Sample Lecturette 14: ISRO | Preparation Tips for SSB Interview - CDS PDF Download
Missiles have been used in India since the 18th century. Haider Ali and his son, Tipu Sultan, employed Mysore rockets, an early version of modern missiles, against the British East India Company.
In 1979, the idea to initiate the Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP) emerged. The "Missile Policy Committee" was established to recommend the launch of IGMDP and the acquisition of missiles for the Armed Forces.
During the 1980s, Dr Kalam and his team successfully launched Project SLV-3. In 1983, Dr Kalam became the director of the Defence Research Development Laboratory (DRDL). A Missile Technology Committee was formed to devise a plan for missile development.
In July 1983, the IGMDP was initiated at the DRDL. Five projects were launched, each led by a project head, with Dr Abdul Kalam overseeing the entire program.
The five missile systems under this programme are as follows (remember the acronym PATAN for the enemy):
- PRITHVI (earth): Short-range ballistic missiles
- AGNI (fire): Medium-range ballistic missiles
- TRISHUL (Trident): Short-range surface-to-air missiles
- AKASH (sky): Medium-range surface-to-air missiles
- NAG (cobra): Anti-tank guided missiles
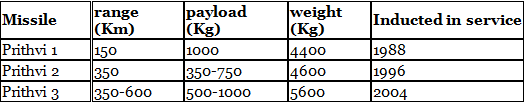
PRITHVI
- Prithvi is a missile that travels from the ground to the ground and can also carry a nuclear warhead.
- The Prithvi missile's propulsion system is derived from the Russian SA-2 missile, which is used for air defense. It uses either liquid fuel or a combination of liquid and solid fuels.
- It operates using a single-stage, twin-engine liquid propulsion system, with real-time software integrated into the onboard computer to ensure accurate impact.
Variants:
- Prithvi-I - Used by the Army
- Prithvi-II - Used by the Air Force
- Prithvi-III - Used by the Navy

AKASH
- Akash is a missile designed to be launched from the ground and shoot down targets in the air. It can reach speeds of Mach 2.5.
- It is highly effective at targeting objects at low, medium, and high altitudes. It employs a phased array radar to simultaneously detect multiple targets.
- The missile is capable of intercepting drones, missiles, fighter jets, and other objects flying at an altitude of 18 km.
- With a launch weight of 720kg, it can carry a payload weighing between 50kg and 60kg.
- Akash can be launched from various platforms.

Components of Akash include:
- Integrated ramjet engine
- Switchable guided antenna
- Command guidance system
- Onboard power supply
- Arming and detonation mechanism
- Rajendra phased-array radar
- Digital autopilot
TRISHUL
Trishul is a short-range missile that can be launched from the ground to target airborne threats within a range of 9km. It has a carrying capacity of 5.5 kg.
By utilising radar-guided command-to-line-of-sight guidance, this missile can successfully hit fast-moving targets travelling at speeds between 300-500 m/s.
The Indian government discontinued the Trishul project in 2008; however, it will still be employed as a technology demonstrator, as stated in official reports.
NAG
Nag is an anti-tank missile designed to eliminate targets at distances ranging from 500 meters to 20km. It can achieve a maximum speed of 230m/s. This missile operates on a "Fire and forget" principle, locking onto its target prior to launch. It also possesses the ability to correct its trajectory and locates targets using thermal imaging technology.
 Moreover, Nag is capable of penetrating the explosive reactive armour (ERA) of tanks.
Moreover, Nag is capable of penetrating the explosive reactive armour (ERA) of tanks.Variants
- Prospina (Infantry version): This variant has a range of 500m-4km and can be launched from various platforms, including the light infantry vehicle BMP-2.
- HeliNa (Helicopter version): Designed for use with the RUDRA helicopter and LCH, this variant has a range of 7-10km. It is utilised by both the army and the air force.
- Helina (SANT): This is an upgraded version of Helina, boasting an extended range of 20km.
- Man-Portable Anti-tank Guided Missile (MPATGM): A lighter version of the Helina missile, it can be launched from the shoulder and has a range of up to 2.5km on the battlefield.
AGNI
The Agni series of ballistic missiles is being developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation of India (DRDO) under the IGMD Programme.
- AGNI-1: The Agni-I is a ballistic missile with a short to intermediate range. It has a single engine and can carry a nuclear payload. Made of all-carbon composite materials, it provides protection to the payload during re-entry. It has a payload capacity of 1,000kg (conventional or nuclear) and a range between 700km - 800km. The missile can be transported by rail and road.
- AGNI-2: The Agni-II is a medium-range ballistic missile with two solid-fuel stages. It has a range of over 2,000km, covering most of China's western, central, and southern regions.
- AGNI-3: The Agni-3 is a two-stage ballistic missile with a strike range of 3,000km to 5,000km. It can carry conventional and nuclear warheads weighing up to 1.5 tonnes. Powered by a two-stage solid propellant engine, it was inducted into the Armed Forces in June 2011.

- AGNI-4: The Agni-4 is a two-stage solid propellant missile with a maximum range of 4,000km. It can accommodate a warhead weighing 1 tonne.
- AGNI-5: The Agni-5 is an Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM) powered by solid fuel, developed by DRDO. It has three stages and is capable of intercontinental ballistic surface-to-surface strikes. With a payload capacity of 1,500kg, it is nuclear-capable and can target any location in Asia, as well as parts of Africa and Europe.
|
99 videos|112 docs|65 tests
|



















