UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 29th April 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-II
Scope of Automatic Exchange of Information (AEOI) Framework
Why in News?
India is pressing for expanding the scope of the Common Reporting Standard (CRS) at the G20 to include non-financial assets, like real estate properties, under the Automatic Exchange of Information (AEOI) among OECD countries.
The rationale behind India's Demand
- As per the OECD’s Tax Transparency report, amid the current geopolitical and debt crisis, there is a need to check tax evasion and illicit financial flows, especially by Asian nations which are estimated to have lost €25 billion in revenue in 2016.
- The current global landscape makes the fight against tax evasion and other illicit financial flows (IFFs) even more pressing: the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic and the geopolitical crisis resulted in slower economic growth
- Tax evasion and other forms of IFFs are a global problem that hinder domestic revenue mobilisation.
- Therefore, there is a need to broaden the scope of AEOI so that the information could be used not only to check tax evasion but also for other non-tax law enforcement purposes.
- There is also a need to expand the CRS from financial to new other non-financial accounts and assets because the risks are not only in financial assets, there is a risk of tax evasion in non-financial and real assets, properties, etc.
About Automatic exchange of information (AEOI) framework
- It provides for the automatic exchange of a predefined set of information between tax authorities.
- The AEOI Standard requires the annual exchange of information on financial accounts held by non-resident individuals and entities in a pre-defined format.
- The information exchanged includes details about the financial account (e.g. the financial institution maintaining it, the account number and the account balance) and details about the account holder (e.g. their name, address, date of birth, and taxpayer identification number).
- Importance: Under the AEOI framework, signatory countries follow a CRS and obtain information from their financial institutions and automatically exchange that information with other jurisdictions on an annual basis.
- the AEOI Standard provides a powerful tool to help deter and identify offshore tax evasion through holding financial assets abroad.
- It provides for sharing of financial account details among signatory countries with the aim to check tax evasion.
- Developments: In August 2022, the OECD also approved the Crypto-Asset Reporting Framework (CARF) which provides for the reporting of tax information on transactions in crypto assets in a standardised manner, with a view to automatically exchanging such information.
- Indian Scenario: India currently has AEOI with 108 jurisdictions for receiving financial information and with 79 jurisdictions for sending information automatically.
Source: Indian Express
Achieving Universal Health Care

Why in News?
Universal Health Care can help to address the current health disparities that exist in India, as it would ensure that everyone, regardless of their social status, has access to essential health services.
About Universal Health Coverage/Care:
- The United Nations defines UHC as “everyone, everywhere should have access to the health services they need without risk of financial hardship.”
- Sustainable Development Goals target 3.8 also focuses on achieving universal health coverage.
- In the context of India, this includes health promotion, prevention, treatment, rehabilitation, and palliative care, without experiencing any financial hardship or risk of impoverishment.
The Evolution of Universal Health Care:
- In 1977, the World Health Assembly endorsed the slogan “Health for All by 2000,” implying universalization.
- Thus, nobody is denied this and everybody is eligible without being discriminated against on the basis of financial status, gender, race, place of residence, affordability to pay, or any other factors.
- India committed itself to this goal through its National Health Policy in 1983.
India’s Initiatives for UHC:
- National Health Mission (NHM): NHM was launched by the Union Government in 2013 subsuming the National Rural Health Mission (2005) and the National Urban Health Mission (2013).
- Main components:
- Health System Strengthening
- Reproductive-Maternal- Neonatal-Child and Adolescent Health (RMNCH+A)
- Communicable and Non-Communicable Diseases
- NHM envisages achievement of universal access to equitable, affordable & quality health care services that are accountable and responsive to people’s needs.
- Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0: Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0 is an Integrated Nutrition Support Programme.
- It seeks to address the challenges of malnutrition in children, adolescent girls, pregnant women and lactating mothers through a strategic shift in nutrition content and delivery and by creation of a convergent eco-system to develop and promote practices that nurture health, wellness and immunity.
- Components:
- Nutrition Support for POSHAN through Supplementary Nutrition Programme (SNP);
- Early Childhood Care and Education [3-6 years] and early stimulation for (0-3 years);
- Anganwadi Infrastructure including modern, upgraded Saksham Anganwadi; and
- Poshan Abhiyaan aims to reduce stunting, undernutrition, anaemia and reduce low birth weight by 2%, 2%, 3% and 2% per annum r
- National Food Security Act (NFSA): The Union Government provides food grains at low cost under the NFSA.
- The act aims to ensure people’s food and nutritional security by assuring access to enough high-quality food at reasonable prices.
Advantages of Universal health coverage in India:
- Improved access to health services: UHC would ensure that all Indians have access to necessary healthcare services, including preventive care, treatment, and rehabilitation, regardless of their financial status or geographic location.
- Better health outcomes: Access to healthcare services will improve health outcomes and reduce mortality rates by diagnosing and treating illnesses and diseases at an earlier stage.
- Reduced financial burden: UHC would protect individuals and families from catastrophic healthcare expenses, reducing the financial burden on households and preventing them from falling into poverty due to healthcare costs.
- Increased government accountability: UHC would increase government accountability in healthcare, as the government would be responsible for ensuring that all citizens have access to essential health services.
- Increased productivity: Improved health outcomes would lead to increased productivity and economic growth as a healthy workforce is more productive.
Challenges in Implementing UHC in India:
Inequitable Access to Health Insurance:
- The lowest coverage of health insurance is among households with the lowest wealth quintile and underprivileged sections, indicating a lack of equitable access to health insurance.
- The NFHS-5 results paint a different picture for India, where insurance coverage is lowest (36.1%) among households with the lowest wealth quintile.
Lack of Financial Protection:
- Despite the existence of schemes like Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakram, the average out-of-pocket expenditure per delivery in public health facilities is still high, particularly in urban areas.
- The latest report of NFHS revealed that the average out-of-pocket expenditure per delivery in a public health facility is Rs. 2,916, which in the case of urban and rural stands at Rs. 3,385 and Rs. 2,770.
Inclusion and Exclusion Errors in Health Insurance Policies:
- Recent studies have shown that like earlier health insurance policies, the Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY) is also not free from inclusion and exclusion errors, which could lead to the inclusion of ineligible households and exclusion of eligible households.
Availability of Services:
- Although 56% of empanelled hospitals under the PMJAY are in the public sector, 40% are in the private for-profit sector, indicating that the availability of services may be concentrated in areas with previous experience implementing publicly funded health insurance schemes.
Inadequate Infrastructure:
- In many low- and middle-income countries, the lack of proper infrastructure is a significant challenge to achieving UHC.
- This includes inadequate health facilities, inadequate equipment, and inadequate medical supplies.
- There is a shortfall of 79.5% of specialists at the Community Health Centers (CHCs) as compared to the requirement.
Poor Health Education:
- Lack of education and awareness regarding healthy lifestyles and preventive health measures can lead to an increase in preventable illnesses and conditions.
Way Forward:
India’s National Health Mission, with concurrent intersectoral thrusts on Poshan Abhiyan, National Food Security, Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan, etc., is a better model of fully tax-funded Universal Health Care.
Thus, moving forward with a newer concept of Universal Health Care is necessary to encompass primary, secondary, and tertiary care for all who need it at an affordable cost without discrimination.
Source: The Hindu
Indiahandmade portal

Why in News?
Recently, the government launched a new e-commerce portal ‘Indiahandmade’.
About Indiahandmade:-
- Indiahandmade Portal is an e-commerce portal launched by the Indian Government.
- Objective: Empower artisans and weavers by providing them with a platform to sell their products directly to customers.
- This initiative is part of the government’s efforts to promote local artisans and craftsmanship and support the “Vocal for Local” movement.
- It provides a platform for artisans and weavers to showcase their products to a wide customer base.
- It connects artisans and weavers directly to buyers through a common platform.
- Indiahandmade Portal offers an opportunity for weavers and artisans to become future e-entrepreneurs.
- The portal provides free handholding to sellers from registration to order fulfilment, helping them with logistics, payments, and other aspects of online selling.
- This empowers weavers and artisans with the necessary tools and support to become successful e-entrepreneurs and grow their businesses.
- The portal does not charge any commission from sellers, ensuring that artisans and weavers receive the full value of their products.
- Free shipping is provided to customers, making it convenient and cost-effective for them to purchase products from the portal.
- It also provides a return option to customers, ensuring a seamless buying experience.
- Multiple payment gateways are available for customers to pay online, providing flexibility and convenience in payment options.
- The portal complements the PM-VIKAS initiative by providing a platform for artisans and weavers to showcase their products and sell them directly to customers.
- PM Vishwakarma Kaushal Samman Yojana (PM-VIKAS): aims to provide small artisans and craftsmen with training on quality, scale, and reach, as well as access to advanced skill training, modern digital techniques, brand promotion, linkage with local and global markets, digital payments, and social security.
Source: Financial Express
Nuclear liability law

Why in News?
The issues regarding India’s nuclear liability law came to continue to hold up the plan to build six nuclear power reactors in Maharashtra’s Jaitapur.
About Nuclear liability law:-
- The laws on civil nuclear liability ensure that compensation is available to the victims for nuclear damage caused by a nuclear incident or disaster and set out who will be liable for those damages.
- The international nuclear liability regime consists of multiple treaties and was strengthened after the 1986 Chornobyl nuclear accident.
- Convention on Supplementary Compensation (CSC): it is an umbrella convention adopted in 1997.
- Objective: Establish a minimum national compensation amount.
- India was a signatory to the CSC, Parliament ratified the convention in 2016.
- To keep in line with the international convention, India enacted the Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act (CLNDA) in 2010, to put in place a speedy compensation mechanism for victims of a nuclear accident.
- The CLNDA provides for strict and no-fault liability on the operator of the nuclear plant, where it will be held liable for damage regardless of any fault on its part.
- It establishes legal liability for nuclear harm as well as rapid compensation for victims of nuclear disasters.
- It specifies the experts who will assess claims of nuclear injury, sanction compensation, and provide financial assurance.
- It also specifies the amount the operator will have to shell out in case of damage caused by an accident and requires the operator to cover liability through insurance or other financial security.
- The operator’s maximum liability under Section 6(2) of the Act is Rs. 1500 crore.
- In case the damage claims exceed ₹1,500 crore, the CLNDA expects the government to step in, in accordance with Section 7(1)(a) of the CLND Act.
- However, it has limited the government liability amount to the rupee equivalent of 300 million Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) or about ₹2,100 to ₹2,300 crores.
- It specifies the limitations on the amount and time when an action for compensation can be brought against the operator.
- Section 7 (2) of the CLND Act provides that the Central Government may establish a “Nuclear Liability Fund” by charging such amount of levy from the operators, in such manner, as may be prescribed.
- Any violations of the terms of the act could result in fines.
- India currently has 22 nuclear reactors.
- All the existing reactors are operated by the state-owned Nuclear Power Corporation of India Limited (NPCIL).
- Nuclear Power Corporation of India Limited (NPCIL) is a Public Sector Enterprise.
- It is under the administrative control of the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE), Government of India.
- The Company was registered as a Public Limited Company under the Companies Act, 1956.
- Objective: operating atomic power plants and implementing atomic power projects for generation of electricity in pursuance of the schemes and programmes of the Government of India under the Atomic Energy Act, 1962.
- NPCIL is responsible for design, construction, commissioning and operation of nuclear power reactors.
- Mission: To develop nuclear power technology and to produce nuclear power as a safe, environmentally benign and economically viable source of electrical energy to meet the increasing electricity needs of the country’.
- Objectives:-
- To maximise the power generation and profitability from nuclear power stations with the motto ‘safety first and production next’.
- To increase nuclear power generation capacity in the country, consistent with the available resources in a safe, economical and rapid manner, in keeping with the growth of energy demand in the country.
- To continue and strengthen QA activities relating to nuclear power programme.
- To develop personnel at all levels to further improve their skills and performance consistent with the high technology.
- To strengthen the environmental protection measures relating to nuclear power generation.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
Gangetic Dolphin

Why in News?
Thickly knitted fishing gill nets have recently caused the death of another Gangetic Dolphin in the Bhagirathi River.
About Gangetic Dolphin:
- It is a freshwater species and one of the few river dolphins found in the world.
- It inhabits the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna and Karnaphuli-Sangu river systems of Nepal, India, and Bangladesh.
- Common Names: Blind dolphin, Ganges dolphin, Ganges susu, hihu, side-swimming dolphin, South Asian River Dolphin
- Scientific name:Platanista gangetica
- The Gangetic Dolphin has been recognized as India's National Aquatic Animal.
- Description:
- A long thin snout, rounded belly, stocky body and large flippers are characteristics of the Ganges River dolphin.
- It feeds majorly on fishes and is are usually found in counter-current systems of the main river channel.
- Its eyes lack lens, and as a result, this species is also referred to as the "blind dolphin".
- They have a highly developed bio-sonar system that facilitates them to hunt for fish even in murky waters.
- Being a mammal, the Ganges River dolphin cannot breathe in the water and must surface every 30-120 seconds. Because of the sound it produces when breathing, the animal is popularly referred to as the 'Susu'.
- Conservation status:
- IUCN: Endangered
- Wildlife (Protection) Act: Schedule-I
- CITES: Appendix I
Source: PIB
Rising Sea Level
Why in News?
- The 'State of the Global Climate 2022’ report released by WMO highlighted that sea level is rising at an unprecedented rate.
More about Report
- The rate of global mean sea-level [GSML] rise has doubled in three decades i.e., rate of sea-level rise was 2.27 mm/year in 1993-2002, it shot up to 4.62 mm/year in 2013-2022.
- Ocean Heat content (OHC) in 2022 touched a new record high. Around 90% of the energy trapped in the climate system by greenhouse gases goes into the ocean.
- In 2022, 58 percent of the ocean surface suffered at least one marine heatwave event and 25 per cent of the surface experienced at least one marine cold spell.
- Concentrations of the three main greenhouse gases – carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide – reached record observed highs in 2021.
- Earth’s ice cover known as cryosphere has thinned. The cumulative thickness loss since 1970 amounts to almost 30?m. Six of the ten most negative mass balance years on record (1950-2022) occurred since 2015
- Ocean Acidification: Global mean ocean pH has been steadily declining at rates not seen for at least the past 26,000 years.
What causes accelerated sea-level rise?
- According to the report during 2005-2019:
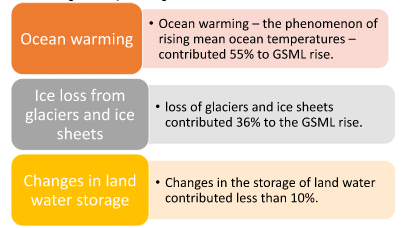
- According to the report during 2005-2019:
Impacts
- Increase inFrequency of cyclones: This will affect coastal communities and lead to large economic liabilities for tropical countries like India and South Africa, which have high population densities. For instance, South Africa was affected by five cyclones in over two months in 2022.
- Salinization of Groundwater: More seawater could seep into the ground, leading to the groundwater – which is usually freshwater – turning more and more saline. This in turn can exacerbate water crises in coastal areas as well as agriculture in adjacent regions.
- Forced migration: coastal ecosystems could be “completely changed”. In the Sundarbans delta in West Bengal, rising sea levels and coastal erosion has forced members of local communities to migrate.
- Record breaking rain: For instance, extensive flooding in Pakistan.
- Record breaking heat waves affected Europe during the summer. China had its most extensive and long-lasting heatwave since national records began
- Food insecurity: As of 2021, 2.3 billion people faced food insecurity, of which 924 million people faced severe food insecurity.
Source: The Hindu
What is Machine Learning?
Why in News?
A team of researchers used machine learning tools to recently confirm evidence of a previously unknown planet outside our solar system.
About Machine Learning:
- What is it? It is a branch of Artificial Intelligence (AI)and computer science which focuses on the use of data and algorithms to imitate the way that humans learn, gradually improving its accuracy.
- It gives computers the capability to learn without being explicitly programmed.
- It enables computers to learn automatically from past data.
- Machine learning uses various algorithms for building mathematical models and making predictions using historical data or information.
- Features of Machine learning:
- It is a data driven technology. Large amount of data generated by organizations on daily bases. So, by notable relationships in data, organizations makes better decisions.
- Machine can learn itself from past data and automatically improve.
- From the given dataset it detects various patterns on data.
- It is similar to data mining because it is also deals with the huge amount of data.
Source: Indian Express
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 29th April 2023 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the importance of daily current affairs for the UPSC exam? |  |
| 2. How can I stay updated with daily current affairs for the UPSC exam? |  |
| 3. Are there any specific topics that I should focus on while studying daily current affairs for the UPSC exam? |  |
| 4. How can I effectively revise daily current affairs for the UPSC exam? |  |
| 5. Can I solely rely on current affairs for my preparation for the UPSC exam? |  |


















