Skeletal and Muscular System - 1 Class 5 Worksheet Science
Q1: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
(i) Which of the following is a function of the skeletal system?
(a) Produces body heat
(b) Provides support and shape to the body
(c) Stores fat
(d) Controls body temperature
Ans: (b)
The skeletal system provides support and shape to the body by forming its structural framework. It also protects vital organs and helps in movement.

(ii) How many bones are there in the human body?
(a) 206
(b) 215
(c) 220
(d) 230
Ans: (a)
There are 206 bones in the human body. These bones provide support and protection to the body and its vital organs. They also aid in the movement of the body.
(iii) What type of joint allows movement in all directions?
(a) Hinge joint
(b) Pivot joint
(c) Ball-and-socket joint
(d) Gliding joint
Ans: (c)
Ball-and-socket joints, like the hip and shoulder joints, enable a wide range of motion, allowing the bones to move in multiple directions.
(iv) Which of the following is a type of muscle found in the body?
(a) Cardiac muscle
(b) Sinew muscle
(c) Plasma muscle
(d) Bone muscle
Ans: (a)
Cardiac muscle is a type of muscle found in the heart. It is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. Other types of muscles found in the body include skeletal and smooth muscles.
(v) What is the longest bone in the human body?
(a) Tibia
(b) Femur
(c) Humerus
(d) Ulna
Ans: (a)
The femur, also known as the thigh bone, is the longest bone in the human body. It extends from the hip to the knee and is responsible for supporting the weight of the body.
Q2: Fill in the blanks
(i) The human body has _____ bones.
Ans: The human body has 206 bones.
(ii) Bones are connected to each other by ____.
Ans: Bones are connected to each other by joints.
(iii) The _____ is the longest bone in the human body.
Ans: The femur is the longest bone in the human body.
(iv) The _____ is the largest and strongest bone in the face.
Ans: The mandible is the largest and strongest bone in the face.
(v) Muscles are attached to bones by _____.
Ans: Muscles are attached to bones by tendons.
Q3: Match the column
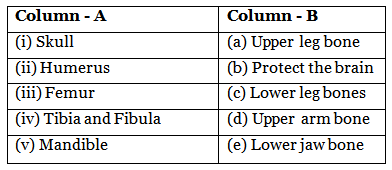
Ans: (i) - (b) Protect the brain
The skull is a bony structure that surrounds and protects the brain from injury.
(ii) - (d) Upper arm bone
The humerus is the long bone in the upper arm, connecting the shoulder to the elbow.
(iii) - (a) Upper leg bone
The femur is the longest bone in the human body and is located in the upper leg.
(iv) - (c) Lower leg bones
The tibia and fibula are the two bones in the lower leg. The tibia is the larger, weight-bearing bone, while the fibula is the smaller, non-weight-bearing bone.
(v) - (e) Lower jaw bone
The mandible is the lower jaw bone and is responsible for the movement of the lower jaw during talking and chewing.
Q4: True or False
(i) Bones produce blood cells.
Ans: True
Bones produce blood cells in the bone marrow, which is the soft, spongy tissue found in the center of bones.
(ii) There are 107 bones in the human body.
Ans: False
There are 206 bones in the human body, not 107.
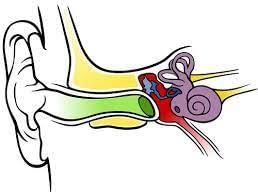
(iii) The smallest bone in the human body is the stapes.
Ans: True
The smallest bone in the human body is the stapes, a tiny bone in the middle ear that helps transmit sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear.
(iv) Muscles can only push, not pull.
Ans: False
Muscles can both push and pull. They work in pairs, with one muscle contracting (shortening) while the other muscle relaxes (lengthens) to create movement.
(v) There are two types of muscles: voluntary and involuntary.
Ans: True
There are two types of muscles: voluntary muscles, which are controlled consciously and can be moved at will (e.g., skeletal muscles), and involuntary muscles, which are not under conscious control and move automatically (e.g., smooth muscles in organs and blood vessels).
Q5: Arrange in Correct Order
(i) Arrange the following bones in the correct order, from the top of the body to the bottom:(a) Skull
(b) Spine
(c) Femur (thigh bone)
(d) Ankle bones
Ans: a) Skull → (b) Spine → (c) Femur (thigh bone) → (d) Ankle bones
The skull is at the topmost part of the body, followed by the spine (vertebral column), then the femur (thigh bone), and finally, the ankle bones.
(ii) Arrange the following muscle types in the correct order, from largest to smallest in size:
(a) Cardiac muscles
(b) Skeletal muscles
(c) Smooth muscles
Ans: b) Skeletal muscles →(c) Smooth muscles → (a) Cardiac muscles
Skeletal muscles are the largest type of muscles, followed by smooth muscles, and then the cardiac muscles, which are found in the heart.
(iii) Arrange the steps involved in muscle contraction in the correct sequence:
(a) Relaxation of muscle fibres
(b) Nerve signal reaches muscle
(c) Actin and myosin filaments slide past each other
(d) Calcium release within muscle fibres
Ans: Nerve signal reaches muscle → (d) Calcium release within muscle fibres → (c)
Actin and myosin filaments slide past each other → a) Relaxation of muscle fibres
(iv) Arrange the bones of the human hand in the correct order, starting from the wrist:
(a) Phalanges
(b) Carpals
(c) Metacarpals
Ans: (b) Carpals → (c) Metacarpals → (a) Phalanges
The carpals are the wrist bones, followed by the metacarpals in the palm, and finally, the phalanges, which are the finger bones.
(v) Arrange the stages of bone formation (ossification) in the correct order:
(a) Bone remodelling
(b) Bone resorption
(c) Bone formation
(d) Cartilage formation
Ans: (d) Cartilage formation → (c) Bone formation → (b) Bone resorption → (a) Bone remodelling
The process of bone formation starts with cartilage formation, which is later replaced by bone in the process of ossification. Bone resorption occurs when old bone tissue is broken down, and bone remodeling happens to maintain the bone's strength and structure.
 |
Download the notes
Worksheet Solutions: Skeletal & Muscular System - 1
|
Download as PDF |
Q6: Choose the Odd One Out
(i) Which of the following bones is the odd one out?
(a) Femur (thigh bone)
(b) Humerus (upper arm bone)
(c) Patella (kneecap)
(d) Mandible (jawbone)
Ans: (c)
The patella is the odd one out as it is a sesamoid bone, found within a tendon, while the others are long bones.
(ii) Which of the following muscles is the odd one out?
(a) Biceps
(b) Quadriceps
(c) Hamstrings
(d) Triceps
Ans: (b)
The quadriceps is the odd one out as it is a group of four muscles located at the front of the thigh, while the others are individual muscles.
(iii) Which of the following bones is the odd one out?
(a) Radius
(b) Ulna
(c) Femur
(d) Tibia
Ans: (c)
The femur is the odd one out as it is located in the leg, while the others are bones of the forearm.
(iv) Which of the following muscles is the odd one out?
(a) Deltoid
(b) Pectoralis major
(c) Gluteus maximus
(d) Tibialis anterior
Ans: (d)
The tibialis anterior is the odd one out as it is located in the front of the lower leg, while the others are muscles of the upper body.
(v) Which of the following bones is the odd one out?
(a) Scapula (shoulder blade)
(b) Sternum (breastbone)
(c) Clavicle (collarbone)
(d) Coccyx (tailbone)
Ans: (d)
The coccyx is the odd one out as it is a vestigial tailbone, while the others are bones that form part of the human axial skeleton.
Q7: Short Answer Questions
(i) What are the three types of muscles found in the human body?
Ans: The three types of muscles found in the human body are skeletal muscles, smooth muscles, and cardiac muscles.

(ii) What is the function of tendons?
Ans: Tendons are strong, fibrous tissues that connect muscles to bones. Their function is to transmit the force generated by the contraction of muscles to the bones, allowing movement.
(iii) What are the two main parts of the human skeletal system?
Ans: The two main parts of the human skeletal system are the axial skeleton, which consists of the skull, vertebral column, and rib cage, and the appendicular skeleton, which includes the limbs and the pelvic and shoulder girdles.
(iv) What is the difference between voluntary and involuntary muscles?
Ans: Voluntary muscles are muscles that can be consciously controlled, such as the skeletal muscles used in walking, running, or lifting objects. Involuntary muscles are muscles that cannot be consciously controlled, such as the smooth muscles found in the digestive system and the cardiac muscle in the heart.
(v) How do muscles work to produce movement?
Ans: Muscles work to produce movement by contracting and relaxing. When a muscle contracts, it pulls on the bone it is attached to, causing the bone to move. Muscles usually work in pairs, with one muscle contracting while the opposing muscle relaxes, allowing for smooth and controlled movement.
|
45 videos|202 docs|45 tests
|
FAQs on Skeletal and Muscular System - 1 Class 5 Worksheet Science
| 1. What are the main functions of the skeletal system? |  |
| 2. How do muscles work with the skeletal system to enable movement? |  |
| 3. What types of muscles are there in the human body? |  |
| 4. What role do ligaments and tendons play in the skeletal and muscular system? |  |
| 5. How can I maintain a healthy skeletal and muscular system? |  |




























