UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 2nd June 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Phukot Karnali Hydro Electric Project
Why in News?
Recently, NHPC Limited and Vidhyut Utpadan Company Limited (VUCL), Nepal signed an MoU for development of Phukot Karnali Hydro Electric Project (480MW) in Nepal.
About Phukot Karnali Hydro Electric Project:
- It is located in Kalikot district, Karnali Province of Nepal.
- The project will use the flow from the Karnali River for power generation and the generated power will be fed into integrated power system of Nepal.
- Key features of the project:
- The installed capacity of the project shall be 480 MW with average annual generation of about 2448 GWh.
- 109 metre high RCC dam and an underground power house where the 06 turbines of 79 MW each shall be housed.
- To utilize minimum environmental release one Surface Power House of 6 MW capacity is also planned.
- This project is conceived as a Peaking Run-of-River (PRoR) type scheme.
Other Hydropower project betwwen India and Nepal:
- Pancheshwar Multipurpose Project: on Mahakali River.
- Lower Arun Hydroelectric Project : on Arun River (tributary of Koshi River)
About National Hydro Electric Power Corporation Private Limited (NHPC)
- NHPC Limited, a Schedule ‘A’ Enterprise of the Government of India with ‘MINI RATNA’ status, is a premier PSU in India for development of hydropower.
- It was incorporated in 1975 under Companies Act, 1956.
- The company is mandated to plan, promote and organize an integrated and efficient development of power in all its aspects through Conventional and Non-Conventional Sources in India and abroad.
Source: Mint
Necrophilia
Why in News?
The Karnataka High Court ruled that raping the dead body of a woman will not come under the ambit of rape or unnatural offences under Sections 377 (unnatural sex) and 376 (rape) of the Indian Penal Code(IPC).
About Necrophilia
- It is defined as sexual attraction or sexual relations with corpses and dead bodies.
- The act of necrophilia, though not defined as illegal by law in many counties
- It is deemed unnatural and frowned upon, also seen as a psychological disease.
- Global Scenario: Necrophilia is an offence in the United Kingdom, Canada, New Zealand, and South Africa where necrophilia is an offence,.
- Status in India: Unfortunately in India no specific legislation is enacted, including under the provisions of IPC.
Coutr’s recommendations
- High Court of Karnataka has recommended that the Union government amend the Indian Penal Code (IPC) to bring necrophilia under the definition of the offence of unnatural sex or introduce a new provision in IPC to make necrophilia an offence.
- the Bench directed the State government to ensure CCTV cameras are installed, mortuaries are regularly cleaned so that body is preserved in a proper manner to maintain its dignity and that staff of mortuary are sensitised to handle bodies with care in the mortuaries of all the government and private hospitals, to prevent an offence against dead, particularly of women, within six months.
Source: IE
GS-II
NCERT drops Periodic Table from Class X book

Why in News?
Changes notified by NCERT: The NCERT notified changes in its June 2022 circular, omitted the Periodic Table from 10th class books. This has been widely debated in academic circles.
- New textbooks hit the market: The textbooks with the deletions and changes have now been released in the market.
What is Periodic Table?
| Description | |
| History | Developed by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869. He arranged elements based on their atomic masses and predicted the existence of undiscovered elements. |
| Organization | Elements are arranged based on their atomic numbers, electron configurations, and properties. |
| Periods | There are seven periods (rows) in the table, representing different principal energy levels. |
| Groups | The table has 18 groups (columns), with elements in the same group sharing similar properties. |
| Main Groups | Elements in groups 1, 2, and 13 to 18 are referred to as main group elements. |
| Transition Metals | Groups 3 to 12 consist of transition metals, known for their variable oxidation states. |
| Lanthanides | The first row of the f-block contains the 15 lanthanide elements. |
| Actinides | The second row of the f-block contains the 15 actinide elements. |
| Periodic Trends | Various trends exist across the table, such as atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity. |
| Periodic Law | The chemical and physical properties of elements repeat in a periodic manner based on their atomic numbers. |
| Modern Versions | Modern versions incorporate atomic numbers and reflect our understanding of atomic structure. |
| International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) | IUPAC is the international organization responsible for the standardization of chemical nomenclature, symbols, and the Periodic Table. |
| Database Management | Several organizations and databases manage and maintain comprehensive information about the elements, their properties, and the Periodic Table. Examples include the IUPAC, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), and the Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC). |
Why this matters?
- NCERT textbooks as a cornerstone: NCERT textbooks are considered a cornerstone for guiding the publication of State board textbooks, affecting nearly 60 State boards.
- Concerns for non-science stream students: With a significant number of students opting for Arts and Commerce streams, they may lose the opportunity to learn crucial basic Chemistry concepts now only accessible in Class XI.
Controversial Deletions and Omissions by NCERT
- Fundamental knowledge of chemistry: Experts argue that leaving out the periodic table and logical organization of elements from the textbooks hinders students’ understanding of fundamental chemistry concepts.
- Rationalization of contents due to the pandemic: The NCERT claims that the exercise of reducing the content load on students is carried out across all classes in response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Previous controversial deletions: Earlier, NCERT dropped Darwin’s theory of evolution from Class X textbooks and deleted chapters from Political Science textbooks, including Democracy and Diversity, Popular Struggles and Movements, Political Parties, and Challenges to Democracy.
Additional controversial omissions
- Exclusion of Maulana Abul Kalam Azad: Any mention of Maulana Abul Kalam Azad, a freedom fighter and India’s first Education Minister, has been deleted from the textbooks.
- Omission of J&K’s accession to India: The fact that Jammu and Kashmir acceded to India on the basis of autonomy has been removed from the revised Class XI textbook.
- Further omissions in the CBSE syllabus: The history of Mughal courts, references to the 2002 communal riots in Gujarat, the Naxalite movement, and mention of Dalit writers were also omitted from the CBSE syllabus.
Reasons cited for curriculum revamp
- Multiple sets of authors: Textbooks have undergone changes over the years, written by different sets of historians. There have been no controversies regarding these changes.
- Celebration of diversity and assimilation: Exclusively holding on to one set of textbooks is contrary to the spirit of a civilization that celebrates diversity and assimilation.
- NCF’s efforts for inclusive representations: The National Curriculum Framework (NCF) aims to bring a plurality of voices and more inclusive representations of marginalized and previously excluded history.
Allegations of Distortions in history textbooks
- Deliberate distortions: Some sections of the media allege that the corrections and improvements made in the NCERT history textbooks are deliberate distortions or rewriting of history.
- Sense of entitlement: The charge of rewriting history under a specific ideology betrays a sense of entitlement, suggesting that only one set of historians had the knowledge to determine what should be taught.
- Autonomy breach: While autonomy in academic and intellectual activities is crucial, the notion that institutional autonomy has been undermined and academic freedom is under stress is a one-sided and pointless exercise.
Way forward
- Logical revision: There is an urgent need for a comprehensive revision of NCERT textbooks, not only in history but in all subjects, to incorporate new knowledge and discoveries.
- Prudent use of existing textbooks: Until a detailed plan and advice for a comprehensive revision of books and syllabi is formulated, NCERT has chosen to use the existing textbooks.
- Presenting facts lucidly: Textbooks should present facts lucidly, allowing students to acquire the knowledge they seek.
- Avoid politicizing: Academics and politicians should refrain from politicizing school textbooks and instead focus on telling students the stories of the past without weaving in half-truths or erasing vast chunks of history.
- Addressing gaps and inclusivity: Continuous revision of the curriculum is necessary to address gaps, make textbooks relevant, and ensure inclusivity.
Source: The Hindu
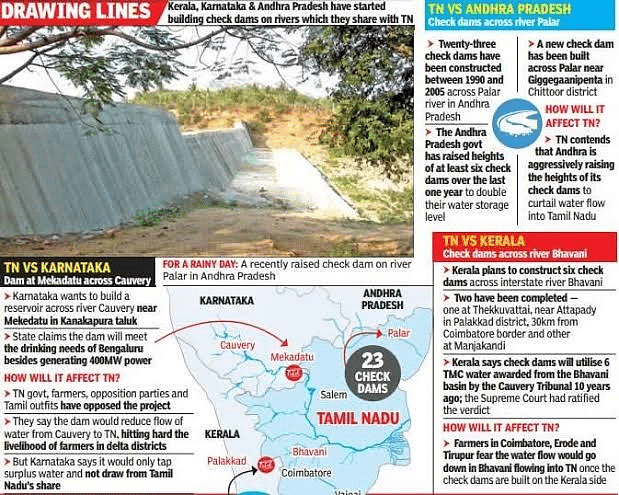
Row over Mekedatu Project
Why in News?
The Deputy CM of Karnataka announced plans for the construction of a dam and reservoir called Mekedatu near the state’s border with Tamil Nadu.
- Objections raised by Tamil Nadu: Tamil Nadu expressed strong objections to the project, arguing that it goes against the rulings of both the Cauvery Water Disputes Tribunal and the Supreme Court.
- Warning of protests: Political parties in Tamil Nadu have warned of potential protests and opposition if the construction of the Mekedatu dam proceeds.
What is Mekedatu Project?
- Location and purpose: The Mekedatu dam project is planned to be constructed in Ramanagaram district, approximately 100 km south of Bengaluru. Its primary purpose is to address the drinking water needs of Bengaluru and replenish the regional groundwater table.
- Proposed capacity and estimated cost of the dam: The dam is proposed to have a capacity of 48 TMC (thousand million cubic) feet and is estimated to cost Rs 6,000 crore.
- Background and previous developments of the project: The idea of the Mekedatu dam has been under consideration for several years. In 2014, the Karnataka government invited expressions of interest for the project and allocated funds for a detailed project report in the following year.
Opposition to the Project
- Widespread protests and state-wide bandh in TN: When the project was initially proposed, Tamil Nadu witnessed widespread protests against it. These protests culminated in a statewide bandh, supported by various stakeholders.
- Resolutions passed by TN Assembly against the project: The Tamil Nadu Assembly, representing the voice of the people, passed unanimous resolutions expressing strong opposition to the Mekedatu project in December 2018 and January 2022.
- Political actions and legal involvement in the dispute: Various political leaders and parties in Tamil Nadu have taken actions, including raising the issue with the central government and approaching the Supreme Court to challenge the project’s legality.
Arguments against the Project
- Concerns over modification of river flow: Critics of the Mekedatu project argue that constructing reservoirs on the Cauvery River would modify its natural flow, potentially leading to adverse effects downstream.
- Violation of the final award of the water disputes tribunal: Tamil Nadu contends that the proposed dam violates the final award of the Cauvery Water Disputes Tribunal, which determined the water-sharing arrangements between the two states.
- Impact on water flow in catchment areas: Tamil Nadu raises concerns that the project’s implementation would impound the flow in catchment areas, affecting the availability of water downstream and potentially leading to water scarcity in the state.
Justifications and proposals
- Ensuring adequate flow to TN: Karnataka argues that the construction of the Mekedatu dam will not hinder the stipulated quantum of water release to Tamil Nadu nor be utilized for irrigation purposes.
- Allocation of funds and willingness to negotiate: The Karnataka government has earmarked Rs 1,000 crore for the project, indicating its commitment. It also expresses willingness to engage in discussions and negotiations with Tamil Nadu to address concerns and find a resolution.
- Clearance of feasibility study: The Central Water Commission cleared a feasibility study for the Mekedatu project in 2018, providing additional support for Karnataka’s justifications and indicating the project’s viability.
Historical context of the dispute
- Past opposition and protests against the dam: The Mekedatu dam has been a subject of contention and opposition for several years. Tamil Nadu has witnessed widespread protests, reflecting public sentiment against the project.
- Political actions and involvement of state delegations: Political leaders from Tamil Nadu and Karnataka have been actively involved in addressing the issue. Delegations from both states have approached the central government seeking support or intervention.
- Legal challenges and the role of the Supreme Court: Tamil Nadu’s approach to the Supreme Court against the Mekedatu project highlights the legal dimension of the dispute. The involvement of the court plays a crucial role in considering the arguments and reaching a resolution.
Environmental and Economic considerations
- Potential benefits of the dam for water supply: Proponents of the Mekedatu project argue that it will address the pressing drinking water needs of Bengaluru, ensuring a stable water supply for the growing city.
- Concerns about environmental impact and ecosystem disruption: Critics raise concerns about the potential environmental impact of constructing the dam and reservoir. They highlight potential disruptions to local ecosystems and the natural flow of the river.
- Evaluating the economic viability of the project: Given the significant estimated cost of the Mekedatu project, there is a need to evaluate its cost-effectiveness and long-term economic viability, considering factors such as funding sources, returns on investment, and sustainable utilization of resources.
Way forward
- Importance of negotiation and finding common ground: The conflict surrounding the Mekedatu project emphasizes the importance of dialogue, negotiations, and finding mutually acceptable solutions that address the concerns of both Karnataka and Tamil Nadu.
- Role of the Supreme Court and other mediators in resolving conflicts: The involvement of the Supreme Court and other mediators can play a crucial role in facilitating discussions, mediating conflicts, and reaching a resolution that adheres to legal frameworks and considers the interests of both states.
- Promoting inter-state cooperation for sustainable water management: The dispute underscores the need for robust inter-state cooperation and collaboration on water management issues. It is crucial to ensure sustainable and equitable utilization of shared water resources, respect legal frameworks, and address the concerns of all stakeholders involved.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
What is Higgs Boson?
Why in News?
The European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN), which hosts the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), recently announced that scientists at the organisation found the first evidence of the rare process by which the Higgs boson decays into a Z boson and a photon.
About Higgs boson:
- It is the fundamental force-carrying particle associated with the Higgs field, a field that gives mass to other fundamental particles such as electrons and quarks.
- It is one of the 17 elementary particles that make up the Standard Model of particle physics, which is scientists' best theory about the behaviors of the universe's most basic building blocks.
- Higgs boson plays such a fundamental role in subatomic physics that it is sometimes referred to as the "God particle."
- It was proposed in 1964 by Peter Higgs, François Englert, and four other theorists to explain why certain particles have mass.
- The particle was finally discovered on July 4, 2012, by researchers at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC).
- Features:
- The Higgs boson has a mass of 125 billion electron volts — meaning it is 130 times more massive than a proton , according to CERN.
- It is also chargeless with zero spin — a quantum mechanical equivalent to angular momentum.
- The Higgs Boson is the only elementary particle with no spin.
- Its a "force carrier" particle that comes into play when particles interact with each other, with a boson exchanged during this interaction.
Key facts about Large Hadron Collider (LHC):
- It is the world’s largest and most powerful particle accelerator.
- Location: Near Geneva, Switzerland; across the border of France and Switzerland.
- The LHC, built by the European Organisation for Nuclear Research (CERN), is on the energy frontier of physics research, conducting experiments with highly energised particles.
- The LHC can reproduce the conditions that existed within a billionth of a second of the Big Bang.
- The colossal accelerator allows scientists to collide high-energy subatomic particles in a controlled environment and observe the interactions.
- One of the most significant LHC breakthroughs came in 2012 with the discovery of the Higgs Boson.
Source: Indian Express
Combined Maritime Forces (CMF)

Why in News?
The United Arab Emirates has withdrawn from the Combined Maritime Forces.
About Combined Maritime Forces (CMF)
- It is a multinational maritime partnership, which exists to uphold the International Rules-Based Order (IRBO) by countering illicit non-state actors on the high seas and promoting security, stability and prosperity.
- The Bahrain-headquartered CMF was established in 2001, initially as a partnership between 12 nations.
- Focused areas: Counter-narcotics, counter-smuggling, suppressing piracy, encouraging regional cooperation and engaging with regional and other partners to strengthen relevant capabilities in order to improve overall security and stability, and promote a safe maritime environment free from illicit non-state actors.
- When requested, CMF assets at sea will also respond to environmental and humanitarian crises.
Source: IE
Implications of Pakistan’s Internal Unrest for India’s National Security
Why in News?
The events of May 9, 2023, which saw violent protests and attacks on military installations in Pakistan, are expected to have far-reaching consequences for the country. The repercussions of these developments raise questions about the implications for India’s national security, given the limited influence India has over the situation in Pakistan.
Factors attributed to the Pakistan’s Internal Unrest
- Political Turmoil: Pakistan has witnessed political instability over the years, with frequent changes in government and power struggles among political parties. The arrest of former Prime Minister Imran Khan and the subsequent protests by PTI activists have added fuel to the political turmoil, leading to further unrest.
- Dissatisfaction with Governance: Widespread dissatisfaction with governance, corruption, and economic challenges have fuelled public discontent. High levels of poverty, unemployment, inflation, and inadequate public services have contributed to frustrations among the population, especially the youth.
- Military Interference: The history of military intervention and its influence on civilian affairs in Pakistan has created a complex power dynamic. The perception of the military’s meddling in political matters has raised concerns about democratic processes and civilian control over governance.
- Radicalization and Extremism: Pakistan has been grappling with the rise of radicalization and extremist ideologies within certain segments of society. Militant groups, such as Tehrik-e-Taliban Pakistan (TTP) and sectarian organizations, pose a significant threat to stability. Their ability to exploit social unrest and ideological divisions further exacerbates internal tensions.
- Socio-economic Disparities: Pakistan faces significant socio-economic disparities, with a large portion of the population living in poverty and lacking access to basic necessities. Economic inequalities, coupled with ethnic and regional grievances, contribute to social unrest and political instability.
- Ethnic and Sectarian Divisions: Pakistan is a diverse country with various ethnic and sectarian groups. Historical grievances, competition for resources, and political marginalization of certain groups have led to tensions and sporadic violence.
Internal Dynamics within the Pakistani Army
- Leadership Disputes: In recent years, there have been instances of discord between political leaders and successive army chiefs, including the prolonged discord between former Prime Minister Imran Khan and two successive chiefs. These leadership disputes have highlighted potential fissures within the army’s leadership and raised questions about unity and loyalty within its ranks
- Perceptions of Political Support: There have been perceptions that support for political actors, such as Imran Khan, exists at various levels within the army. While initial perceptions suggested that support for Khan was mainly concentrated in the middle and lower ranks and among retired service personnel. These perceptions add complexity to the army’s internal dynamics and raise concerns about its role in political affairs.
- Influence on Civilian Affairs: The Pakistani army has a long history of interfering in civilian affairs and exerting influence over the country’s political processes. This interference has often been seen as undermining democratic institutions and civilian control over governance.
- Institutional Cohesion: The recent events, such as the attacks on military installations and the subsequent arrests have tested the army’s unity and revealed potential fault lines within the Pakistan Army set up.
Implications for National Security of India
- Regional Stability: The events of internal unrest in Pakistan can have spillover effects on regional stability. A political and economic meltdown leading to widespread chaos and social unrest in Pakistan can create a volatile environment in the region. India shares a long and sensitive border with Pakistan, and any instability in its neighbor directly affects India’s security interests.
- Security of Pakistan’s Nuclear Arsenal: The internal unrest and potential vulnerabilities within the Pakistani army raise questions about the safety and security of Pakistan’s nuclear weapons. The risk of extremist elements or terrorist organizations gaining access to nuclear components or fissile material could have severe implications for the entire region, including India.
- Potential for Terrorist Exploitation: The presence of numerous terrorist organizations within Pakistan, such as Tehrik-e-Taliban Pakistan (TTP), creates a fertile ground for extremist elements to exploit situations of chaos and instability.
- Escalation of Cross-Border Tensions: In the past, during periods of internal instability, Pakistan has attempted to divert attention and rally support by escalating tensions with India. Any provocative actions or attempts to divert attention from internal issues could lead to increased border tensions, posing risks to regional stability.
- Impact on Counterterrorism Efforts: If internal unrest in Pakistan leads to a weakening of the country’s institutions and security apparatus, it could hamper the effectiveness of counterterrorism efforts.
- Humanitarian and Refugee Concerns: A political and economic meltdown in Pakistan could result in a significant humanitarian crisis, including a large influx of refugees across the border into India. This could strain resources and infrastructure in border areas, creating additional security challenges for India.
Way ahead
- Strengthening Governance and Institutions: Efforts should be made to strengthen democratic institutions, enhance transparency, and promote good governance. This includes addressing issues of corruption, improving public service delivery, and ensuring the rule of law.
- Counterterrorism Measures: Pakistan needs to accelerate its efforts to counter terrorism effectively. This includes robust intelligence gathering, coordination among security agencies, and targeted operations against terrorist networks. Enhancing border security and cooperation with neighboring countries, including intelligence sharing, can help in curbing cross-border terrorism.
- Addressing Socio-Economic Disparities: Addressing socio-economic disparities and promoting inclusive development are essential to undermine the appeal of radical ideologies. This involves investing in education, healthcare, infrastructure, and job creation to uplift marginalized communities.
- Balancing National Security and Civil Liberties: While ensuring national security is crucial, it should be done in a manner that respects civil liberties, human rights, and the rule of law. Striking a balance between security measures and preserving individual freedoms is essential for maintaining societal harmony and preventing further radicalization.
Conclusion
- The internal unrest in Pakistan following the violent events implications for both Pakistan’s national security and India’s interests. The security of Pakistan’s nuclear arsenal, the potential influence of terrorist organizations, and the internal dynamics within the Pakistani army are critical considerations. In light of these developments, India must exercise caution and adopt a prudent approach, focusing on regional stability and maintaining a cautious stance rather than embracing triumphalism.
Source: Indian Express
|
44 videos|5271 docs|1113 tests
|

























