UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 7th June 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
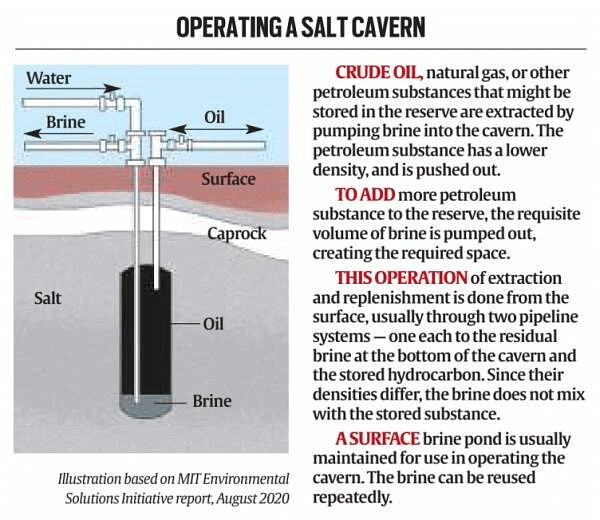
Salt caverns
Why in News?
Recently, a Government-owned engineering firm studied the prospects of developing petroleum reserves in Rajasthan’s salt caverns.
About salt caverns:-
- Salt caverns are created by dissolving salt deposits with water, and then pumping out the brine (salt water) to create a hollow space.
- This process is much faster and cheaper than excavating rock caverns and can be done in flat or low-lying areas where salt deposits are found.
- Rock caverns: created by excavating hard rock formations, such as granite or basalt, using explosives or mechanical methods.
Advantages:-
- Salt caverns are naturally well sealed.
- The salt lining acts as a natural barrier against liquid and gas migration, preventing oil from escaping or contaminating groundwater.
- They have low oil absorbency, which prevents leakage and contamination of the stored oil.
- They are relatively easy and cheap to create and operate.
- The process of solution mining is faster and simpler than excavating rock caverns, which requires more time, labour, and equipment.
- They are suitable for storing natural gas, compressed air and hydrogen.
- Salt caverns can also be located closer to the surface than rock caverns, which reduces the drilling costs and the risk of leakage.
- Salt caverns can withstand high pressure and temperature variations, allowing for faster filling and emptying of oil.
- This makes them ideal for emergencies or market fluctuations when the oil needs to be released or stored quickly.
Disadvantages:-
- Salt caverns require a large amount of water.
- The water used for solution mining has to be treated to prevent corrosion and bacterial growth, which adds to the operational costs.
- The water also has to be disposed of safely after extracting the brine (water with dissolved salt), which can pose environmental challenges.
- The brine can contain harmful substances such as heavy metals or radioactive elements, which have to be removed before discharging into surface water or injecting into deep wells.
- Salt caverns are limited by the availability and quality of salt deposits.
Source: Indian Express
Social Justice Ministry report on manual scavenging

Why in News?
The Union Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment has said that only 508 districts out of the total 766 districts in the country have declared themselves manual-scavenging free.
- The data was revealed in a booklet the Ministry has prepared to outline its achievements under the current government since 2014.
NAMASTE Scheme
- NAMASTE stands for National Action for Mechanised Sanitation Ecosystem.
- It has been launched with an objective to ensure safety and dignity of sanitation workers in urban India as well as providing sustainable livelihood to these workers.
- Ministries involved: It is launched as a joint initiative of the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment (MoSJE) and the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA).
- Implementing agency - National Safai Karamchari Financial Development Corporation (NSKFDC) would be implementing agency for NAMASTE.
- Coverage: Five hundred cities (converging with AMRUT cities) will be taken up under this phase of NAMASTE. It will be implemented for the period 2022-26.
Aim
- Zero fatalities in sanitation work in India
- All sanitation work is performed by skilled workers
- No sanitation workers come in direct contact with human faecal matter
- Sanitation workers are collectivized into SHGs and are empowered to run sanitation enterprises
- All Sewer and Septic tank sanitation workers (SSWs) have access to alternative livelihoods
Components
- Extending Insurance Scheme Benefits
- These workers and their families will be covered under the Ayushyaman Bharat- Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY).
- The premium for AB-PMJAY for those identified SSWs families who are not covered earlier shall be borne under NAMASTE.
- Livelihood Assistance
- The Action Plan will promote mechanization and enterprise development.
- Identified SSWs and their dependants will be given counselling on available livelihood choices and an opportunity to acquire alternative skills, if they so desire. The worker may choose to explore an alternative livelihood option or an entrepreneurial venture
- An SSW may choose to continue working in the sanitation sector, thereby becoming eligible for receiving capacity building training.
- Saturation with Social Security Schemes’ benefits
- The identified SSWs and their family members will be extended benefits of all the social security schemes.
- Other assistance
- The scheme will include capital subsidies of up to ₹5 lakh on sanitation machinery costing up to ₹15 lakh and interest subsidies on loans.
- Interest rates will be capped between 4-6% for the beneficiaries.
- The scheme also provides for training the workers in the use of these machines, during which time a stipend of up to ₹3,000 per month will be provided.
- The scheme will include capital subsidies of up to ₹5 lakh on sanitation machinery costing up to ₹15 lakh and interest subsidies on loans.
Status of manual scavenging in India
- Deaths related to manual scavenging
- The Social Justice Ministry has maintained in almost every Parliament session in the last two years that there are no manual scavenging deaths taking place across the country.
- These deaths have been attributed to hazardous cleaning of sewers and septic tanks.
- As per the officials, the Ministry have differentiated manual scavenging from hazardous cleaning of sewers.
- They maintained that the surveys conducted in 2013 and 2018 had identified all existing manual scavengers (about 58,000).
- Hence, manual scavenging no longer existed in the country.
- Districts as manual scavenging free
- 508 districts have reported themselves as manual scavenging free.
- Rehabilitation of manual scavengers
- According to the scheme for rehabilitation of manual scavengers, the 58,000 identified sewer workers have been given a one-time cash pay-out of ₹40,000 each.
- Self-Employment Scheme for the Rehabilitation of Manual Scavengers (SRMS) was started in 2007.
- Under the SRMS, the Social Justice Ministry had identified a total of 58,098 eligible manual scavengers in a nationwide survey conducted in 2018.
- After identifying the scavengers, the Ministry of Social Justice had announced that the practice of manual scavenging no longer takes place in the country.
- This is because all manual scavengers had been accounted for and enrolled into the rehabilitation scheme.
- In addition, around 22,000 of them (less than half) have been connected to skills training programmes.
- Subsidies and loans are available to any of them wishing to set up their own business.
- According to the scheme for rehabilitation of manual scavengers, the 58,000 identified sewer workers have been given a one-time cash pay-out of ₹40,000 each.
- NAMASTE scheme
- The scheme for rehabilitation of manual scavengers has now been merged with the NAMASTE scheme for 100% mechanisation of sewer work.
- The guidelines for this scheme are yet to be finalised, according to the Ministry.
- The FY 2023-24 Union Budget showed no allocation for the rehabilitation scheme and ₹100 crore allocation for the NAMASTE scheme.
- The scheme for rehabilitation of manual scavengers has now been merged with the NAMASTE scheme for 100% mechanisation of sewer work.
Source: The Hindu
GS-II
Fixed Dose Combinations (FDCs) Ban Issue
Why in News?
The Union Health Ministry has published a gazette notification banning 14 Fixed Dose Combination (FDC) drugs citing lack of therapeutic justification and an expert committee’s recommendation for their prohibition.
About Fixed Dose Combination (FDC) Drugs:
- Combination products or fixed dose drug combinations (FDCs) consist of two or more active drugs in a single dosage form.
- The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the USA defines a combination product as a product composed of a drug and a device, a biological product and a device, a drug and a biological product, or a drug, device, and a biological product.
- It is widely accepted that most drugs should be formulated as single compounds.
- Examples: Phenytoin + Phenobarbitone Sodium, Chlorpheniramine + Codeine Phosphate + Menthol Syrup, Salbutamol + Bromhexine, Paracetamol + Bromhexine + Phenylephrine + Chlorpheniramine + Guaiphenesin etc
Justification for Ban:
- The ban, which comes into effect immediately, follows recommendations of the Expert Committee formed to examine the efficacy of these drug combinations and the Drugs Technical Advisory Board.
- The expert committee recommended, “there is no therapeutic justification for these FDCs and the FDCs may involve risk to human beings”.
Advantages of FDC Drugs:
- Complementary Mechanism of Action: FDC formulations combine drugs with complementary mechanisms of action, which can enhance the therapeutic effectiveness of the treatment.
- The combined action of multiple drugs in a single dosage form can target different aspects of a disease or provide a more comprehensive treatment approach.
- Synergistic Effects: FDCs can exhibit synergistic effects, where the combined action of the drugs produces a greater therapeutic effect compared to individual drugs used alone.
- This can result in improved efficacy and better treatment outcomes for patients.
- Better Tolerability: In some cases, combining drugs in an FDC can help reduce side effects or improve tolerability.
- The interaction between the drugs can minimize adverse reactions, making the treatment more manageable for patients.
- Elongated Product Life-Cycle Management: FDC formulations can extend the life cycle of a product by combining drugs that have already been individually approved.
- This allows pharmaceutical companies to innovate and offer new treatment options without going through the lengthy process of developing and gaining approval for completely new drugs.
- Cost Savings: FDCs can lead to cost savings for both patients and healthcare systems. By combining multiple drugs into a single formulation, the overall cost of treatment may be reduced.
- This can make the medication more affordable and accessible, particularly in resource-constrained settings.
- Minimized Pill-Burden: Using FDCs reduces the number of pills a patient needs to take.
- This can simplify treatment regimens and improve patient adherence to medication schedules, especially for individuals who need to take multiple drugs regularly.
Disadvantages of FDCs:
- There may not be an FDC available with the appropriate drugs and/or in the most appropriate respective strength(s) for a given patient, which can lead to some patients getting too much of an ingredient and others getting too little.
- Thus, FDCs “limit clinicians’ ability to customize dosing regimens.”
- If an adverse drug reaction occurs from using an FDC, it becomes difficult to identify the active ingredient responsible for causing the reaction.
- Scientists face challenges in the development stages of multi-drug formulations such as compatibility issues among active ingredients and excipients affecting solubility and dissolution.
- If one drug is contraindicated for a patient, whole FDC cannot be prescribed.
Source: The Hindu
National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF)

Why in News?
The National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) announced the India Rankings 2023 of higher education institutions.
- For the 2023 rankings, 5,543 unique institutions applied for ranking.
National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF)
- It has been accepted by the MoE and launched by the Honourable Minister for Education on 29th September 2015.
- This framework outlines a methodology to rank institutions across the country.
- This is the eighth consecutive edition of India Rankings of HEIs in India.
Distinct additions of the 2023 edition
- Introduction of a new subject namely Agriculture & Allied Sectors
- Integration of the “Innovation” ranking previously executed by the Atal Ranking of Institutions on Innovation Achievements (ARIIA) into the India Rankings with an aim to reduce the burden on institutions of providing similar data to two different agencies.
- Expansion of scope of “Architecture” to “Architecture and Planning” to include institutions imparting courses in Urban and Town Planning.
Key Highlights of India Rankings 2023
- Indian Institute of Technology Madras retains its 1st position in Overall Category for a fifth consecutive year, i.e. 2019 to 2023, and in Engineering for an eighth consecutive year, i.e. from 2016 to 2023.
- Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru tops the Universities Category for the eighth consecutive year, i.e. from 2016 to 2023.
- It stood first in the Research Institutions Category for the third consecutive year, i.e. from 2021 to 2023.
- IIM Ahmedabad tops in Management subjects retaining its first position for the fourth consecutive year, i.e. from 2020 to 2023. It was ranked among the top two in Management subject of the India Rankings from 2016 to 2019.
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), New Delhi occupies the top slot in Medical for the sixth consecutive year, i.e. from 2018 to 2023.
- Moreover, AIIMS is ranked at 6th position in the Overall category thereby improving from its 9th position in 2022.
- National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, Hyderabad tops the ranking in Pharmacy for the first time pushing Jamia Hamdard to the second slot.
- Miranda House retains the 1st position amongst Colleges for the seventh consecutive year, i.e. from 2017 to 2023.
- IIT Roorkee stands at 1st position in Architecture subject for the third consecutive year, i.e. from 2021 to 2023.
- National Law School of India University, Bengaluru retains its first position in Law for the sixth consecutive year, i.e. from 2018 to 2023
- Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi takes the top slot in Agriculture and Allied Sectors.
- Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur tops in the Innovation category.
Importance of rankings
- Ranking and accreditation are vital for evaluating the quality of educational programs offered by higher education institutions in colleges and universities.
- India Rankings serve as a valuable tool for students in identifying universities based on their relative standing in various categories and subject domains among higher educational institutions (HEIs) in the country.
- It has also helped universities in identifying areas for improvement in teaching, research, resources, and infrastructure.
Source: The Hindu
India and Suriname

Why in News?
President Droupadi Murmu is on a 3-day state visit to Suriname.
- She has been decorated with the highest civilian honour of Suriname - The Grand Order of the Chain of Yellow Star.
- She is the first Indian to receive this award.
Key Highlights of the Visit
- Both the countries discussed ways to deepen India-Suriname relations and held wide-ranging discussions on multiple areas including defence, agriculture, IT, and capacity building,"
- 3 MoUs were signed between the two countries.
- Two MoUs were signed in the field of Health and one in the field of Agriculture.
- The Government of India also announced the supply of essential medicines worth 5.1 Cr rupees to Suriname to aid the Caribbean country’s flood relief efforts.
- India has extended the Overseas Citizenship of India (OCI) facility to the 5th & 6th generation of Persons of Indian origin in Suriname.
- This was a long pending demand of the Indian diaspora there.
India-Suriname Relations
- Historical Linkages: India shares close, warm, and friendly relations with Suriname with historical linkages.
- Soon after Suriname’s Independence on November 25, 1975, India established diplomatic relations in 1976.
- Cooperation at the International level: Suriname and India actively cooperate on various multilateral fora.
- Suriname has been supporting India’s candidature on various multilateral platforms including elections of different bodies under the UN.
- Economic: Trade and economic links between India and Suriname are modest.
- Indian export to Suriname consists of boilers, machinery, iron & steel, electrical machinery & equipment, sound recorders, pharmaceutical products, textiles, vehicles, coffee, tea and spices, rubber, paper, tobacco, organic chemicals, furniture, carpets, ceramic products, footwear and printed books.
- Indian import consists of wood, aluminum and electrical machinery.
- Indian diaspora: The first ship carrying 452 Indian labourers arrived in Suriname's capital Paramaribo on June 5, 1873. Most of the labourers hailed from eastern Uttar Pradesh and Bihar.
- India-Suriname relations acquire special significance on account of the Indian diaspora, which is over 27 percent of the Suriname population.
- Culture And Education: Indian Cultural Centre in Suriname was opened in 1978 and is quite active in promoting the Hindi language, Kathak, Yoga, and classical music
- India provided a yearly grant worth US 29500/- for the promotion of Hindi in Suriname through Suriname Hindi Parishad until 2019.
Potential and Importance
- Deep historical and cultural ties provide the foundation for the India-Suriname multifaceted and modern partnership.
- The agreements signed during the recent visit would help boost trade and economic ties.
- The signing of MoUs, in the sector of Health, will open the Suriname market for Indian pharma industries.
Future Outlook
- Bilateral trade between the two countries is well below potential.
- There is scope for further collaboration in sectors like pharmaceuticals, Ayurveda, agriculture, and defence.
- Therefore, there is a need to work together to expand bilateral trade for mutual benefit.
- The recent visit will add fresh momentum too and further strengthen India-Suriname bilateral ties.
Source: News on air
GS-III
Price Support Scheme (PSS)

Why in News?
Recently, in a significant step towards enhancing domestic production of pulses, the government of India has removed the procurement ceilings of 40% for tur, urad and Masur under Price Support Scheme (PSS) operations for 2023-24.
About Price Support Scheme:
- It is being implemented by the Government of India in the state.
- It is one of the components of the Pradhan Mantri Annadata Aay Sanrakshan Abhiyan (AASA) scheme.
- Implemented by: The Department of Agriculture & Cooperation implements this scheme for procurement of oil seeds, pulses and cotton, through NAFED which is the Central nodal agency, at the MSP declared by the government.
- Main crops covered: Bajra, Jowar, Maize, Paddy, Cotton, Tur, Moong, Urad, Groundnut, Sesamum Wheat, Gram, Mustard, Sugarcane etc.
What are the Benefits?
- Farmers get the benefit of the scheme through the sale of their produce at support price in APMC centres opened by the Nodal procurement agency.
- When prices of commodities fall below the MSP, State and central notified procurement nodal agencies purchase commodities directly from the farmers at MSP, Under specified FAQ (fair Average Quality).
- In this way, prices of the main commodities are procured and protect the farmers against economic loss in farming.
Source: PIB
Abaucin
Why in News?
Scientists recently, found a potential new antibiotic named Abaucin, with the help of machine learning.
About Abaucin:-
- This antibiotic compromises the normal function of a protein called CCR2.
- It was originally been developed to treat diabetes.
- It appears to work by disrupting lipoprotein trafficking in baumannii.
- Working: Based on genetic studies, the researchers believe that abduction could be preventing lipoprotein produced inside the bacteria from moving to the outer membrane.
- Abaucin is also a “species-selective” antibiotic.
- It only disrupts the growth of A. baumannii, not other Gram-negative bacteria.
Acinetobacter baumanni
- It is a Gram-negative bacteria.
- Gram-negative bacteria: it has a protective outer membrane that allows it to resist antibiotics.
- It has been associated with hospital-acquired infections in India.
- It was acknowledged to be a “red alert” pathogen because of its exceptional ability to develop resistance to all currently available antibiotics.
Source: The Hindu
Amchang Wildlife Sanctuary

Why in News?
Recently, Indian Army generated a unique ecosystem for peaceful co-existence with wild elephants in Amchang Wildlife Sanctuary, Assam.
About Amchang Wildlife Sanctuary:-
- The Amchang Wildlife Sanctuary is located on the eastern fringe of Guwahati, Assam.
- It comprises three Reserve forests:-
- Khanapara
- Amchang, and
- South Amchang
- It stretches from the Brahmaputra River in the north to the hilly forests of Meghalaya in the south, forming a continuous forest belt through Meghalaya’s Maradakdola Reserve Forests.
- It was declared a wildlife sanctuary in 2004 by the government of Assam.
- Flora: Khasi Hill Sal Forests, East Himalayan Mixed Deciduous Forest, Eastern Alluvial Secondary Semi-Evergreen Forests and East Himalayan Sal Forests.
- Fauna: It is home to Mammals (Flying Fox, Assamese Macaque, Slow Loris, etc.), Birds (Lesser and Greater Adjutant, White-backed Vulture, Slender-billed Vulture), Reptiles (Python, Monitor Lizard, Indian Cobra etc.).
- Tree yellow butterflies (banana harina): found at the Amchang wildlife sanctuary, which are indigenous to Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore and northeast India.
Source: The Print
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|

















