Short Answers
Q.1. If a constant potential difference is applied across a bulb, the current slightly decreases as time passes and then becomes constant. Explain.
As a constant potential difference is applied across a bulb, due to Joule's heating effect, the temperature of the bulb increases. As the temperature of the bulb filament increases, its resistance also increases, as resistance R is the function of temperature T. It is given by R = R0(1+αT). With an increase in the value of resistance, the value of current decreases as i = V/R. Now, the heat generated by the resistance is constantly radiated to the surroundings. Thus, the value of its temperature is maintained and hence its resistance. As a result, current through the bulb filament becomes constant.
Q.2. Two unequal resistances, R1 and R2, are connected across two identical batteries of emf ε and internal resistance r (see the figure). Can the thermal energies developed in R1 and R2 be equal in a given time? If yes, what will be the condition?
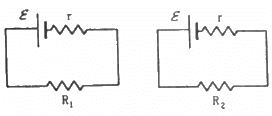
For the given time t, let the currents passing through the resistance R1 and R2 be i1 and i2, respectively.
Applying Kirchoff's Voltage Law to circuit-1, we get:-
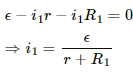
Similarly, the current in the other circuit,
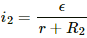
The thermal energies through the resistances are given by
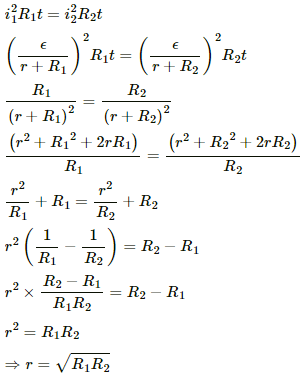
Q.3. When a current passes through a resistor, its temperature increases. Is it an adiabatic process?
No, the rise in the temperature of a resistor on passing current through it is not an adiabatic process. In an adiabatic process, there is no heat exchange between the system and the surroundings. Here, some part of Joule's heat developed inside the resistor increases the temperature of the resistor and the remaining part is dissipated in the surroundings. Thus, the given process cannot be adiabatic.
Q.4. Apply the first law of thermodynamics to a resistor carrying a current i. Identify which of the quantities ∆Q, ∆U and ∆W are zero, positive and negative.
The battery is doing positive work on a resistor carrying current i. Thus, ∆W is positive. The work done on the resistor is used to increase its thermal energy; thus ∆Q is positive. As the temperature of the resistor rises, ∆U is positive.
Q.5. Do all thermocouples have a neutral temperature?
The temperature of the hot junction at which the thermo-emf in a thermocouple becomes maximum is called neutral temperature for that thermocouple. For a thermocouple in which the constants a and b have the same sign, the neutral temperature will be less than the temperature of the cold junction of the thermocouple 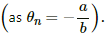
There will be no neutral or inversion temperature, as the temperature of the hot junction cannot be less than the temperature of the cold junction.
Q.6. Is inversion temperature always double the neutral temperature? Does the unit of temperature have an effect in deciding this question?
If the inversion temperature and neutral temperature are measured in degree Celsius, then it is correct to say that "inversion temperature is always double the neutral temperature." When temperature is measured in other units, such as Kelvin, then inversion temperature is not the double of neutral temperature.
Q.7. Is neutral temperature always the arithmetic mean of the inversion temperature and the temperature of the cold junction? Does the unit of temperature have an effect in deciding this question?
No, the neutral temperature is not always the arithmetic mean of the inversion temperature and the temperature of the cold junction. That is valid only when the unit of temperature is degree Celsius.
Q.8. Do the electrodes in an electrolytic cell have fixed polarity like a battery?
No, the electrodes in an electrolytic cell do not have fixed polarity like that of a battery. If we take an electrolytic cell consisting of the Ag electrodes and the AgNO3 as electrolyte. When the battery is connected to it, the end to which the positive terminal of the battery is connected is the anode and the end to which the negative terminal is connected is the cathode.
NO-3 ions are deposited at the anode and Ag+ ions are deposited at the cathode. When the connection of the electrolytic cell is reversed, the polarities of the electrodes are also reversed.
Q.9. As temperature increases, the viscosity of liquids decreases considerably. Will this decrease the resistance of an electrolyte as the temperature increases?
Yes, the resistance of the electrolyte will decrease with an increase in temperature. This is because when the temperature of an electrolytic solution increases, its viscosity decreases and mobility of the ions in the solution increases.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 33: Thermal and Chemical Effects of Current- 1
Try yourself:Consider the following statements regarding a thermocouple.
(A) The neutral temperature does not depend on the temperature of the cold junction.
(B) The inversion temperature does not depend on the temperature of the cold junction.
Explanation
The value of neutral temperature is constant for a thermocouple. It depends on the nature of materials and is independent of the temperature of the cold junction. Inversion temperature depends on the temperature of the cold junction, as well as the nature of the material.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 33: Thermal and Chemical Effects of Current- 1
Try yourself:The heat developed in a system is proportional to the current through it.
Explanation
Joule heat is directly proportional to the square of the current passing through the resistor. Peltier heat is directly proportional to the current passing through the junction.Thomson heat is also directly proportional to the current passing through the section of the wire. Thus, the heat developed can be either Thomson heat or Peltier heat. But it cannot be Joule heat.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 33: Thermal and Chemical Effects of Current- 1
Try yourself:Consider the following statements.
(A) Free-electron density is different in different metals.
(B) Free-electron density in a metal depends on temperature.
Seebeck Effect is caused _______.
Explanation
In Seebeck Effect, a temperature difference between two dissimilar electrical conductors produces a potential difference across the junctions of the two different metals. The cause of this potential difference is the diffusion of free electrons from a high electron-density region to a low electron-density region. The free electron-density of the electrons is different in different metals and changes with change in temperature. Hence, both the statements are the causes of Seebeck Effect.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 33: Thermal and Chemical Effects of Current- 1
Try yourself:Consider the following statements.
(A) Free-electron density is different in different metals.
(B) Free-electron density in a metal depends on temperature.
Peltier Effect is caused _______ .
Explanation
In Peltier Effect, one of the junctions gets heated up and the other cools down when electric current is maintained in a circuit of material consisting of two dissimilar conductors.
This is caused due to the difference in density of free electrons in different metals. When two different metals are joined to form a junction, the electrons tend to diffuse from the side with higher concentration to the side with lower concentration. If current is forced through the junction, positive or negative work is done on the charge carriers, depending on the direction of the current. Accordingly, thermal energy is either produced or absorbed. Thus, Peltier Effect is caused due to A but not due to B.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 33: Thermal and Chemical Effects of Current- 1
Try yourself:Consider the following statements.
(A) Free-electron density is different in different metals.
(B) Free-electron density in a metal depends on temperature.
Thomson Effect is caused _______ .
Explanation
If a metallic conductor has non-uniform temperature distribution along its length, the density of the free electrons is different for different sections. The electrons diffuse from the sections with higher concentration to those with lower concentration of free electrons. Thus, there is an emf inside the metal that is known as Thomson emf. If a current is forced through the given conductor, positive and negative work is done on the charge carriers, depending on the direction of current. Thus, thermal energy is either produced or absorbed. Thus, the correct cause of the given effect is given by statement B alone.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 33: Thermal and Chemical Effects of Current- 1
Try yourself:Faraday constant _________.
Explanation
Faraday's constant is a universal constant. Its value is 9.6845×107 C/kg. It does not depend on the amount of the electrolyte, current in the electrolyte and on the amount of charge passed through the electrolyte.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 33: Thermal and Chemical Effects of Current- 1
Try yourself:Two resistors of equal resistances are joined in series and a current is passed through the combination. Neglect any variation in resistance as the temperature changes. In a given time interval,
Explanation
In a resistor of resistance R, current i is passed for time t then the thermal energy produced in the resistor will be given by
H = i2Rt.
As the resistors are in series, the current through them will be same. Thus, the amount of thermal energy produced in the resistors is same. The rise in the temperature of the resistance will depend on the shape and size of the resistor. Thus, the rise in the temperature of the two resistances may be equal.
Report a problem
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 33: Thermal and Chemical Effects of Current- 1
Try yourself:A copper strip AB and an iron strip AC are joined at A. The junction A is maintained at 0°C and the free ends B and C are maintained at 100°C. There is a potential difference between _______ .
Explanation
The copper strip AB and an iron strip AC are joined at A and the junction A is maintained at 0°C and the free ends B and C are maintained at 100°C. In this case, there will be generation of thermo-emf between the points that are at different temperatures. Here, the two ends of the copper, the copper end and the iron end at the junction, the two ends of the iron strip and the free ends B and C are at different temperatures. Hence, there will be potential difference among them.
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 33: Thermal and Chemical Effects of Current- 1
Try yourself:The constants a and b for the pair silver-lead are 2.50 μV°C−1 and 0.012μV°C−2, respectively. For a silver-lead thermocouple with colder junction at 0°C, _______ .
Explanation
The temperature of the hot junction at which the thermo-emf in the thermocouple becomes maximum is called neutral temperature for that thermocouple. The signs of the constants a and b are same. Therefore from the relation, 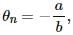 the neutral temperature will be less than the temperature of the cold junction of thermocouple.
the neutral temperature will be less than the temperature of the cold junction of thermocouple.
Hence, there will be no neutral or inversion temperature, as the temperature of the hot junction cannot be less than the temperature of the cold junction.
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 33: Thermal and Chemical Effects of Current- 1
Try yourself:An electrolysis experiment is stopped and the battery terminals are reversed.
Explanation
In an electrolytic cell, both the electrodes are made of the same material. Thus, on reversing the terminals of the battery, the direction of the flow of charges will be reversed, but the rate of the electrolysis will remain the same.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 33: Thermal and Chemical Effects of Current- 1
Try yourself:The electrochemical equivalent of a material depends on _____ .
Explanation
The electrochemical equivalent of a substance is the ratio of the relative atomic mass of the substance to its valency. Thus, it is only dependent on the nature of the material.
Report a problem



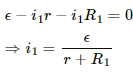
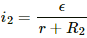
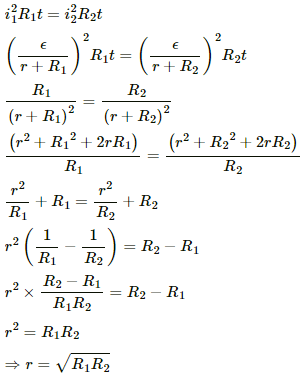
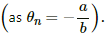
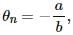 the neutral temperature will be less than the temperature of the cold junction of thermocouple.
the neutral temperature will be less than the temperature of the cold junction of thermocouple.


















