UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 16th May 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
What is ‘Adopt a Heritage’ Scheme?
Why in News?
Private firms, companies, and public sector units can adopt and maintain State-owned archaeological sites or monuments through agreements with the Union Ministry of Culture.
- These businesses are referred to as “Monument Mitras” under the ‘Adopt a Heritage’ Scheme.
Adopt a Heritage scheme
- The ‘Adopt a Heritage: Apni Dharohar, Apni Pehchaan’ scheme is a collaboration between the Ministry of Tourism, Ministry of Culture, and the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI).
- Launched in September 2017, it aims to develop selected monuments and heritage sites across India with the participation of public and private entities.
- The scheme focuses on providing and maintaining basic amenities, improving accessibility, cleanliness, illumination, and advanced facilities like surveillance systems and night-viewing facilities.
Selection and Adoption Process
- Sites/monuments are selected based on tourist footfall and visibility, and they can be adopted by private and public sector companies and individuals known as “Monument Mitras.”
- The Oversight and Vision Committee, co-chaired by the Tourism Secretary and the Culture Secretary, selects the Monument Mitras based on their vision for developing the site.
- No financial bid is involved in the selection process, and corporate entities are expected to use their Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) funds for the upkeep of the site.
- The adopted sites provide limited visibility to the Monument Mitras on the premises and on the Incredible India website.
- The oversight committee has the authority to terminate the memorandum of understanding in case of non-compliance or non-performance.
Previous Initiatives and Controversy
- The government previously formed the National Culture Fund and initiated the ‘Campaign Clean India’ scheme to involve the corporate sector in maintaining tourist sites.
- The ‘Adopt a Heritage’ scheme faced controversy when it was reported that Dalmia Bharat, under a MoU, would build infrastructure and maintain the Red Fort.
- Critics argued that the involvement of private parties in iconic monuments raised concerns about the preservation of India’s heritage.
- The government defended the scheme, stating that it aimed to increase tourist footfall and improve the maintenance of sites.
Perils and Challenges of the Scheme
- Diminishing role of ASI: The scheme sidelines the role of the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) and disregards established guidelines for presenting excavated objects.
- Undue commercialization: Allowing businesses to occupy prime public land and build their brands can further diminish the grounds around iconic monuments.
- Demographic impacts: The involvement of big businesses in guided tours and illumination of monuments may impact local communities and their livelihoods.
- Disregarding historical preservation: Concerns arise about businesses altering the historical character of monuments not protected by the ASI or located in states without Archaeology Directorates.
Govt intention behind the scheme
- Businesses can help citizens understand why monuments matter: This can be done by earmarking CSR funds for grants for researching, writing, and publishing high-quality textbooks, and developing imaginative and effective ways of teaching history.
- Skillful conservation: Industrial houses can support the meaningful conservation of heritage buildings by looking within through their CSR.
- Collaborative efforts: The private sector’s resources and expertise may also help the ASI and State Archaeology Directorates to secure monuments from dams, mining projects, defacement, and looting.
- Cultural contribution: By embracing principles of historical preservation, businesses and organizations can showcase India’s progress in safeguarding its pluralistic heritage and inspire citizen participation in this endeavour.
Way ahead
- Transparent selection process: Implement a fair and transparent process for selecting entities or Monument Mitras to adopt heritage sites, ensuring accountability and avoiding favoritism.
- Robust monitoring mechanism: Develop a strong monitoring system to ensure that the adopted sites are maintained and developed according to the agreed-upon standards and guidelines.
- Preservation protocols: Strictly adhere to preservation guidelines set by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) and other relevant authorities to protect the historical and cultural integrity of heritage sites.
- Engagement with local communities: Involve local communities and stakeholders in decision-making processes, encouraging their participation, ownership, and contribution to the conservation efforts.
- Sustainable tourism practices: Promote sustainable tourism practices that minimize the environmental impact, respect the local culture and heritage, and provide socio-economic benefits to the communities living around the heritage sites.
Source: The Hindu
Satavahana
Why in News?
Explorers in Telangana recover artefacts which link Cherial village in Siddipet district to Satavahana period
About the news:
Field researchers have retrieved:
- several terracotta figurines of dolls, yakshini puppets, etc.
- pottery shreds of different designs,
- Colourful stone beads and terracotta beads which were part of ornaments during the Satavahana period.
- Coin from the Satavahana period. The coin bears the insignia of Ujjain on one side and Brahmi script on the other.
- Large bricks measuring 14 X 12 X 4 inches and figures of goddesses belong to the Ikshvaku as well as Satavahana periods.
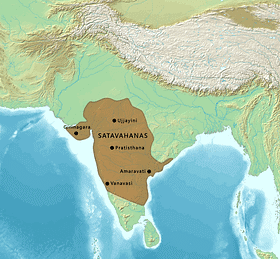
About Satavahanas:
- The Satavahanas came to power in the Deccan area after the decline of Mauryans in the region.
- The first king of the Satavahana dynasty was Simuka. Most glorious period under Gautamiputra Satkarni.
- Territorial spread: The Satavahana kingdom majorly comprised present Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra and Telangana. At times, their rule also included parts of Gujarat, Karnataka as well as Madhya Pradesh.
- Matronyms: The Satavahana kings used matronyms like Gautamiputra and Vaishishthiputra. This is a unique feature of Satavahana But this does not indicate that they were matriarchal or matrilineal in any sense.
- Multiple capitals: Two of the capitals were Amaravati and Pratishthana (Paithan).
- They assumed the title of Dakshinapatha Pati (Lord of Dakshinapatha).
- Grants: The Satavahanas started the practice of giving royal grants of land to Brahmans and Buddhist monks.
- For instance, the Karle inscription mentions the grant of Karajika village, near Pune, Maharashtra.
- Coins: The Satavahanas were the first native Indian kings to have issued their own coins.
- Gautamiputra Satakarni started this practice.
- Nahapana coins: Nahapana was a powerful Western Satraps king and the adversary of Gautamiputra Satkarni. Gautamiputa defeated him and more than 800 Nahapana silver coins (found near Nasik) bear the marks of being restruck by the Satavahana king.
- They mostly issued coins of lead, which is found on the Deccan and also coins of silver, copper and bronze.
- The coins had the portraits of rulers on them.
- These coins sometimes had bilingual legends, one side Prakrit and the other side in Tamil, Telugu or Kannada.
- Language: They patronised Prakrit more than Sanskrit. Sanskrit was rarely used. They used the Brahmi script.
- Religion: Even though the rulers were Hindus and claimed Brahmanical status, they supported Buddhism They revived Vedic Brahmanism and the corresponding rituals like the Ashvamedha yajna.
- Polity:
- The king was at the apex of the administrative hierarchy and considered the guardian of the established social order.
- The state was divided into aharas, each being governed by a minister called Amatya.
- The Satavahana kingdom had three grades of feudatories – Raja (who had the right to strike coins), Mahabhoja and Senapati.
- Art and architecture: Amravati Stupa was constructed by them. Paintings at Ajanta caves 9 and 10 are from Satavahana period.
- Major inscriptions:
- The earliest inscriptions of the Satavahans belong to the first century BCE when they defeated the Kanvas and established their power in parts of Central India.
- Nashik prashasti inscription by Gautami Balashri: It states that the horses of Gautamiputra drank waters of the “three oceans”(Arabian Sea, Bay of Bengal and Indian Ocean). It gives detailed account of Satavahana administration.
- Karle inscription: It mentions about donation of land to Buddhist monks.
Source: Indian Express
GS-II
The PoSH Act: The Indian law on sexual harassment in the workplace

Why in News?
The SC found “serious lapses” and “uncertainty” in the implementation of the PoSH Act 2013 and issued directions to the Union, States, and UTs to verify if all government bodies had formed the Internal Complaint Committees (ICCs).
- The Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) Act/PoSH Act, which came into force in 2013 applies to all public and private sector organisations throughout India.
How was the PoSH Act Formed?
- SC 1997 guidelines/Vishakha Guidelines: While hearing pleas filed against the crime, the SC noted the absence of any law that guarantee against “sexual harassment at workplaces”.
- The apex court laid down a set of guidelines to fill the statutory vacuum till a law could be enacted.
- The Court drew its guidelines from:
- Article 15 (protection against discrimination on grounds only of religion, race, caste, sex, and place of birth) of the Indian constitution.
- International Conventions and norms such as the General Recommendations of the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW), which India ratified in 1993.
- The PoSH Bill: It was introduced by the Women and Child Development Ministry in 2007. It went through several amendments and came into force on December 9, 2013, after being enacted by the Parliament.
Key Provisions of the PoSH Act:
- Defines sexual harassment: To include unwelcome acts such as physical, verbal/non-verbal conduct - a demand or request for sexual favours, making sexually coloured remarks, showing pornography, etc.
- Lists down five circumstances that would constitute sexual harassment:
- Implied or explicit promise of preferential treatment in employment
- Implied or explicit threat of detrimental treatment in employment
- Implied or explicit threat about present or future employment status
- Interference with work or creating an intimidating or offensive or hostile work environment and
- Humiliating treatment likely to affect health or safety.
- Defines an employee (not just in accordance with the company law): All women employees, whether employed regularly, temporarily, contractually, on an ad hoc or daily wage basis, as apprentices or interns, can seek redressal to sexual harassment in the workplace.
- Expands the definition of ‘workplace’: Beyond traditional offices to include all kinds of organisations across sectors, even non-traditional workplaces (for example, telecommuting) and places visited by employees for work.
The Internal Complaints Committee (ICC) and Local Committees (LC):
- The law requires any employer with more than 10 employees to form an ICC, where a formal sexual harassment complaint can be filed by a woman.
- Composition of ICC: It is required to consist of a minimum of four members (at least half of whom should be women):
- A Presiding Officer who has to be a woman employed at a senior level at the workplace.
- Two Members from amongst employees and who have had experience in social work or have legal knowledge.
- One “External Member” from NGOs to pre-empt any undue pressure from senior levels.
- Besides, the Act mandates every district in the country to create a LC to receive complaints from women working in firms with less than 10 employees and from the informal sector, including domestic workers, etc.
Role of ICCs and LCs:
- These two bodies have to conduct inquiries in line with the POSH Act and comply with the “principles of natural justice” stated in the Rules of the Act.
- A woman can file a written complaint either to the internal or local complaints committee within three to six months of the sexual harassment incident.
- There are two ways to resolve the issue by the committee -
- “Through conciliation” between the complainant and the respondent (which cannot be a financial settlement), or
- Committees could initiate an inquiry, taking appropriate action based on what it finds.
Duties of the Employer:
- An employer has to file an annual audit report with the district officer about the number of sexual harassment complaints filed and actions taken at the end of the year.
- An employer is duty-bound to organise regular workshops and awareness programmes to educate employees about the Act, and conduct orientation and programmes for ICC members.
- If the employer fails to constitute an ICC or does not abide by any other provision, they must pay a fine of up to ₹50,000, which increases for a repeat offence.
The Hurdles to the Act’s Implementation:
- The law is largely inaccessible to women workers in the informal sector: As more than 80% of India’s women workers are employed in the informal sector.
- Huge underreporting: Due to the power dynamics of organisations, fear of professional repercussions (loss of employment), concrete evidence is often lacking, etc.
- Lacunae in the constitution of ICCs: 16 out of the 30 national sports federations in the country had not constituted an ICC to date.
- Improper composition of ICCs: ICCs either had an inadequate number of members or lacked a mandatory external member.
- Lack of clarity in the law: About how to conduct such inquiries, lack of awareness in women employees about who to approach in case of facing harassment, etc.
Reasons behind these Hurdles:
- The Act does not satisfactorily address accountability, not specifying who is in charge of ensuring that workplaces comply with the Act, and who can be held responsible if its provisions are not followed.
- The government maintains no centralised data regarding cases of harassment of women at workplaces.
Source: The Hindu
United Nations Forum on Forests (UNFF)
Why in News?
Discussions on integrated policies on sustainable forest management (SFM) and energy to meet the United Nations-mandated Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) took centre stage at the United Nations Forum on Forests (UNFF18).
About UNFF:
- The United Nations Forum on Forests (UNFF) was established in 2000 with the primary goal of promoting “the management, conservation, and sustainable development of all types of forests and to strengthen long-term political commitment to this end” based on the Rio Declaration, the Forest Principles, Chapter 11 of Agenda 21, and the Intergovernmental Panel on Forests (IPF) report.
- It is a subsidiary body created by the UN Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC).
- Every Member State of the United Nations as well as specialized agencies make up the Forum’s universal membership.
- The Collaborative Partnership on Forests (CPF), a grouping of 15 forest-related international organizations, institutions and convention secretariats, was established in April 2001, to support the work of the UNFF.
- Because of UNFF, in 2007, the UN General Assembly adopted the ‘Non-Legally Binding Instrument on All Types of Forests’, updating it to the ‘United Nations Forest Instrument’ in 2015.
Source: DTE
Meri LiFE Mera Swachh Shehar Campaign launched

Why in News?
The Union Ministry for Housing and Urban Affairs has launched the ‘Meri LiFE, Mera Swachh Shehar’ campaign.
Meri LiFE Mera Swachh Shehar
- The campaign focuses on waste management and promotes the principles of Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle (RRR).
- It aims to create awareness and encourage individuals to adopt sustainable daily habits for environmental protection.
- The campaign strengthens citizens’ commitment to reducing, reusing, and recycling under Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban 2.0.
- It aligns with Mission LiFE’s objective of adopting sustainable daily habits for environmental conservation.
Objectives of the Campaign
- The campaign involves setting up RRR Centres where citizens can contribute items such as clothes, shoes, books, toys, and plastic for reuse or recycling.
- The collected items will be refurbished or transformed into new products, aligning with the vision of a circular economy.
- The RRR approach empowers craftsmen, recyclers, Self Help Groups, entrepreneurs, and startups to convert waste into various products.
Key initiatives: RRR Centres and Circular Economy
- The RRR Centres to be launched nationwide will serve as one-stop collection centers for various unused or used items.
- Citizens, institutions, and commercial enterprises can deposit plastic items, clothes, shoes, books, and toys at these centers.
- The collected items will be refurbished for reuse or transformed into new products, promoting the government’s vision of a circular economy.
Source: PIB
GS-III
WPI Inflation rate
Why in News?
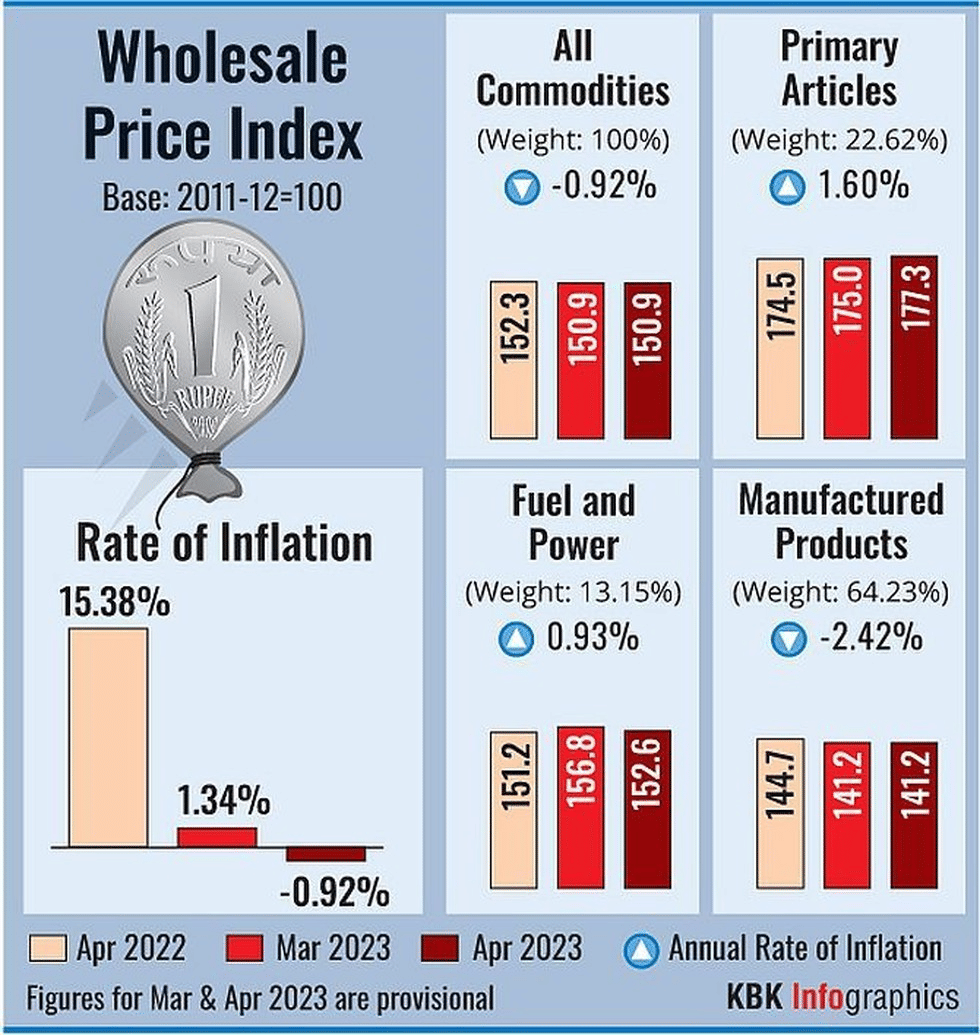
According to data released by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, INFLATION RATE based on Wholesale Price Index (WPI) fell to a near three-year low of (-) 0.92 % in April, slipping into negative territory for the first time in 33 months.
- Causes:
- A high base effect along with moderation in global commodity prices reflected in easing of food, fuel and other input costs.
- The decline in the WPI inflation rate in April 2023 was primarily contributed by fall in prices of basic metals, food products, mineral oils, textiles, non-food articles etc.
What Is a Wholesale Price Index (WPI)?
- Wholesale Price Index (WPI) represents the price of goods at a wholesale stage i.e. goods that are sold in bulk and traded between organizations instead of consumers.
- The index has a total of 697 items, including Primary Articles (117), fuel and power (16), and Manufactured Products (564).
- The percentage increase in WPI over a year gives the rate of inflation for that year.
- Currently, the base year of WPI is 2011-12.
- WPI is used as an important measure of inflation in India.
What is A Base Year?
- The inflation rate is calculated based on indices — WPI and CPI. The indices are set to 100 in a particular year and the year is the base year.
- For instance, a basket of goods was Rs 2 lakh in the base year and the index is set as 100 in that year. Now, if the price of the basket increases to Rs 2.2 lakh in the next year, the index will change to 110 that year. The change in the index value from 100 to 110 indicates 10 per cent inflation.
What is a Base Effect?
- The base effect refers to the effect that the choice of a basis of comparison or reference can have on the result of the comparison between data points.
- It often involves the use of some kind of ratio or index value between two points in a time-series data set and can also apply to cross-sectional or other types of data.
Source: Business Today
What is iDEX (Innovations for Defence Excellence)?


Why in News?
Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX) recently reached a milestone with the signing of the 250th contract, the first one under the Mission DefSpace.
About iDEX (Innovations for Defence Excellence):
- It is the flagship initiative of the Ministry of Defence (MoD), launched in April 2018.
- Aim: To achieve self-reliance and foster innovation and technology development in Defence and Aerospace by engaging Industries including MSMEs, start-ups, individual innovators, R&D institutes and academia.
- iDEX has partnered with leading incubators in the country to provide handholding, technical support and guidance to the winners of iDEX challenges.
- iDEX will be funded and managed by a ‘Defence Innovation Organization (DIO)’ which has been formed as a ‘not for profit company as per Section 8 of the Companies Act 2013 by the two founder members, i.e. Defence Public Sector Undertakings (DPSUs) - HAL & BEL.
- iDEX will function as the executive arm of DIO, carrying out all the required activities, while DIO will provide high-level policy guidance to iDEX.
- Under iDEX, financial support is provided to Start-ups/MSMEs/individual innovators and Partner Incubators through DIO.
What is Mission DefSpace?
- It was launched by the Prime Minister during DefExpo in October 2022.
- The goal of Mission DefSpace is to make India Atmanirbhar in defence technologies in the space domain.
- It will encourage technology development in space for defence applications by startups and young entrepreneurs through 75 Defence Space Challenges launched across various Department for Defence Production (DDP) initiatives viz iDEX, ‘Make 1’, and ‘Make 2’.
- The challenges are classified into five buckets, viz. Launch System, Satellite System, Communication & Payload System, Ground System and Software System provide a holistic 3600 overview of space.
Source: The Hindu
Hammerhead sharks
Why in News?
As per study, Hammerhead sharks can hold their breath to survive almost freezing-cold waters during deep dives.
About Hammer Shark heads:
- Hammerhead Sharks are characterized by a flattened hammer- or shovel-shaped head.
- These distinctive heads serve multiple purposes, including granting the sharks 360-degree vision as well as better hunting abilities.
- Distribution:
- They are widely distributed in tropical and temperate marine waters near the coasts and above the continental shelves.
- They may migrate seasonally, moving equatorward during the winter and poleward during the summer.
- Features:
- They have very impressive triangular, serrated teeth—like the edge of a saw’s blade.
- The hammerhead also has special sensors across its head that helps it scan for food in the ocean.
- Unlike many fish, hammerheads do not lay eggs. They are viviparous i.e. the female gives birth to young ones.
Source: The New York Times
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|