Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animal Class 7 Notes Science
Weather and climate affect our daily lives in many ways. Understanding the difference between weather and climate is important. This chapter will discuss weather, climate, and how animals adapt to their natural habitats
Weather and Climate
The state of atmospheric conditions at a given place and time is called weather. Weather elements include temperature, humidity, rainfall, snow, cloud cover, and wind. The characteristic pattern of weather elements in a place over a period of time is called climate. Climate tells us what it is like in the place where we usually live. Our way of living, clothes we wear, crops we grow, and food we eat depend on weather and climate
 Hygrometer
Hygrometer Maximum Minimum Thermometer
Maximum Minimum Thermometer- Weather Forecast
Weather forecast predicts weather conditions for a place over a short period of time. Scientists known as meteorologists monitor weather elements every day to make weather forecasts. Maximum-minimum thermometer measures maximum and minimum temperatures in a day. Rain gauge measures the amount of rainfall. Hygrometer measures the relative humidity of the air. - Factors Affecting Climate
Several factors affect the climate of the Earth. Latitude, altitude, distance from the sea, and ocean currents are some of the main factors. Latitude affects the amount of sunlight received by a place .Altitude affects the temperature of a place. Distance from the sea affects the temperature and rainfall of a place. Ocean currents affect the temperature and precipitation of a place. - Adaptation to Climate
Animals adapt to their natural habitats in various ways. Adaptation to climate includes changes in physical features, behaviour, and food habits. Animals in colder regions have thicker fur, larger body size, and hibernate during winters. Animals in hotter regions have thinner fur, lighter body size, and are active during nights.
Factors that affect the climate of the Earth
- Distance from the Sun
The sun is our main source of energy, and the Earth receives a small portion of the energy that the sun radiates. The distance of the Earth from the sun determines the climate on the Earth. The temperature on the Earth is just right for the survival of life forms on it. - Earth's Tilt
The Earth rotates about an imaginary line joining its North and South Poles called its axis of rotation, or simply its axis. The Earth's axis is inclined at an angle or has a 'tilt' of about 23.5°. Because of this tilt and the Earth's revolution around the sun, we have seasons on the Earth.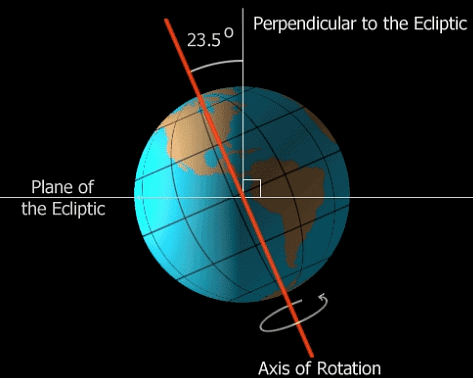 Earth with its axis of rotation
Earth with its axis of rotation
 Spinning top
Spinning top
- Sunrise and Sunset
The length of a day is given by the difference in the times of the sunrise and sunset. The area of the Earth's surface lit by the sun varies due to the Earth's tilt and its position in its orbit around the sun. The longest day of the year in the Northern Hemisphere is around 22nd June, and the shortest day is around 22nd December. - Adaptations to Climate
Plants and animals have adapted to the climate of their respective regions. Some animals have thick fur or feathers to keep warm in cold regions, while others have thin fur in hot regions to release heat. Plants have adapted to different levels of rainfall and temperature in various ways, such as developing deep roots to access groundwater or growing thorns to protect themselves from herbivores. - Human Adaptations to Climate
Humans have adapted to different climates by developing various practices and technologies. People living in hot regions wear light-coloured and loose clothing to stay cool, while those in cold regions wear heavy clothing to keep warm. Humans have also developed technologies such as air conditioning and heating systems to control indoor temperature.
Activity: Plotting Changes in the Length of the Day
- To plot a graph of changes in the length of the day, you will need a centimetre graph sheet, data from your local newspaper for at least a month, a sharp pencil, and an eraser.
- Note the times of sunrise and sunset every day from the daily newspaper for at least a month.
- Plot the sunrise and sunset times on the y-axis and the date on the x-axis.
- Join the points plotted for the sunrise times and separately join the points for the sunset times.
- Colour the space between the sunrise and sunset lines with a yellow or orange coloured pencil.
- You can choose any city on the globe and plot the sunrise-sunset graph for it, such as a city close to the Equator and a city close to the North/South Pole.
Climate of a Place
Climate is the long-term pattern of weather in a particular area. It affects the life of people, animals, and plants in that area. In this chapter, we will learn about the factors that influence the climate of a place and how people and animals adapt to different climates.
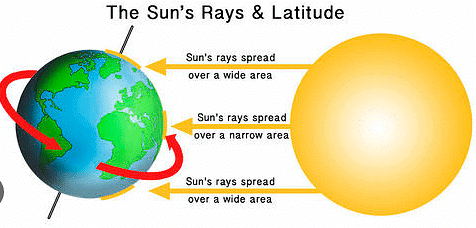
Factors that Affect Climate
- Distance from the Equator (Latitude)
Places closer to the equator are warmer than the places closer to the poles. The sun's rays fall directly on the equator and at an angle on the poles. Example: India is warmer than Greenland. - Height Above Sea Level and Distance from the Sea and Mountains
The higher a place is, the cooler it is. The height of a place above sea level is called altitude. The sea has a moderating influence on the climate of a place. Places near the coast, such as Mumbai, Chennai, and Kolkata, are neither too hot nor too cold. Mountains can change or even stop winds and also influence the rainfall in a place. - Weather of a Place:
Weather is the day-to-day condition of the atmosphere in a particular area. It is influenced by temperature and humidity. - Temperature
The temperature on any day depends on the amount of sunlight received. It is generally cooler during the nights than in the day time. Urban areas may have higher temperatures than rural areas due to pollution, higher density of people and houses, less number of trees, etc. - Humidity
The amount of water vapour present in the atmosphere determines humidity. Places near the sea coast, such as Kolkata and Mumbai, generally have greater humidity than places far away from the sea, such as Delhi and Uttar Pradesh. Humidity of a region is usually higher in the rainy season than during summer and winter.
Adaptation to Climate:
- People
People in different parts of the world have adapted to different climates. For example, people in cold regions wear warm clothes and use firewood to keep themselves warm. People in hot regions wear light clothes and use fans or air conditioners to keep themselves cool. - Animals
Animals have also adapted to different climates. For example, animals in cold regions, such as polar bears, have thick fur to keep themselves warm. Animals in hot regions, such as camels, have humps to store fat, which they can use as food and water when it is scarce.
 |
Download the notes
Chapter Notes: Climate & Adaptation
|
Download as PDF |
Adaptations in Animals for Different Climates
Climate refers to the weather conditions prevailing in an area over a long period of time. Animals have special characteristics that enable them to live in a particular climate, known as adaptations.
Adaptations in Animals for Hot and Dry (Desert-like) Climates
Water is scarce in hot and dry climates, and animals need adaptations to conserve water. Camels have long eyelashes, ear hair, and nostrils that they can close to keep sand out. Camels also have a hump that stores fatty tissue as a water reservoir. Kangaroo rats live in burrows and get their food and water requirements by digesting dry seeds. Various species of desert-dwelling ground squirrels and toads remain dormant during the hottest part of the summer.
Camels also have a hump that stores fatty tissue as a water reservoir. Kangaroo rats live in burrows and get their food and water requirements by digesting dry seeds. Various species of desert-dwelling ground squirrels and toads remain dormant during the hottest part of the summer.
Adaptations in Animals for Hot Tropical and Temperate Climates
Animals found in hot tropical and temperate climates have adaptations mainly for regulating temperature and for faster evaporation of water. Gorillas, monkeys, jaguars, sloths, and colorful birds, such as macaws, can be found in this region. Many animals in this region have long legs and tails, and very large ears that work like fans. Leaf insects and stick insects are shaped or colored to match their surroundings, which makes them harder to spot. Several animals, such as monkeys, live on trees to avoid predators on the ground.
Many animals in this region have long legs and tails, and very large ears that work like fans. Leaf insects and stick insects are shaped or colored to match their surroundings, which makes them harder to spot. Several animals, such as monkeys, live on trees to avoid predators on the ground.
Extremely Cold Climates
Climate refers to the prevailing weather conditions of a particular region. Different animals have adaptations to survive in extreme climates.

Adaptations in Extremely Cold Climates
Animals living in cold areas have adaptations to keep their bodies warm. Layers of fat deposits keep animals warm, and they take on the temperature of the water. Polar bears and many other animals have a thick layer of fat called blubber under their skins, which keeps their bodies warm and insulated from the cold. The white fur of the polar bear acts as a good insulator against the cold and helps them camouflage from prey.
 Female polar bears dig dens in the snow to hibernate and survive without food or water during the winter. Penguins huddle together in groups to stay warm and protect their eggs from the cold. Arctic foxes, Canadian lynxes, and Arctic hares are larger in colder climates and have furry paws and ears to keep warm and move easily in the snow. Arctic birds such as the ptarmigans have feathers up to their feet to keep their bodies warm.
Female polar bears dig dens in the snow to hibernate and survive without food or water during the winter. Penguins huddle together in groups to stay warm and protect their eggs from the cold. Arctic foxes, Canadian lynxes, and Arctic hares are larger in colder climates and have furry paws and ears to keep warm and move easily in the snow. Arctic birds such as the ptarmigans have feathers up to their feet to keep their bodies warm.
Key Words
"Activity:
Aim: The aim of the activity is to plot a graph of daily changes in temperature.
Materials needed: A centimetre graph sheet, temperature data from your local newspaper for at least ten days, and red and blue pencils.
Method: Note down the date and the maximum and minimum temperatures from the newspaper for ten days. On a graph sheet, plot the date on the x-axis and the corresponding maximum temperatures on the y-axis. Join these points with a red pencil to get the maximum temperature graph. Repeat the steps for the minimum temperatures. Join the points with a blue pencil to get the minimum temperature graph.
Observation: A curved graph is obtained, indicating that the maximum and minimum temperatures vary from one day to the next. Also, make a note of the season during which you are collecting the data. How do you think the maximum and minimum temperature will vary during the course of the year
Conclusion: Climate is influenced by various factors such as distance from the equator, altitude, distance from the sea and mountains, temperature, and humidity. People and animals have adapted to different climates in various ways. By understanding the climate of a place, we can adapt to it and make the best use of its resources."
Let's Remember
Fill in the blanks with the correct words.
Q.1. The weather forecast predicts the weather of a place for the next few ____(days/years).
The weather forecast predicts the weather of a place for the next few days.
The weather forecast is a prediction of the weather conditions in a particular location for a specific period. It usually forecasts the weather for the next few days, up to a week or two.
Q.2. The diameter of the Earth is about twelve ____ (thousand /million) kilometres.
The diameter of the Earth is about twelve thousand kilometres.
The diameter of the Earth is the distance across the widest point of the planet, passing through its center. The diameter of the Earth is approximately 12,742 km, which is equivalent to around 7,917.5 miles.
Q.3. Temperature, humidity, rainfall, cloud cover, etc. are called ____ (Earth/weather)elements.
Temperature, humidity, rainfall, cloud cover, etc. are called weather elements.
Temperature, humidity, rainfall, cloud cover, wind speed, and direction are some of the essential components that are considered while determining the weather. These variables change from time to time, and it is their combination that creates different weather conditions.
Q.4. A hygrometer is used to measure _____(rainfall/relative humidity).
A hygrometer is used to measure relative humidity.
A hygrometer is an instrument used to measure the relative humidity in the air. Relative humidity is a measure of the amount of moisture present in the air compared to the maximum amount of moisture that the air could hold at that temperature.
Q.5. The climate of the Earth ____(has/has not) remained the same through the ages.
The climate of the Earth has not remained the same through the ages.
The Earth's climate has undergone significant changes over millions of years due to various natural and human factors. There have been periods of extreme cold and warmth, glacial ages and ice ages, and warmer periods like the present interglacial period. These fluctuations in climate have led to the evolution of new species and the extinction of others.
Q.6. The Earth's tilt is about____ (23.5/90").
The Earth's tilt is about 23.5 degrees.
The Earth's tilt, also known as axial tilt, is the angle between the planet's rotational axis and its orbital plane. The Earth's tilt is currently about 23.5 degrees, and it is responsible for the changing seasons in different parts of the planet.
Q.7. The Earth rotates about its____ (equator/axis).
The Earth rotates about its axis.
The Earth rotates around its axis, an imaginary line passing through its center from the North Pole to the South Pole. The rotation of the Earth takes approximately 24 hours to complete one full rotation, resulting in day and night cycles.
|
140 videos|108 docs|18 tests
|






















