UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 27th April 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Konark Sun Temple
Why in News?
A petition has been filed in the Orissa High Court challenging the minimum eligibility criteria of matriculation adopted by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) for issuing licences to photographers to operate inside Sun Temple at Konark.
About Konark Sun Temple:
- Location: It is located on the coastline of Odisha in Puri district.
- It was built by King Narasimha Deva I of the Eastern Ganga Dynasty in 1244.
- It was given the status of a World Heritage Site in 1984 by UNESCO.
- Features:
- Also called the Surya Devalaya, the temple is dedicated to the Hindu god Surya.
- It is a classic example of the Odisha style of Architecture or Kalinga Architecture.
- The temple complex has the appearance of a 100-foot high solar chariot, with 24 wheels and pulled by six horses, all carved from stone.
- It is oriented towards the east so that the first rays of the sunrise strike the main entrance.
- The wheels of the temple are sundials, which can be used to calculate time accurately to a minute.
- Around the base of the temple, there are images of animals, foliage, warriors on horses and other interesting structures.
- On the walls and roof of the temple, beautiful sensual figures are carve
- The temple, built from Khondalite rocks, is also known as 'BLACK PAGODA' due to its dark colour.
- The temple remains a site of contemporary worship for Hindus, during the annual Chandrabhaga Festival, around the month of February.
Source: Indian Express
Understanding Temperature Anomalies
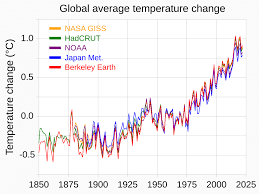
Why in News?
March 2023 was the second warmest March on record.
More about the news
- Warm March:
- March 2023 was the second warmest in the instrumental record.
- The warmest March occurred just a few years ago in 2016, when the biggest El Niño of the 21st century triggered a ‘mini’ global warming.
- In India, we expect March to be the beginning of the scorching summer season.
- But a particular year’s March may be cooler due to some other climate factors, such as a La Niña, and especially when averaged over a region as large as India or even an Indian State.
- Heating of the Arabian Sea:
- The Arabian Sea has also warmed more than expected this March.
- This situation can favour a stronger monsoon but may also enhance cyclogenesis (i.e. birth of cyclonic circulation) over the Arabian Sea.
- Temperature anomaly:
- The January-to-March average temperature anomaly ranks 2023 as the fourth warmest such period on record.
About the “Temperature anomalies”
- What is a temperature anomaly?
- The term temperature anomaly means a departure from a reference value or long-term average.
- A positive anomaly indicates that the observed temperature was warmer than the reference value, while a negative anomaly indicates that the observed temperature was cooler than the reference value.
- The term temperature anomaly means a departure from a reference value or long-term average.
- Significance:
- This product is a global-scale climate diagnostic tool and provides a big picture overview of average global temperatures compared to a reference value.
- Global warming does not mean each month or each year will be warmer than the previous month or the previous year.
- Instead, a better place to begin would be by averaging the weather over a decade.
- Decade-to-decade warming clearly shows that humans are now ensuring each decade is warmer than the one before.
- What causes the anomalies?
- The global distribution of temperature anomalies is due to land-ocean-atmosphere processes that dynamically determine the weather and climate.
Rising global temperatures
- Human induced warming:
- Air temperatures on Earth have been rising since the Industrial Revolution.
- While natural variability plays some part, the preponderance of evidence indicates that human activities—particularly emissions of heat-trapping greenhouse gases—are mostly responsible for making our planet warmer.
- What does the analysis say?
- According to an ongoing temperature analysis led by scientists, the average global temperature on Earth has increased by at least 1.1° Celsius (1.9° Fahrenheit) since 1880.
- The majority of the warming has occurred since 1975, at a rate of roughly 0.15 to 0.20°C per decade.
- Pattern of warming:
- Global warming does not mean temperatures rise everywhere at every time at the same rate. Temperatures might rise 5 degrees in one region and drop 2 degrees in another.
- For instance, exceptionally cold winters in one place might be balanced by extremely warm winters in another part of the world.
- Generally, warming is greater over land than over the oceans because water is slower to absorb and release heat (thermal inertia).
- Warming may also differ substantially within specific land masses and ocean basins.
- Global warming does not mean temperatures rise everywhere at every time at the same rate. Temperatures might rise 5 degrees in one region and drop 2 degrees in another.
- Influence of rise:
- The temperatures we experience locally and in short periods can fluctuate significantly due to predictable, cyclical events (night and day, summer and winter) and hard-to-predict wind and precipitation patterns.
- Challenge for India:
- India’s large population experiences adaptation challenges due to severe heat waves in the summer and extreme rainfall during the monsoon season.
- Heatwaves cause mortality and pose challenges for public health infrastructure.
- Prolonged extreme rainfall results in floods, which damage agriculture and infrastructure and cause human migration and loss of lives.
- India’s large population experiences adaptation challenges due to severe heat waves in the summer and extreme rainfall during the monsoon season.
Possibility of intense heatwaves
- Excessively hot summer:
- The summer this year is predicted to be excessively hot because of the end of the strong La Nina phase in equatorial Pacific Ocean, something that has a general cooling effect on the earth’s atmosphere.
- Possibility of El Nino’s occurrence:
- New forecasts suggest that El Nino, which has the opposite impacts of La Nina, is expected to kick in from the May-July period itself, earlier than expected.
- El Nino also tends to result in suppression of monsoon rainfall over India.
- Shortfall in rain:
- A shortfall in rains is already being apprehended, which could exacerbate the effects of a hot summer, even though the India Meteorological Department has predicted a normal monsoon.
Way ahead
- Climate scientists need to provide the proper context when they compare and rank individual months against each other.
- This will help the people at large better understand global warming as well as its cascading effects on the weather they experience every day.
- And the better people understand the impact of global warming in their backyard, the likelier they can be engaged in climate action.
Source: The Hindu
GS-II
Operation Kaveri

Why in News?
Recently, the first batch under Operation Kaveri was sent.
About Operation Kaveri:-
- India has initiated an operation to evacuate its nationals from conflict-hit Sudan.
- The operation was launched in response to the conflict and breakdown of essential services in Sudan that had brought the country to a standstill.
- Stranded Indian citizens are being evacuated from Port Sudan.
- India has positioned two transport aircraft of the IAF in the Saudi Arabian city of Jeddah and a naval ship at a key port in Sudan as part of its contingency plans to evacuate its stranded nationals.
- The choice of naming this operation as ‘Operation Kaveri’ has a lot of significance.
- Kaveri is sacred to the people of the region and is worshipped as the Goddess Kaveriamma (mother Kaveri).
- It’s like a mother who will ensure she will bring her children back to safety.
Source: Indian Express
Digital Services Act (DSA)

Why in News?
The European Union (EU) has confirmed the names of 19 platforms that will be subject to its landmark online content rules.
- Five subsidiaries of Google’s parent Alphabet, two Meta units, two Microsoft businesses, Apple’s AppStore, Twitter, and Alibaba’s AliExpress are among the entities that the EU has identified.
- The rules notified under the Digital Services Act (DSA), aim at overhauling the EU’s social media and e-commerce rules.
- It is an EU regulation which came into force in EU law in November 2022 and will be directly applicable across the EU.
- The act aims to address several issues related to digital services, including online safety, content moderation, and the responsibilities of online platforms.
- The legislation includes new rules for large online platforms, such as social media networks and online marketplaces, to ensure greater accountability and transparency in their operations.
- Goals
- To create a safer digital space in which the fundamental rights of all users of digital services are protected;
- To establish a level playing field to foster innovation, growth, and competitiveness, both in the European Single Market and globally.
What are the key features of the Digital Services Act?
- Faster removals and provisions to challenge
- Social media companies will have to add new procedures for faster removal of content deemed illegal or harmful.
- They will also have to explain to users how their content takedown policy works.
- The DSA also allows for users to challenge takedown decisions taken by platforms and seek out-of-court settlements.
- Bigger platforms have greater responsibility
- Very Large Online Platforms and Very Large Online Search Engines, those having more than 45 million users in the EU, will have more stringent requirements.
- Hence, the law avoids a one-size fits all approach and places increased accountability on the Big Tech companies.
- Direct supervision by European Commission
- These requirements and their enforcement will be centrally supervised by the European Commission itself.
- This is to ensure that companies do not sidestep the legislation at the member-state level.
- More transparency on how algorithms work
- Very Large Online Platforms and Very Large Online Search Engines will face transparency measures and scrutiny of how their algorithms work.
- They will be required to conduct systemic risk analysis and reduction to drive accountability about the society impacts of their products.
- Clearer identifiers for ads and who’s paying for them
- Online platforms must ensure that users can easily identify advertisements and understand who presents or pays for the advertisement.
- They must not display personalised advertising directed towards minors or based on sensitive personal data.
How does the EU’s DSA compare with India’s online laws?
- Information Technology Rules, 2021
- In February 2021, India had notified extensive changes to its social media regulations in the form of the Information Technology Rules, 2021 (IT Rules).
- These rules placed significant due diligence requirements on large social media platforms such as Meta and Twitter. This included:
- Appointing key personnel to handle law enforcement requests and user grievances,
- Enabling identification of the first originator of the information on its platform under certain conditions,
- Deploying technology-based measures on a best-effort basis to identify certain types of content.
- Amendments to the IT Rules
- In 2023, with a view to make the Internet open, safe and trusted, and accountable, the IT Ministry notified the creation of government-backed grievance appellate committees.
- These committees would have the authority to review and revoke content moderation decisions taken by platforms.
- Other laws
- India is also working on a complete overhaul of its technology policies and is expected to soon come out with a replacement of its IT Act, 2000.
- This law is expected to look at ensuring net neutrality and algorithmic accountability of social media platforms, among other things.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
Lesser flamingo
Why in News?
Recently, after a six-year absence, the lesser flamingos have finally found their way back to Pulicat Lake.
About Lesser Flamingo:
- It is the smallest of all flamingos but has the largest population.
- It possesses the "hallux" or hind toe that some other flamingos do not have.
- Males are a little taller than females.
- Habitat: It inhabits coastal and inland wetlands.
- Geographical distribution: Africa, Asia continents and in that especially Sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia, North Africa
- They mostly eat blue-green algae but occasionally will take crustaceans and small insects.
- It is serially monogamous, meaning they form pairs that remain together while they are raising the young
- Conservation status
- IUCN: Near Threatened
Key Facts about the Pulicat Lake
- It is the second-largest brackish water lake in the country.
- It lies at the border of the states of Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu. (Majorly lies in Andhra Pradesh)
- The long and narrow Sriharikota Island, which separates Pulicat Lake from the Bay of Bengal,
- It is popular as a flamingo-watching site and for water activities.
- Both the South West and North-East monsoons provide rain to the area where Pulicat Lake is located.
Source: The Hindu
State of the Global Climate 2022 Report: WMO
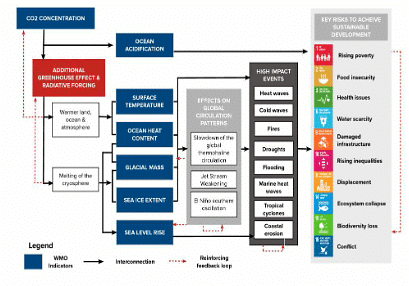
Why in News?
The State of the Global Climate 2022 report has been released by the World Meteorological Organization.
About the Report
- It focuses on key climate indicators – greenhouse gases, temperatures, sea level rise, ocean heat and acidification, sea ice and glaciers. It also highlights the impacts of climate change and extreme weather.
- It shows the planetary scale changes on land, in the ocean and in the atmosphere caused by record levels of heat-trapping greenhouse gases.
Major Highlights of the Report
- Increase in Greenhouse Gases (GHGs) emissions: Global GHGs emissions continued to increase in 2022. Carbon dioxide is at 149% of pre-industrial levels, Methane is at 262% of pre-industrial levels, Nitrous oxide is at 124% of pre-industrial levels.
- The annual increase of methane was 18 ppb from 2020 to 2021. This is the largest increase on record.
- High Global Mean Temperature: In 2022, the planet was 1.15 ± 0.13 °C warmer than the pre-industrial (1850-1900) average, making the last 8 years the warmest on record.
- Despite cooling La Niña conditions , 2022 was the 5th or 6th warmest year.
- Above Normal Precipitation: In 2022, large areas with above normal precipitation included large parts of Asia and the south-west Pacific, areas of northern South America and the Caribbean, the eastern Sahel region, parts of southern Africa, Sudan, and eastern Europe.
- Meanwhile, regions with rainfall deficits included western and central Europe, northwest Africa, parts of the Middle East, Central Asia and the Himalayas, Eastern Africa and Madagascar, central and southern South America, and central and western North America.
- Ocean Heat Content: As GHGs accumulate in the atmosphere, temperatures warm on land and in the ocean. It is expected that the ocean will continue to warm well into the future – a change which is irreversible on centennial to millennial time scales.
- In 2022, 58 percent of the ocean surface suffered at least one marine heatwave event and 25 per cent of the surface experienced at least one marine cold spell.
- Rise in Sea Level: In 2022, global mean sea level continued to rise. The sea has risen approximately 3.4 ± 0.3 mm per year over the past 30 years .
- Ocean Acidification: Global mean ocean pH has been steadily declining at rates not seen for at least the past 26,000 years.
- Sea Ice Extent: Arctic sea-ice extent was below the long-term average for most of the year.
- Antarctic sea-ice extent dropped to the lowest level and almost 1 million km 2 below the long-term (1991-2020) mean. The total extent of Antarctic sea ice continued to be below average.
- The Greenland Ice Sheet ended with a negative total mass balance for the 26th year in a row. Summit Station, the highest point in Greenland, had its warmest September and experienced melting for the first time. Heavy rain fell on the ice sheet for the first time.
- Glacier Mass Balance: The glaciers have been losing mass nearly every year.
- Exceptional Melt in Swiss Alps: In Switzerland 6% of the glacier ice volume was lost between 2021 and 2022.
- For the first time in history, no snow outlasted the summer season even at the very highest measurement sites and therefore no accumulation of fresh ice occurred.
- Extreme Events: Rising global temperatures have contributed to more frequent and severe extreme weather events around the world, including cold and heat waves, floods, droughts, wildfires and storms.
Socio-economic and Environmental Impacts
- Drought gripped East Africa: Rainfall has been below-average in five consecutive wet seasons, the longest such sequence in 40 years. As of January 2023, it was estimated that over 20 million people faced acute food insecurity across the region, under the effects of the drought and other shocks.
- Record breaking rain: In July and August led to extensive flooding in Pakistan. There were over 1 700 deaths, and 33 million people were affected, while almost 8 million people were displaced. Total damage and economic losses were assessed at US$ 30 billion.
- Record breaking heatwaves: It affected Europe during the summer. In some areas, extreme heat was coupled with exceptionally dry conditions. Excess deaths associated with the heat in Europe exceeded 15 000 in total across Spain, Germany, the UK, France, and Portugal.
- China had its most extensive and long-lasting heatwave since national records began resulting in the hottest summer on record by a margin of more than 0.5 °C.
- Food insecurity: As of 2021, 2.3 billion people faced food insecurity, of which 924 million people faced severe food insecurity. Projections estimated 767.9 million people facing undernourishment in 2021, 9.8% of the global population. Half of these are in Asia and one third in Africa.
- Heatwaves in the 2022 pre-monsoon season in India and Pakistan caused a decline in crop yields. This, combined with the banning of wheat exports and restrictions on rice exports in India after the start of the conflict in Ukraine, threatened the availability, access, and stability of staple foods within international food markets and posed high risks to countries already affected by shortages of staple foods.
- Population Displacement: In Somalia, almost 1.2 million people became internally displaced by the catastrophic impacts of drought on pastoral and farming livelihoods and hunger during the year. Concurrently, Somalia was hosting almost 35 000 refugees and asylum seekers in drought-affected areas. A further 512 000 internal displacements associated with drought were recorded in Ethiopia.
- The flooding in Pakistan affected some 33 million people, including about 800 000 Afghan refugees hosted in affected districts around 8 million people have been internally displaced by the floods.
- Environment: Climate change has important consequences for ecosystems and the environment. For example, a recent assessment focusing on the unique high-elevation area around the Tibetan Plateau, the largest storehouse of snow and ice outside the Arctic and Antarctic, found that global warming is causing the temperate zone to expand.
- Climate change is also affecting recurring events in nature, such as flowering of cherry blossoms in Japan has been documented since AD 801 and has shifted to earlier dates since the late nineteenth century. In 2021, the full flowering date was 26 March, the earliest recorded in over 1200 years.
- Ecosystems: Ecosystems – including terrestrial, freshwater, coastal and marine ecosystems – and the services they provide, are affected by the changing climate and some are more vulnerable than others.
- Ecosystems are degrading at an unprecedented rate, limiting their ability to support human well-being and harming their adaptive capacity to build resilience.
Suggestions as per the Report
- Adaptation: Early Warning Systems allow people to know hazardous weather is on its way, and informs how governments, communities and individuals can act to minimize the impending impacts.
- However, even if adaptation is improved, the climate will continue to change unless the underlying drivers are addressed.
- Without immediate and deep greenhouse gases emissions reductions across all sectors and regions, it will be impossible to keep warming below 1.5° C.
- Mitigation: It is urgent to mitigate, or reduce, greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuels wherever possible.
- Transitioning to renewable energy sources is a critically important part of reducing emissions.
Source: Down To Earth
European Free Trade Association (EFTA)
Why in News?
India and the four-nation bloc EFTA recently discussed ways to resume negotiations for a free trade agreement with a view to strengthening economic ties between the two regions.
About European Free Trade Association (EFTA):
- It is an intergovernmental organization established in 1960 by the Stockholm Convention.
- Objective: Promotes free trade and economic integration between its members within Europe and globally.
- EFTA currently has 4 member countries: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland.
- The EFTA countries have developed one of the largest networks of Free Trade Agreements (FTAs). These FTAs span over 60 countries and territories, including the European Union (EU).
- In contrast to the EU, EFTA is not a customs union. This means that the individual EFTA States are free to set their own customs tariffs and arrange other foreign trade measures vis-à-vis the non-EFTA States.
- Governance Structure:
- EFTA’s highest governing body is the EFTA Council. It generally meets 8 times a year at the ambassadorial level and twice a year at the ministerial level.
- The headquarters of the EFTA Secretariat is located in Geneva. It assists the EFTA Council in the management of relations between the 4 EFTA States and deals with the negotiation and operation of EFTA’s FTAs.
- EFTA Surveillance Authority (ESA): It monitors compliance with European Economic Area (EEA) rules in Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway.
- EFTA Court: It is based in Luxembourg and has the competence and authority to settle internal and external disputes regarding the implementation, application or interpretation of the EEA agreement.
What is the European Economic Area (EEA)?
- It consists of the Member States of the European Union (EU) and three countries of the European Free Trade Association (EFTA)(Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway, excluding Switzerland).
- The Agreement on the EEA entered into force on 1 January 1994.
- It seeks to strengthen trade and economic relations between the member countries.
- It is principally concerned with the four fundamental pillars of the internal market, namely: the free movement of goods, people, services and capital.
Source: The Hindu
LockBit ransomware

Why in News?
Recently, the LockBit ransomware was found to be targeting Mac devices.
About LockBit ransomware:-
- It was first reported in September 2019 and dubbed the “abcd” virus, due to the file extension used when encrypting victims’ files.
- The LockBit ransomware is designed to infiltrate victims’ systems and encrypt important files.
- The virus is categorized as a “cryptovirus” due to its requests for payment in cryptocurrency to decrypt files on the victim’s device.
- The ransomware is therefore typically deployed against victims who feel hindered enough by the disruption to pay heavy sums in exchange for access to the files and can afford to do so.
- The gang behind the LockBit ransomware reportedly maintains a dark web portal to recruit members and release data of victims who refuse to meet their demands, as part of their business model.
- In the past, LockBit ransomware has been used to target enterprises and organizations in the U.S., China, India, Ukraine, and Indonesia.
- Attacks have also been recorded throughout Europe, including France, Germany, and the U.K.
Working:-
- It works as a self-spreading malware, not requiring additional instructions once it has successfully infiltrated a single device with access to an organisational intranet.
- It also known to hide executable encryption files by disguising them in the PNG format, thereby avoiding detection by system defences.
- Attackers use phishing tactics and other social engineering methods to impersonate trusted personnel or authorities to lure victims into sharing credentials.
- Once it has gained access, the ransomware prepares the system to release its encryption payload across as many devices as possible.
- It then disables security programs and other infrastructures that could permit system data recovery.
- The goal is to ensure that data recovery without assistance from the LockBit gang is impossible.
- Once this is ensured, the ransomware places an encryption lock on all system files, which can only be unlocked via a custom key created by the LockBit gang.
- The process leaves behind a ransom note, with instructions to restore the system, and has reportedly also included threatening blackmail messages.
- Victims are then left with no choice but to contact the LockBit gang and pay up for the data.
Source: The Hindu
|
63 videos|5408 docs|1146 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 27th April 2023 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are the three main subjects covered in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of General Studies Paper-I in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 3. How does General Studies Paper-II contribute to the UPSC exam? |  |
| 4. What is the role of General Studies Paper-III in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 5. How can candidates prepare for the General Studies papers in the UPSC exam? |  |



















