both in the public and private sectors, due to the numerous benefits they enjoy. Many of these aspirants are likely to be curious about the facilities provided to IAS officers in the country. Following the implementation of the 7th Pay Commission, IAS officers are now compensated with salaries that are comparable to those offered in the private sector. Additionally, IAS officers are granted a range of perks that are simply unattainable for private-sector professionals, beyond just their salaries.
What sets IAS officers apart, however, is the significant power that the government bestows upon them. They have the ability to effect positive change, particularly in the lives of ordinary citizens. This article discusses the salary and other facilities provided to IAS officers, as well as the benefits of pursuing a career as an IAS officer. Continue reading to learn more about the life of an IAS officer in general.
Salary structure for IAS officers- 7th Pay Commission
In the 7th Central Pay Commission, the system of 'Pay Grades for Civil Services' has been replaced with 'Consolidated Pay Levels'. As a result, the IAS pay scale is now determined solely on the basis of 'Basic Pay', in addition to other allowances such as TA, DA, and HRA.
Salary of IAS Officer | |||||
Pay Level | Basic Pay(INR) | Number of years required in service | Post | ||
District Administration | State Secretariat | Central Secretariat | |||
10 | 56100 | 1-4 | Sub-Divisional Magistrate | Undersecretary | Assistant Secretary |
11 | 67,700 | 5-8 | Additional District Magistrate | Deputy Secretary | Undersecretary |
12 | 78,800 | 9-12 | District Magistrate | Joint Secretary | Deputy Secretary |
13 | 1,18,500 | 13-16 | District Magistrate | Special Secretary-cum-Director | Director |
14 | 1,44,200 | 16-24 | Divisional Commissioner | Secretary-cum-Commissioner | Joint Secretary |
15 | 1,82,200 | 25-30 | Divisional Commissioner | Principal Secretary | Additional Secretary |
16 | 2,05,400 | 30-33 | No Equivalent Rank | Additional Chief Secretary | No Equivalent Rank |
17 | 2,25,000 | 34-36 | No Equivalent Rank | Chief Secretary | Secretary |
18 | 2,50,000 | 37+ years | No Equivalent Rank | No Equivalent Rank | Cabinet Secretary of India |
The table below provides information on the monthly salary of an IAS officer at the entry-level and at the highest level of the pay scale:
Post | Pay Level | Basic Pay | Dearness Allowance (DA) | Travel Allowance (TA) | House Rent Allowance (HRA) | Gross Salary per Month |
IAS Entry-level | Level 10 | INR 56,100 | 17% of Basic Pay | INR 4,000 | Based on City of Residency (24%, 16%, or 8% of Basic Pay) | INR 68,000 (approx.) |
Apex Level | Level 18 | INR 2,50,000 | 17% of Basic Pay | INR 7,000 | Based on City of Residency (27%, 18%, or 9% of Basic Pay) | INR 3,50,000 (approx.) |
IAS Officers: Career Growth
A newly recruited IAS officer undergoes extensive training at the Lal Bahadur Shastri National Academy of Administration (LBSNAA) in Mussoorie, where they are equipped with the knowledge and skills required to handle various administrative tasks.
- After the training, the IAS officer is appointed as a Sub-divisional Magistrate (SDM) and based on their performance, they are given more responsibilities and promotions to higher posts.
- The job of an IAS officer involves a diverse range of responsibilities, postings, and promotions, making it a dynamic and constantly evolving profession.
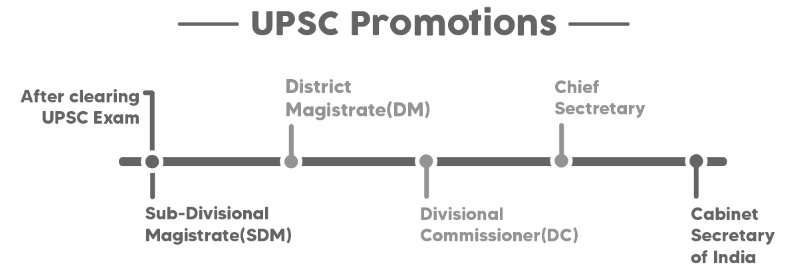
Requirements for IAS Promotions
- Successfully cleared candidates become IAS officers and receive promotions during their service period.
- IAS officers undergo training at LBSNAA, Mussoorie before taking charge as SDM.
- SDMs communicate with various government departments and are eligible for promotions based on their skills.
IAS Officer Posts | Years of Work |
ASP/ Assistant Commissioner/SDM | 1-4 |
Deputy Secretary (State)/ Undersecretary/ ADM(Center) | 5-8 |
DM/ Joint Secretary (State)/Deputy Secretary (Center) | 9-12 |
DM/ Special Secretary cum Director (State)/ Director (Center) | 13-16 |
Divisional Commissioner/ Joint Secretary (Center)/ Secretary cum Commissioner (State) | 16-24 |
Principal Secretary (State)/ Additional Secretary/ Divisional Commissioner(Center) | 25-30 |
Additional Chief Secretary | 30-33 |
Chief Secretary | 34-36 |
Cabinet Secretary of India | 37+ |
Post wise IAS Pay
Basic Pay (INR) | Posts | ||
State Secretariat | District Administration | Central Secretariat | |
56,100 | Undersecretary | Sub-Divisional Magistrate | Assistant Secretary |
67,700 | Deputy Secretary | Additional District Magistrate | Undersecretary |
78,800 | Joint Secretary | District Magistrate | Deputy Secretary |
1,18,500 | Special Secretary-cum-Director | District Magistrate | Director |
1,44,200 | Secretary-cum-Commissioner | Divisional Commissioner | Joint Secretary |
1,82,200 | Principal Secretary | Divisional Commissioner | Additional Secretary |
2,05,400 | Additional Chief Secretary | No Equivalent Rank | No Equivalent Rank |
2,25,000 | Chief Secretary | No Equivalent Rank | Secretary |
2,50,000 | No Equivalent Rank | No Equivalent Rank | |
IAS Salary – Perks & Other Benefits
The IAS Salary is determined based on the grade of the officer, which includes basic pay, grade pay, and other perks and allowances. Some of these facilities are:
- Dearness Allowance (DA): This allowance is an essential component of an IAS officer's salary as it is regularly increased by the government. Currently, it can go up to 103% of the basic pay, directly affecting the IAS Salary.
- House Rent Allowance (HRA): HRA is given according to the city where the IAS Officer is posted, and the percentage varies from 8% to 24% of the basic pay, depending on the location.
- Medical Allowance: IAS officers also receive a medical allowance, which they can use to get reimbursed for medical treatment.
Facility | Description |
Residence |
|
Transport |
|
Security |
|
Bills |
|
Trips |
|
Study Leaves |
|
Job Security |
|
Lifetime Pension |
|
Post-retirement |
|
HRA (House Rent Allowances) |
|
DA (Dearness Allowances) |
|
TA (Travel Allowances) |
|
UPSC IAS Officer Salary: HRA And Transport Allowance
The HRA allowances in the IAS Officer Salary depend on the city of posting and range from 24% to 8%, as per the 7th Pay Commission norms. The commission has recommended enhancing the HRA when the DA crosses 50% and 100%. Transport Allowance remains unchanged, but the DA has been merged with it. The Pay Band-Grade Pay System has been discontinued. More details can be found in the table below.
HRA Distribution | |
Class X | 8 Cities only- 24% HRA (Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad, and Pune) |
Class Y | Around 100 Towns (With a Population above 5 Lakhs) – 16% HRA |
Class Z | Rural Areas – 8% HRA |
Dearness Allowance | |
DA | DA now crosses 50 to 100 % |
Transport Allowance | |
The Transport allowance is not included in the DA which can reach upto 125% now | |
IAS Pension
Here is a possible rephrased statement and table: IAS officers are eligible for lifetime pension benefits. The pension scheme for all civil servants, excluding the armed forces, has been revised since January 1, 2004. As per the revised scheme, IAS officers and other government employees are required to contribute 10% of their salaries towards pension, while the government contributes 14%.
Scheme | Contribution from IAS Officer | Contribution from Government |
Pension (since Jan 2004) | 10% | 14% |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on IAS Salaries and Facilities
What is the salary of an IAS officer?
An IAS officer's basic salary is Rs 56,100 as per 7th Pay Commission, and additional allowances like Travel Allowance and Dearness Allowance are also provided. The per month salary of an IAS officer can reach up to Rs. 2,50,000 for a Cabinet Secretary.
What is IAS take home salary?
An entry-level IAS officer's total salary includes basic salary, DA, House Rent Allowance, and Transport Allowance. The stipend/salary during IAS training at LBSNAA is around Rs. 55,000 per month, which further reduces due to mess bills, LBSNAA apparels, and other activities. After deducting all expenses, the IAS trainee salary is around Rs. 40,000 per month.
Is IAS exam difficult?
The IAS exam's success rate is low, with around a thousand candidates selected out of approximately 10 lakh aspirants. However, with hard work, planning, practice, patience, perseverance, and dedication, cracking the IAS Exam is achievable.
Do IAS officers get a salary during training?
IAS officers receive a stipend/salary of around Rs. 55,000 per month during their training at LBSNAA, which is reduced after deducting mess bills, payments for LBSNAA apparels and uniforms, and other activities. The IAS trainee's salary is around Rs. 40,000 per month after deducting all expenses.
What are the powers of an IAS officer?
IAS officers can be a part of the State Cadre or the Centre Deputation, and they control the district administrative machinery in the early years of their career. With time and good performance, IAS officers can represent India abroad, become head of PSUs, and become the Cabinet Secretary.
Is the IAS Officer Salary more than the IPS Officer Salary?
An IAS Officer's basic salary begins at Rs. 56,100, which can go up to Rs. 2,50,000 for a Cabinet Secretary. The IPS Salary ranges from 56,100 INR per month to as high as 2,25,000 INR per month upon attaining the post of the Director-General of Police (DGP). Detailed differences between IPS and IAS Salary are available in the linked article.




















