UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 5th May 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Heat index
Why in News?
India to launch its own heat index next year to quantify heat hazard, generate impact-based heat wave alerts for specific locations.
About Heat index:
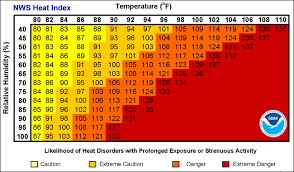
- Heat index is a measure of how hot it feels when humidity is factored in along with the air temperature, and the figures were calculated using data from the India Meteorological Department (IMD).
- It is also known as the apparent temperature.
- When the body gets too hot, it begins to perspire or sweat to cool itself off.
- If the perspiration is not able to evaporate, the body cannot regulate its temperature.
- Evaporation is a cooling process. When perspiration is evaporated off the body, it effectively reduces the body's temperature. When the atmospheric moisture content (i.e. relative humidity) is high, the rate of evaporation from the body decreases.
- In other words, the human body feels warmer in humid conditions. The opposite is true when the relative humidity decreases because the rate of perspiration increases.
- The body actually feels cooler in arid conditions.
- There is direct relationship between the air temperature and relative humidity and the heat index, meaning as the air temperature and relative humidity increase (decrease), the heat index increases (decreases).
Source: The Hindu
Food Street Project

Why in News?
Union Minister of Health and Family Welfare, Dr Mansukh Mandaviya recently reviewed the ‘Food Street Project’.
About:
- It is aimed at developing 100 healthy and hygienic food-streets across the country.
- The project seeks to encourage safe and healthy food practices, reduce foodborne illnesses and improve overall health outcomes.
- To operationalize the food streets, the National Health Mission will provide assistance of one crore rupees per food street.
- Financial assistance would be provided for activities such as the provision of safe drinking water, hand washing, toilet facilities, and appropriate liquid and solid waste disposal.
- The initiative will be implemented through NHM in convergence with the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
- The Health Ministry has taken various steps to improve the hygiene and food safety standards protocols for food street hubs.
- These initiatives include training of food handlers, independent third-party audits, and certification under the Clean Street Food Hub initiative of the Eat Right India movement.
Source: Newsonair
GS-II
Star campaigners
Why in News?
The Election Commission of India (ECI) recently issued an advisory urging star campaigners to “maintain the dignity of the political discourse.”
About Star Campaigners:-
- A star campaigner is a celebrity vote seeker in an election for a party.
- This person can be anyone, a politician or even a film star.
- There is no law governing who can or cannot be made a star campaigner.
- They are nominated by the concerned political parties specifying their constituencies and duration of the status.
Terms and Conditions:-
- Numbers of Star Campaigners:
- A ‘recognised’ National or State party declared as such by the ECI can nominate a maximum of 40-star campaigners.
- An unrecognised political party can nominate a maximum of 20-star campaigners.
- Section 77 (b) of The Representation of People’s Act, 1951 says that most of the expenses incurred by the campaigner “shall not be deemed to be an expenditure in connection with the election”.
- In other words, all expenses will be borne by the respective political party.
- For example, expenses borne by star campaigners on account of travel by air or by any other means of transport shall not be deemed as expenditure in connection with the election.
- The manual to the Model Code of Conduct states that for the benefit of availing Section 77 (1) of The RP Act, a permit for the mode of transport for every star campaigner will be issued centrally and against their name.
- It is also mandatory for this permit to be stuck on a prominent and visible place on the vehicle.
- If a star campaigner campaigns specifically for one candidate:-
- If a candidate or her election agent shares the stage with a star campaigner at a rally, then the entire expenditure on that rally, other than the travel expenses of the star campaigner, is added to the candidate’s expenses.
- Even if the candidate is not present at the star campaigner’s rally, but there are posters with her photographs or her name on display, the entire expenditure will be added to the candidate’s account.
- This applies even if the star campaigner mentions the candidate’s name during the event.
- When more than one candidate shares the stage, or there are posters with their photographs, then the expenses of such rally/meeting are equally divided between all such candidates.
Prime Minister as Star Campaigner:-
- The MCC guidelines say when a prime minister or a former prime minister is a star campaigner, the expenditure incurred on security including bullet-proof vehicles will be borne by the government and will not be added to the election expenses of the party or the individual candidate.
- However, if another campaigner travels with the prime minister, the individual candidate will have to bear 50% of the expenditure incurred on the security arrangements.
Source: Indian Express
CU-Chayan portal
Why in News?
Recently, UGC launched the ‘CU-Chayan’ portal for faculty recruitment in Central varsities.
About CU-Chayan portal:-
- CU-Chayan portal is a new platform to hire faculty members in central universities.
- The portal will provide a consolidated list of job openings across all 46 central universities under the Union Ministry of Education.
- Central universities will still be responsible for advertising job openings, accepting applications, screening applicants, conducting interviews, and hiring faculty members, just as they did before.
- However, all of these tasks will be managed through the admin dashboard for each university on the portal.
Process:-
- Applicants will find a consolidated list of openings across the central universities, personalized dashboards to help manage the application process, and filters such as location, designation, subject, experience, and education level to view openings that suit them.
Benefits for Applicants and Universities:-
- Both applicants and universities will benefit from it as it provides a simple interface to apply for job openings.
- The portal will also throw up real-time data on vacancies, applications under consideration, and whether the reservation policy is being followed or not.
- It will fast-track the recruitment process without centralizing the faculty hiring for the central universities.
About UGC:-
- UGC came into existence in 1953.
- It became a statutory body by an Act of Parliament in 1956.
- Background:-
- UGC was formed in 1946 to oversee the work of the three Central Universities of Aligarh, Banaras and, Delhi.
- In 1947, the Committee was entrusted with the responsibility of dealing with all the then existing Universities.
- After independence, the University Education Commission was set up in 1948 under the Chairmanship of S. Radhakrishnan and it recommended that the UGC be reconstituted on the general model of the University Grants Commission of the United Kingdom.
- The UGC was formally established in November 1956, by an Act of Parliament.
- Objective: for the coordination, determination and maintenance of standards of teaching, examination and research in university education.
- The head office of the UGC is located in New Delhi.
- It is charged with coordination, determination and maintenance of standards of higher education.
- It provides recognition to universities in India.
- It disburses funds to such recognized universities and colleges.
Source: Hindustan Times
Sherpa

Why in News?
India's G20 Sherpa Amitabh Kant has said that the tourism sector is not only a driver of growth but also a driver of job creation and employment.
About:
- Who are they? A Sherpa is a personal representative of the leader of a member country at an international Summit meeting such as the G8, G20, the Nuclear Security Summit etc.
- Task: The Sherpa engages in planning, negotiation and implementation tasks through the Summit. They coordinate the agenda, seek consensus at the highest political levels, and participate in a series of pre-Summit consultations to help negotiate their leaders’ positions.
- Who are appointed Sherpas? Sherpas are career diplomats or senior government officials appointed by the leaders of their countries.
- Etymology: The term is derived from the Nepalese Sherpa people, who serve as guides for mountaineers in the Himalayas.
Source: Newsonair
GS-III
EU’s Artificial Intelligence Act
Why in News?
The European Parliament reached a preliminary deal on a new draft of the European Union’s ambitious Artificial Intelligence Act.
Provisions of the Act
- Aims:
- Bringing transparency, trust, and accountability to AI and creating a framework to mitigate risks to the safety, health, fundamental rights, and democratic values of the EU.
- Strike a balance between promoting “the uptake of AI while mitigating or preventing harms associated with certain uses of the technology”.
- Provisions:
- Act defines AI as “software that is developed with one or more of the techniques that can, for a given set of human-defined objectives, generate outputs such as content, predictions, recommendations, or decisions influencing the environments they interact with. It identifies AI tools based on machine learning and deep learning, knowledge and logic-based approaches and statistical approaches.
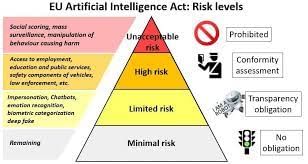
- There are four risk categories in the Act— unacceptable, high, limited and minimal.
- The Act prohibits using technologies in the unacceptable risk category with little exception. These include the use of real-time facial and biometric identification systems in public spaces.
- The Act lays substantial focus on AI in the high-risk category, prescribing a number of pre-and post-market requirements for developers and users of such systems.it includes AI used in healthcare, education, employment etc. ‘conformity assessments’ is mandatory for high-risk AI before coming to market. It also comply with mandatory post-market monitoring obligations such as logging performance data and maintaining continuous compliance.
- AI systems in the limited and minimal risk category such as spam filters or video games can be used with a few requirements like transparency obligations.
- Generative AI such as the language model-based ChatGPT will have to disclose any copyrighted material used to develop their systems.
- EU’s regulatory framework proposal states that “as AI is a fast-evolving technology, the proposal has a future-proof approach, allowing rules to adapt to technological change”.
Global AI regulations
- USA'S AI Bill of Rights (AIBoR) as a guidance or a handbook rather than a binding legislation.
- China regulations targeting specific types of algorithms and AI. It told companies to “promote positive energy”, to not “endanger national security or the social public interest” and to “give an explanation” when they harm the legitimate interests of users.
- India: NITI Aayog has published a series of papers on the subject of Responsible AI for All. However, the government is not considering bringing a law or regulating the growth of artificial intelligence in the country."
Need of AI Regulation
- Omnipresence: AI is capable of performing a wide variety of tasks including voice assistance, recommending music, driving cars, detecting cancer etc.
- Black Box: Many AI tools are essentially black boxes, meaning even those who design them cannot explain what goes on inside them to generate a particular output.
- Complex and unexplainable AI tools have already manifested in wrongful arrests E.g. GPT-4 can generate versatile, human-competitive and genuine looking content, which may be inaccurate and use copyrighted material created by others.
- Industry stakeholders including Twitter CEO Elon Musk and Apple co-founder Steve Wozniak signed an open letter asking AI labs to stop the training of AI models more powerful than GPT-4 for six months, citing potential risks to society and humanity.
Challenges in AI regulation
- Lack of understanding: AI is a complex and rapidly evolving technology, which makes it difficult for regulators to fully understand its capabilities and potential risks. Sometimes it is often not possible for even developers to explain the functioning of algorithms.
- Privacy and security: AI systems can collect, store, and analyze vast amounts of personal data, raising concerns about privacy and security. Companies are criticizing transparency requirements, fearing that it could mean divulging trade secrets.
- Accountability: It can be challenging to hold individuals or organizations accountable for the actions of AI systems, particularly if the systems are autonomous and evolving.
- International coordination: AI is a global technology, which means that regulation must be coordinated across borders to be effective. However, different countries may have different regulatory approaches and priorities.
Way forward for AI Regulation
- Compliance: Compliance is at the heart of policy implementation. Policymakers should consider how the regulations and the implementation machinery could be adjusted to lower costs and barriers to innovation without adversely impacting safety or public good.
- Multi-stakeholder approach: AI can be a major driver of economic growth and social progress if industry, civil society, government, and the public work together to support development of the technology and implement checks and balances to ensure accountability.
- International cooperation: In the context of various interrelated technological applications, and the cross-border reach of AI technology, international engagement and cooperation, and regulatory harmonization are crucial.
Source: The Hindu
‘Go First’ Files for Voluntary Insolvency

Why in News?
The carrier Go Airlines (India) Ltd (Go First), filed for voluntary insolvency proceedings with the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT).
Why this drastic step?
- The Wadia Group-owned air carrier with more than 5,000 employees has taken the decision amid severe fund crunch.
- Go First took the step due to the increasing number of failing engines supplied by Pratt & Whitney's International Aero Engines. This resulted in the airline being forced to ground 25 aircraft, which is approximately 50 percent of its Airbus A320neo aircraft fleet as of 1 May 2023.
- The engine supplier, according to the airline, has failed to repair those engines and/or provide sufficient spare leased engines as it was required to do pursuant to its obligations under the relevant agreements.
National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT)
- About: NCLT is a quasi-judicial authority incorporated for dealing with corporate disputes that are of civil nature arising under the Companies Act.
- It was established on the recommendations of the V. Balakrishna Eradi committee.
- Principal Bench: New Delhi
- Objectives: Adjudicates issues relating to Indian companies.
- NCLT has to adjudicate the insolvency resolution process of companies and limited liability partnerships under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016.
- Composition of NCLT bench: President, 16 judicial members, and 9 Technical members.
What are Voluntary Insolvency Proceedings?
- The voluntary insolvency means that the company has accepted its business is insolvent.
- It is a process in which the company says it cannot pay debts and needs help from someone to sort it out. When the company goes insolvent, it can proceed to voluntary liquidation.
- This process refers to the dissolution of a company with approval from shareholders and creditors of the company. It is a time-bound process which needs to be completed in 270 days from the date of commencement of Voluntary Liquidation.
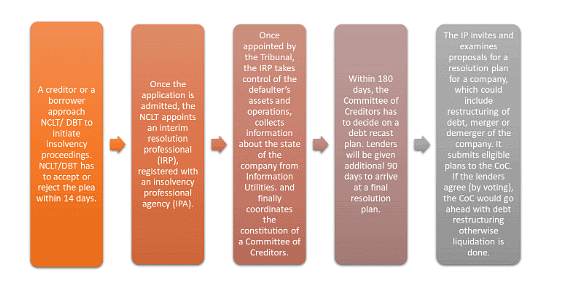
Sequence of Steps under IBC
Source: Indian Express
The US Federal Reserve
Why in News?
The US Federal Reserve has raised interest rates by 25 basis points to check inflation.
About the US Federal Reserve:
- The US Federal Reserve, often referred to in short as "The Fed", is the central banking system of the United States of America, created in 1913.
- Events such as the Great Depression (1930s) and the Great Recession (2000s) have resulted in its roles and responsibilities expanding over time.
- It consists of three major entities - the Board of Governors, the Federal Reserve Banks and the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC).
- The Fed takes the Monetary policy actions (such as raising or reducing the benchmark interest rate) to influence the availability and cost of money and credit to help promote national economic goals.
Source: Newsonair
|
38 videos|5288 docs|1117 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 5th May 2023 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the UPSC exam and how does it work? |  |
| 2. What are the three general studies papers in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 3. How can I prepare for the UPSC exam effectively? |  |
| 4. What are some recommended study materials for the UPSC exam? |  |
| 5. Is coaching necessary to crack the UPSC exam? |  |


















