What is a Pilot Aptitude Battery Test (PABT) | Preparation Tips for SSB Interview - CDS PDF Download
PILOT APTITUDE BATTERY TEST (PABT).
The Pilot Aptitude Battery Test (PABT) is a special assessment used to evaluate a candidate's suitability for pilot training. It is employed as an independent selection tool for recruiting potential officers into the Flying Branch of the Indian Air Force. PABT consists of three tests: the Instrument Battery Test (INSB), the Sensory Motor Apparatus Test (SMA), and the Control Velocity Test (CVT). INSB is a written test, while the other two are conducted using machines. INSB has two parts.
INSB measures a candidate's ability to understand briefings and interpret the dials on an aircraft's instrument panel. Candidates who achieve the minimum required score are eligible for the machine tests. The machine tests, comprising SMA and CVT, assess the individual's psychomotor coordination skills. These tests are conducted on a single day and can only be taken once in a lifetime.
Best Tips for PABT, Pass your PABT for Flying branch
INSB consists of 75 questions divided into two parts: 15 and 60. You have 35 minutes to complete the test. It involves determining the direction of a fighter plane, such as ascending, descending, left bank, or right bank. The Officer Incharge will provide a proper explanation and show you large dummy meters to aid your understanding. The test covers important aircraft meters, including the compass meter, climbing or diving meter, horizon detector, and altimeter. After familiarizing yourself with these meters, you will be tested on them. Only those who pass this test are eligible for the machine tests.
- The machine tests have two parts. The first part involves adjusting a dot within a small rectangle on a screen and executing a beep-killing action by pressing a jockey button. The second part requires simultaneously turning off yellow and red lights using a left-hand lever while the test is conducted.
- Another machine test is control velocity test in which by jockey a small dot should be superimposed on free falling yellow dots coming from upper screen. You get three chances to appear all these machine test.

Pilot Aptitude Battery Test (PABT) is a unique test. It is aimed at assessing a candidate’s aptitude to be trained as a pilot. PABT is being used as an independent selection device to induct potential officers into Flying Branch of Indian Air Force. PABT comprises three tests viz Instrument Battery Test (INSB), Sensory Motor Apparatus Test (SMA) and Control Velocity Test (CVT). Instrument Battery Test (INSB) is a paper pencil test and other two are machine tests. The Instruments Battery Test (INSB) comprises two parts. This test assesses assimilation of the briefing and the ability of an individual to read and interpret the dials of an instrument panel of an aircraft. The candidates who score the minimum laid down criteria are subjected to the machine test. The machine test includes Sensory Motor Apparatus Test (SMA) and Control Velocity Test (CVT). These tests measure the psychomotor co-ordination skill of the individual. These tests are conducted on a single day and administered only once in life time.
- The aim of giving this test is generally to find out whether the candidate possesses mental alertness, presence of mind and self confidence and has adequate control over his nerves, and particularly whether he will be able to balance and control the flight of the aircraft and will not break down under stress.
- These tests are designed to measure the ability relevant to the art of flying a plane. These are : (a) Meter Reading Test (b) Flight Control Test (c) Drum Test.
Meter Reading Test
In this test the candidate is given 5 questions to be answered in 12Minutes. After this there is a second set of 60 questions on two Meters (Horizon and compass) for which 20 minutes are given to answer them.
This test is designed to see whether a candidate has the ability to read meters quickly so as to enable him to adjust his flight with the help of these meter readings.
- The Magnetic Compass – The compass needle always points out to the North. In this the meter reading the needle of the compass shows the bearing of the plane in relation to North. Thus one can find to which direction the plane is moving.
- The Altimeter – In altimeter, the needles move in clockwise direction. By reading the needles in the altimeter, Pilot is able to know the altitude (height) at which the plane is flying at a particular time. Adjustments in the plan’s altitude are made with the help of the altimeter. The accuracy of the altimeter in the plane is very important for its safe flying.
- Air Speed Indicator or Speedometer – The needle in this also moves in clockwise position. By reading the needle, the Pilot can find out the speed of the aircraft per hour. He, therefore, can make adjustments where necessary.
- Turn Indicator – From TI, the Pilot can find out whether the aircraft is turning left or right. If the plane is turning left, in the instrument the black ball remain in the centre and the white needle will move to the right and if the plane is turning right the black ball will remain in the centre and the white needle will move to the left. It means the white needle will invariably move to the direction opposite to which the aircraft is turning.
- Climbing up and Diving Down meter – In this, if the aircraft is climbing the needle will move up and when it dives down the needle will move down. Thus the pilot can find out whether the plane is going up or coming down.
- Gaining or Loosing Height Meter – It shows as to whether the plane is gaining losing or maintaining its height during the flight. Necessary adjustments are made by the Pilot with the help of this instrument.
Flight Control Test
- The entire apparatus is installed in a room. The ground glass screen is in the front and a stool fixed in the centre of the room. There are number of gears along both the sides of the stool. There are mechanical gadgets to control and direct the flights.
- This has two aims. Firstly, it is meant to test a candidate’s aptitude for flying an aircraft and controlling it during the flight, so that it follows a correct route in the air and keeps correct balance which is very essential during flight. Secondly, it also judges a candidate’s presence of mind, nervous control and alertness.
- This test judges the reflexive capabilities of a candidate. In this test, a spot of light (ball) is to be maintained in the centre of 2 concentric squares. The spot of light, if left, moves across randomly all over the screen. Also, there are 2 lights, yellow and red which come up in the top left and top right corners of the screen intermittently.
Now, the devices needed to control the spot are:
- A hand operated stick: This stick controls the movement of the stick in up and down direction. It is of the shape of the gear-changer in cars. Moving the stick back moves the ball up and moving it in forward direction moves it towards the bottom of the screen.
- Foot pedals: The operation of the pedals moves the spot of light (ball) to right or left.
- Light lever: A hand lever is provided which when moved forward puts off red light and when backward puts off yellow light.
- Beep button: A button on the top of the stick is used for putting off the beep sound in the headphones.
Here is a sample window for this test. Its exactly what you see at the screen at some random instant of time.
Drum Test
In this test, a spot of light (red) is to be superimposed on a series of yellow lights running on the screen from top to bottom. Whenever there is a successful superimposition, there is a small blip in the headphone. The more times you succeed in superimposing the red ball on the yellow balls, the more points you get. A sample screen is shown as:
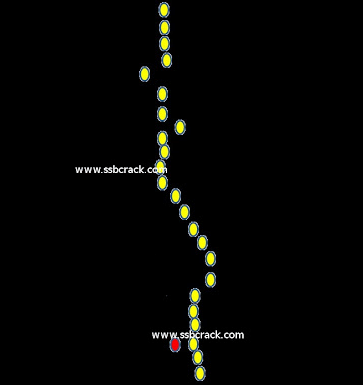
It must be borne in mind that these tests are explained clearly to the candidate by the officer In charge before he administers them, Candidates are, advised not to be afraid of this test and attempt it with confidence.
|
99 videos|112 docs|65 tests
|





















