UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 3rd May 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Shilabhattarika

Why in News?
Recent decoding of Copper plates sheds light on the celebrated ancient Sanskrit poetess Shilabhattarika.
About Shilabhattarika:-
- Shilabhattarika was a Sanskrit poetess who lived in the 9th century.
- M. B. Padma, a scholar of the University of Mysore, speculates that she may be the same as Shila-maha Devi, the queen of the 8th-century Rashtrakuta ruler Dhruva.
- His theory is based on the fact that the suffix “Bhattarika” attached to the poet’s name indicates her high social status and that the queen is known to have made generous grants to scholars.
- The 10th-century poet Rajashekhara praises Shilabhattarika as a leading figure of the Panchali literary style (one of the four major contemporary literary styles)
- The other three are Vaidharbhi, Gaudi, and Lati.
- According to Rajashekhara, the Panchali style can be traced to the works of Shilabhattarika, and possibly to some of the works of the 7th-century poet Bana.
- Shilabhattarika has been quoted by several classical Sanskrit literary critics, and her verses appear in most major Sanskrit anthologies.
- She is known to have written at least 46 poems on topics such as “love, morality, politics, nature, beauty, the seasons, insects, anger, indignation, codes of conduct, and the characteristic features of various kinds of heroines.“
- However, most of her works are now lost.
- Only six of her short poems are extant.
- Sharngadhara-paddhati, a 14th-century anthology, praises her and three other female poets in the following words.
- Shilabhattarika, Vijja, Marula, and Morika are poetesses of renown with great poetic genius and erudition.
GS-II
U.S. Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF)

Why in News?
India recently rejected a report by the U.S. Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF) that alleged "severe violations" of religious freedom in the country.
About U.S. Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF):
- It is an independent, bipartisan federal government entity created by the 1998 International Religious Freedom Act (IRFA).
- Functions:
- Reviews the facts and circumstances of violations of religious freedom internationally;
- Make policy recommendations to the President, the Secretary of State, and the Congress;
- It uses international standards to monitor religious freedom violations globally.
- It is required to issue its own annual report setting forth its independent recommendations for U.S. policy
- Composition: USCIRF has nine commissioners, appointed by either the President or Congressional leaders of each political party, supported by a non-partisan professional staff.
Source: The Hindu
Article 142

Why in News?
In a recent ruling, the Supreme Court rules that it can directly grant a divorce to couples under Article 142.
About Article 142:-
- It deals with the enforcement of decrees and orders of the Supreme Court.
- Article 142 provides discretionary power to the Supreme Court as it states that the Supreme Court in the exercise of its jurisdiction may pass such decree or make such order as is necessary for doing complete justice in any cause or matter pending before it.
- Subsection 1 of Article 142 provides a unique power to the Supreme Court, to do complete justice between the parties.
- According to some eminent jurists, natural justice is above law, and the Supreme Court shall have full right to pass any order that it considers just.
- Therefore, the Supreme Court shall exercise these powers and will not be deterred from doing justice by the provision of any rule or law, executive practice or executive circular or regulation etc.
- The framers of the Constitution felt that this provision is of utmost significance to those people who have to suffer due to the delay in getting their necessary reliefs due to the disadvantaged position of the judicial system.
Significance of Article 142:-
- Prevents Injustice: It provides a special and extraordinary power to the Supreme Court to do complete justice to the litigants who have suffered traversed illegality or injustice in the proceedings.
- Uphold citizen’s rights: Article 142 has been invoked for the purpose of protecting the rights of the different sections of the population.
- Check on Government: Works as a system of checks and balances with the Government or Legislature.
Cases where the Supreme Court has invoked its plenary powers under Article 142:-
- Manohar Lal Sharma v. Principal Secretary(2014): The Supreme Court can deal with exceptional circumstances interfering with the larger interest of the public in order to fabricate trust in the rule of law.
- A.R. Antulay v. R.S. Nayak(1988): The Supreme Court held that any discretion which is given by the court should not be arbitrary or in any way be inconsistent with provisions of any statute laid down.
- Union Carbide Corporation v. Union of India (1989): In Bhopal Gas Tragedy Case, the court ordered to award of compensation to the victims and placed itself in a position above the Parliamentary laws.
- Siddiq v. Mahant Suresh Das (2019): Popularly known as the Ayodhya dispute, the Supreme Court exercised the powers mentioned under Article 142 of the Constitution.
Source: The Hindu
Supreme Court ruling on Consensual Divorce

Why in News?
Recently, a Constitution Bench of the Supreme Court ruled that it can exercise its plenary power to do “complete justice” under Article 142(1) of the Constitution to dissolve a marriage.
More about the news
- The Supreme Court Bench ruled that it can exercise its plenary power to do “complete justice” under Article 142(1) of the Constitution to dissolve a marriage on the ground that it had ‘broken down irretrievably’, without referring the parties to a family court where they must wait 6-18 months for a decree of divorce by mutual consent.
What is “Irretrievable breakdown”?
- What factors can courts consider while deciding if a marriage has irretrievably broken down?
- During the pendency of the case recently, the court said that it would determine what rules should be followed while dissolving marriages directly under Article 142 of the Constitution.
- The first and most “obvious” condition is that the court should be fully convinced and satisfied that the marriage is “totally unworkable, emotionally dead and beyond salvation and, therefore, dissolution of marriage is the right solution and the only way forward”.
- The court has also laid down the following factors:
- The period of time that the parties had cohabited after marriage;
- When the parties had last cohabited;
- Nature of allegations made by the parties against each other and their family members;
- Orders passed in the legal proceedings from time to time;
- Cumulative impact on the personal relationship;
- Whether, and how many attempts were made to settle the disputes by a court or through mediation, and when the last attempt was made.
- During the pendency of the case recently, the court said that it would determine what rules should be followed while dissolving marriages directly under Article 142 of the Constitution.
Current procedure for divorce under the Hindu Marriage Act
- Section 13B of the HMA provides for “divorce by mutual consent”.
- Filing of divorce:
- Both parties to the marriage must together file a petition to the district court “on the ground that they have been living separately for a period of one year or more, that they have not been able to live together and that they have mutually agreed that the marriage should be dissolved”.
- Mandatory “cooling-off” period :
- Under Section 13B(2) of the Act, the parties must move a second motion before the court “not earlier than six months after the date of the presentation of the [first] petition and not later than eighteen months after the said date, if the petition is not withdrawn in the meantime”.
- The mandatory six-month wait is intended to give the parties time to withdraw their plea.
- Decree of divorce:
- Thereafter, “the court shall, on being satisfied, after hearing the parties and after making such inquiry as it thinks fit that the averments in the petition are true, pass a decree of divorce declaring the marriage to be dissolved with effect from the date of the decree”.
- Filing of divorce:
- Exemptions:
- A petition for divorce by mutual consent can be moved only after a year of the marriage.
- However, Section 14 of the HMA allows a divorce petition sooner in case of “exceptional hardship to the petitioner or of exceptional depravity on the part of the respondent”.
- A waiver of the six-month waiting period under Section 13B(2) can be sought in an exemption application filed before the family court.
- A petition for divorce by mutual consent can be moved only after a year of the marriage.
- Issue:
- The process of obtaining a decree of divorce is often time-consuming and lengthy owing to a large number of similar cases pending before family courts.
Social aspects of divorce in India
- Stigma around divorce & increasing number:
- In Indian culture, marriage is a holy institution, and divorce is considered taboo.
- Although the situation is improving as the younger generation is becoming more independent, the term “divorce” is still frowned upon.
- Despite the fact that India’s divorce rate is lower than that of Western countries, the number of divorce cases is steadily increasing as a result of different social and economic changes.
- Mental health:
- Divorce has been identified as a risk factor for mental health disorders and has been linked to negative mental health outcomes.
- Social & financial effects:
- Divorce, in particular, has a detrimental impact on a family’s financial stability, social environment, academic/employment performance, as well as the family’s psychological and physical well-being.
- On Children:
- Divorce has a significant impact on the parent-child connection.
- Usually, it is seen that children, as well as custodial parents, do not have that connection which a child and parent should have.
- Children of divorce are more likely to experience negative feelings, lower self-esteem, behavioral problems, anxiety, depression, and mood disorders.
Way ahead
- The apex court in its previous orders had held that the waiting period should be done away with in cases where there is no way to save the marriage and all efforts at mediation and conciliation have run their course; where parties have genuinely settled their differences including alimony, custody of child, etc, between themselves; and already a year and a half has passed since their first motion for separation.
- The court had observed that application for waiver of waiting period can be filed in court within a week of their first motion for separation.
- The proceedings can be done through video-conferencing
Source: Times of India
GS-III
ASEAN INDIA MARITIME EXERCISE (AIME-2023)

Why in News?
India sent INS Satpura and INS Delhi to participate in the first ever ASEAN-India Maritime Exercise (AIME 2023) scheduled from 02 to 08 May 2023.
More about News
- The maiden exercise will be conducted off the coast of Singapore and will feature harbour and at-sea events off the coast of Singapore.
- The Republic of Singapore Navy (RSN) and the Indian Navy (IN) are co-hosting the ASEAN-India Maritime Exercise.
- With AIME-2023 India becomes the 4th ASEAN dialogue partner, after Russia, China and the US to hold the ASEAN+1 maritime exercise.
Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
- It is a political and economic organization.
- Founded in: 1967 by the five South-East Asian nations of Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore and Thailand.
- Aim: Promoting economic growth and regional stability among its members.
- 10 Members at Present: Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand and Vietnam.
- ASEAN Plus Three:
It is a forum that functions as a coordinator of co-operation between the ASEAN and the three East Asian nations of China, South Korea, and Japan.
- ASEAN Plus Six:
- The group includes ASEAN Plus Three as well as India, Australia, and New Zealand.
Source: The Hindu
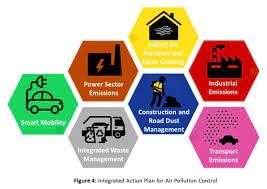
Action plan to reduce Air Pollution
Why in News?
Delhi Chief Minister announced a 14-point action plan to reduce air pollution during the summer months with a focus on controlling dust pollution.
Major Highlights
- The Delhi government will conduct a real-time apportionment study of 13 identified hotspots to find sources of pollution and solutions to curb them.
- People will have to register to carry out construction work on land measuring more than 500 square meters.
- The government will increase green cover by planting 59 lakh saplings.
- Urban farming will also be increased and 400 workshops will be conducted and free training kits will be given to people.
- The government is preparing a new policy to deal with industrial waste management and techniques to collect and scientifically dispose of industrial waste to curb industrial pollution.
About Air pollution
- It is contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment by any chemical, physical or biological agent that modifies the natural characteristics of the atmosphere.
- Household combustion devices, motor vehicles, industrial facilities, and forest fires are common sources of air pollution.
- Pollutants of major public health concern include particulate matter, carbon monoxide, ozone, nitrogen dioxide, and sulfur dioxide.
Causes
- Certain gases in the atmosphere can cause air pollution. For example, in cities, a gas called ozone is a major cause of air pollution.
- Ozone is also a greenhouse gas that can be both good and bad for our environment. It all depends where it is in Earth’s atmosphere.
- It is caused by solid and liquid particles and certain gases that are suspended in the air.
- These particles and gases can come from car and truck exhaust, factories, dust, pollen, mold spores, volcanoes, and wildfires. The solid and liquid particles suspended in our air are called aerosols.
- Air pollution happens when solid and liquid particles—called aerosols—and certain gases end up in our air.
- Scenario in Delhi: During winter, pollution stems from weather patterns, stubble burning, vehicle emissions, and open burning; whereas in summer, it is driven by landfill fires spurred by heat and blazes in areas with dry foliage.
- Dust is one of the main causes of pollution during the summer months.
Impacts
- Breathing in polluted air can be very bad for our health. Long-term exposure to air pollution has been associated with diseases of the heart and lungs, cancers, and other health problems.
- Outdoor and indoor air pollution cause respiratory and other diseases and are important sources of morbidity and mortality.
Steps Taken by Government
- National Clean Air Programme (NCAP): The Government has launched the National Clean Air Programme (NCAP) as a long-term, a time-bound programme to reduce air pollution in a comprehensive manner with a target to achieve up to 40% reduction in PM10 concentration level by the year 2025-2026 w.r.t. baseline of 2017-18.
- The concept of LiFE: It was introduced by the Prime Minister at COP26 in Glasgow on 1 November 2021
- LiFE envisions replacing the prevalent 'use-and-dispose' economy—governed by mindless and destructive consumption—with a circular economy, which would be defined by mindful and deliberate utilisation.
- Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs): India updated its Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) – plans to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius, promising to reduce the emissions intensity of GDP by 45% by 2030, from the 2005 level, and achieve 50% cumulative electric power installed capacity from non-fossil fuel-based energy resources by 2030.
- Commission for Air Quality Management: The Commission has been set up for Air Quality Management in the National Capital Region and Adjoining Areas for better coordination, research, identification, and resolution of problems surrounding the air quality index and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.
- Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP): It is a set of emergency measures that kick in to prevent further deterioration of air quality once it reaches a certain threshold in the Delhi-NCR region.
- The Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana Household LPG program and other schemes have helped to dramatically expand access to clean energy, especially for rural households.
Way Ahead
- The air does not belong to any one State therefore all have to work in close coordination with neighbouring States to curb air pollution.
- Policies to reduce air pollution offer a win-win strategy for both climate and health, lowering the burden of disease attributable to air pollution, as well as contributing to the near- and long-term mitigation of climate change.
- The WHO also prescribed some steps to be taken by governments to improve the air quality and health.
- It urged countries to implement national air quality standards in line with the WHO’s guidelines, usage of clean household energy, and implementation of stricter vehicle emissions and efficiency standards among other measures.
Source: The Hindu
Bluebugging
Why in News?
Recently, Andhra Pradesh police cautioned smartphone users to be wary of “bluebugging”.
About Bluebugging:-
- Bluebugging is a form of hacking that lets attackers access a device through its discoverable Bluetooth connection.
- A hacker can gain unauthorized access to these apps and devices and control them as per their wish through bluebugging.
- Any Bluetooth-enabled device including True Wireless Stereo (TWS) devices or earbuds susceptible to bluebugging.
Preventive Measures:
- Turning off Bluetooth and disconnecting paired Bluetooth devices when not in use.
- Making Bluetooth devices undiscoverable from Bluetooth settings.
- Updating the device’s system software to the latest version.
- Limited use of public Wi-Fi.
- Watch out for suspicious activities on your device.
- Monitoring of sudden spikes in data usage.
- Usage of modern anti-virus software.
SOURCE: THE HINDU
|
38 videos|5254 docs|1109 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 3rd May 2023 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are the subjects covered in GS-I, GS-II, and GS-III exams conducted by UPSC? |  |
| 2. How can I prepare for GS-I, GS-II, and GS-III exams effectively? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of current affairs in GS-I, GS-II, and GS-III exams? |  |
| 4. Can I clear the UPSC exams without scoring well in GS-I, GS-II, and GS-III? |  |
| 5. Are there any specific tips for time management during GS-I, GS-II, and GS-III exams? |  |