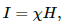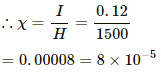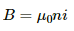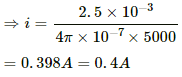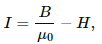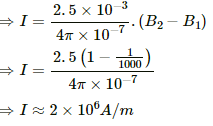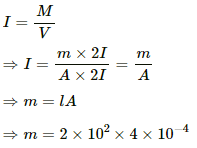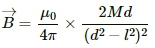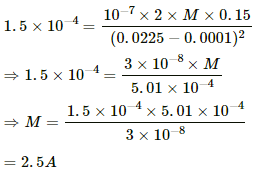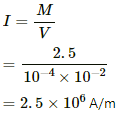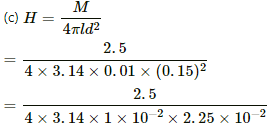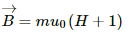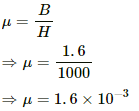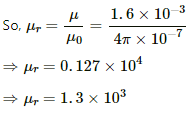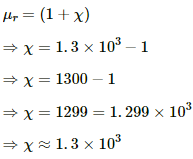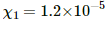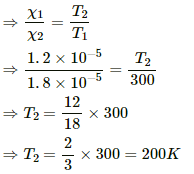HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 37: Magnetic Properties of Matter- 2 | HC Verma Solutions - JEE PDF Download
Exercises
Q.1. The magnetic intensity H at the centre of a long solenoid carrying a current of 2.0 A, is found to be 1500 A m−1. Find the number of turns per centimetre of the solenoid.
Here,
Current in the solenoid, I = 2 A
Magnetic intensity at the centre of long solenoid, H = 1500 Am−1
Magnetic field produced by a solenoid (B) is given by,
B = µ0ni ............(1)
Here, n = number of turns per unit length
i = electric current through the solenoid
Also, the relation between magnetic field strength (B) and magnetic intensity (H) is given by,...(2)
From equations (1) and (2), we get:-
H = ni
⇒ 1500 A/m = n × 2
⇒ n = 750 turns/meter
⇒ n = 7.5 turns/cm
Q.2. A rod is inserted as the core in the current-carrying solenoid of the previous problem. (a) What is the magnetic intensity H at the centre? (b) If the magnetization I of the core is found to be 0.12 A m−1, find the susceptibility of the material of the rod. (c) Is the material paramagnetic, diamagnetic or ferromagnetic?
Given:-
(a) Intensity of magnetisation, H = 1500 A/m
As the solenoid and the rod are long and we are interested in the magnetic intensity at the centre, the end effects may be neglected.
The sole effect of the rod in the magnetic field of the solenoid is that a magnetisation will be induced in the rod depending on rod magnetic properties.
There is no effect of the rod on the magnetic intensity at the centre.
(b) Magnetisation of the core, I = 0.12 A/m
We know:-is the susceptibility of the material of the rod.
(c) The material is paramagnetic.
Q.3. The magnetic field inside a long solenoid of 50 turns cm−1 is increased from 2.5 × 10−3 T to 2.5 T when an iron core of cross-sectional area 4 cm2 is inserted into it. Find (a) the current in the solenoid (b) the magnetisation I of the core and (c) the pole strength developed in the core.
Given:-
Magnetic field strength without iron core, B1 = 2.5 × 10−3 T
Magnetic field after introducing the iron core, B2 = 2.5 T
Area of cross-section of the iron core, A = 4 × 10−4 m2
Number of turns per unit length, n = 50 turns/cm = 5000 turns/m
(a) Magnetic field produced by a solenoid (B) is given by
where i = electric current in the solenoid
2.5 × 10−3 = 4π × 10−7 × 5000 × i
(b) Magnetisation (I) is given by,
where B is the net magnetic field after introducing the core, i.e. B = 2.5 T.
Andwill be the magnetising field, i.e. the difference between the two magnetic field's strengths.
(c) Intensity of magnetisation (I) is given by,
⇒ m = 800 A-m
Q.4. A bar magnet of length 1 cm and cross-sectional area 1.0 cm2 produces a magnetic field of 1.5 × 10−4 T at a point in end-on position at a distance 15 cm away from the centre. (a) Find the magnetic moment M of the magnet. (b) Find the magnetisation I of the magnet. (c) Find the magnetic field B at the centre of the magnet.
Given:-
Distance of the observation point from the centre of the bar magnet, d = 15 cm = 0.15 m
Length of the bar magnet, l = 1 cm = 0.01 m
Area of cross-section of the bar magnet, A = 1.0 cm2 = 1 × 10−4 m2
Magnetic field strength of the bar magnet, B = 1.5 × 10−4 T
As the observation point lies at the end-on position, magnetic field (B) is given by,
On substituting the respective values, we get:-
(b) Intensity of magnetisation (I) is given by,
Net H = HN + HS
= 884.6 = 8.846 × 102
= 314 T
= π × 10−7 (2.5 × 106 + 2 × 884.6)
= 3.14 T
Q.5. The susceptibility of annealed iron at saturation is 5500. Find the permeability of annealed iron at saturation.
Susceptibility of annealed iron,
X = 5500
The relation between permeability and susceptibility:-
Permeability, µ = µ0(1 + x)
µ = 4π × 10−7 (1 + 5500)
⇒ µ = 4 × 3.14 × 10−7 × 5501
⇒ µ = 69092.56 × 10−7
⇒ µ = 6.9 × 10−3
Q.6. The magnetic field B and the magnetic intensity H in a material are found to be 1.6 T and 1000 A m−1, respectively. Calculate the relative permeability µr and the susceptibility χ of the material.
Here,
Magnetic field strength, B = 1.6 T
Magnetising intensity in a material, H = 1000 A/m
The relation between magnetic field and magnetising field is given by
Relative permeability is defined as theratio of permeability in a medium to that in vacuum.
Relative permeability (μr) is given by,
Q.7. The susceptibility of magnesium at 300 K is 1.2 × 10−5. At what temperature will the susceptibility increase to 1.8 × 10−5?
Given,
Susceptibility of magnesium at 300 K,
Let T1 be the temperature at which susceptibility of magnesium is 1.2 × 10−5 and T2 be the temperature at which susceptibility of magnesium is 1.8 × 10−5.
According to Curie's law,
X = C/T,
where C is Curie's constant.
Q.8. Assume that each iron atom has a permanent magnetic moment equal to 2 Bohr magnetons (1 Bohr magneton equals 9.27 × 10−24 A m2). The density of atoms in iron is 8.52 × 1028 atoms m−3. (a) Find the maximum magnetisation I in a long cylinder of iron (b) Find the maximum magnetic field B on the axis inside the cylinder.
Given:-
No of atoms per unit volume, f = 8.52 × 1028 atoms/m3
Magnetisation per atom, M = 2 × 9.27 × 10−24 A-m2
(a) Intensity of magnetisation, I = M/V
⇒ I = 2 × 9.27 × 10−24 × 8.52 × 1028
⇒ I = 1.58 × 106 A/m
(b) For maximum magnetisation ,the magnetising field will be equal to the intensity of magnetisation.
So, I = H
Magnetic field (B) will be,
B = 4π × 10−7 × 1.58 × 106
⇒ B ≈ 19.8 × 10−1 = 2.0 T
Q.9. The coercive force for a certain permanent magnet is 4.0 × 104 A m−1. This magnet is placed inside a long solenoid of 40 turns/cm and a current is passed in the solenoid to demagnetise it completely. Find the current.
Given:-
Number of turns per unit length, n = 40 turns/cm = 4000 turns/m
Magnetising field, H = 4 × 104 A/m
Magnetic field inside a solenoid (B) is given by,
B = µ0nI,
where, n = number of turns per unit length.
I = current through the solenoid.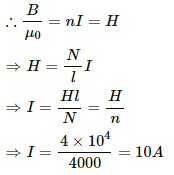
|
134 docs
|