UPSC Daily Current Affairs - 14th June 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Anak Krakatau volcano

Why in News?
Indonesia’s Anak Krakatau volcano erupted recently.
About Anak Krakatau volcano:-
- It is an island in a caldera situated in the Sunda Strait between the islands of Java and Sumatra in Indonesia.
- Caldera: It is a large depression formed when a volcano erupts and collapses.
- Origin: Anak Krakatau, which means the child of Krakatau, is the offspring of the famous Krakatau volcano, whose monumental eruption in 1883 triggered a period of global cooling.
- In 1927, Anak Krakatoa emerged from the caldera formed in 1883 by the explosive volcanic eruption that destroyed the island of Krakatoa.
- It is part of the Ujung Kulon National Park, listed in UNESCO’s World Heritage site.
Ujung Kulon National Park
- It is a national park on the island of Java, in the province of Banten, Indonesia.
- It is best known as the last refuge of the one-horned Javan rhinoceros.
- A remote area of low hills and plateaus, with small lagoons and coastal dunes, it occupies 475 square miles (1,229 square km) on a peninsula and some islands at the extreme western tip of Java.
- The park faces the Sunda Strait, separating Java from Sumatra, and includes Panaitan Island, about 6 miles (10 km) northwest of the peninsula.
- it was set aside as a nature reserve in 1921; the national park was proposed in 1980 and formally established in 1992.
- The area was designated a World Heritage site in 1991.
- The park today contains the last remaining low-relief forest on Java; typical trees are of the genera Ficus and Barringtonia.
- Fewer than 60 Javan, or lesser one-horned, rhinoceroses (Rhinoceros sondaicus) remain alive, although the animals once thrived throughout the islands of Java, Borneo, and Sumatra, the Malay Peninsula, and other areas of Southeast Asia. Poaching and disease are the gravest threats to the remaining Javan rhinoceroses.
- Additional species in the park include bantengs (a type of wild cattle), Javan gibbons, langurs (leaf monkeys), muntjacs (barking deer), chevrotains (mouse deer), crocodiles, green turtles, green peacocks, and jungle fowl. In the late 20th century Javan tigers, which had inhabited the area, were considered extinct.
Source: Indian Express
Festivals in news: Pandharpur Wari

Why in News?
The Sant Tukaram and Sant Dyaneshwar Palkhi processions started their three-week-long journeys from the temple towns of Dehu and Alandi in Pune.
Pandharpur Wari
- Tradition: The Wari tradition is an 800-year-old pilgrimage in Maharashtra, where devotees, known as Warkaris, undertake a foot journey to the Vithoba temple (Incarnation of Vishnu) in Pandharpur.
- Largest walking event: The event is said to be one of the world’s largest and oldest movements where people gather on one day each year and walk a distance of around 250 km.
- Guinness Record: The Wari has been classified by the World Book of Records as “one of the most visited places in a day”
- Essence of Wakari Panth: The Wari is a ritualistic practice and a distinctive part of Maharashtrian culture, representing the essence of the Wakari Panth, which is a sect within the Bhakti tradition.
- Four Processions: The Wari takes place in four months – Chaitra, Ashadh, Kartik, and Magh. The Ashadhi Ekadashi Wari is the most popular and significant among these processions.
Historical Evolution
- Changed over time: Over the years, the Wari procession has evolved with changing practices, associated legends, and unique systems of organization and management.
- Influence of Sant Dyaneshwar: The Wari tradition can be traced back to Sant Dyaneshwar, the father of Sant Dyaneshwar, who played a pivotal role in promoting the pilgrimage to Pandharpur.
- Legacy of Sant Namdev: Sant Namdev (whose verses find mention in Guru Granth Sahib), a contemporary of Sant Dyaneshwar, also followed the tradition and composed devotional compositions expressing his devotion to Lord Vitthala.
Rituals and Cultural Aspects
- Dindi and Musical Fervor: Dindis, comprising groups of devotees, accompany the palkis during the Wari, singing, chanting, and dancing. Musical instruments like the veena and mridangam enhance the devotional fervor.
- Seva Dindis and Social Initiatives: Seva Dindis perform selfless service along the Wari route, including annadana (donation of food), medical assistance, and rural infrastructure development.
- Social Messaging and Initiatives: The Wari has been utilized as a platform for social messaging and initiatives such as promoting cleanliness through the ‘Nirmal Wari’ campaign and women-centric drives like ‘Wari Nari Shakti’ focusing on menstrual hygiene.
Source: The Hindu
What is El Nino and How it impacts the Monsoon?
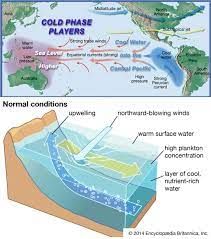
Why in News?
Delay in Monsoon: Any discussion on Indian monsoon delay these days invariably has references to the El Nino phenomenon.
- Sudden rise of El Nino: This year’s monsoon is also progressing under the cloud of an El Nino in the Pacific Ocean.
Understanding El Nino and La Nina
- El Nino and La Nina are two opposite phases of the El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle.
- ENSO is a naturally occurring phenomenon that involves the interaction between the ocean and atmosphere in the equatorial Pacific.
Here is a detailed comparison of El Nino and La Nina
| El Nino | La Nina | |
| Definition | Warmer-than-normal sea surface temperatures | Cooler-than-normal sea surface temperatures |
| Frequency | Every two to seven years | Every two to seven years |
| Duration | Several months to a year or more | Several months to a year or more |
| Impact on winds | Weakens trade winds, leading to changes in patterns | Strengthens trade winds, leading to changes in patterns |
| Impact on rains | Reduces rainfall and can cause droughts | Increases rainfall and can cause flooding |
| Impact on temp. | Warmer-than-average temperatures | Colder-than-average temperatures |
| Global effects | Droughts in Asia and Africa, floods in Americas | Floods in Asia and Africa, droughts in South America |
Impact on India
| El Nino | La Nina |
| Associated with weak monsoons and drought-like conditions in India | Associated with above-normal rainfall and floods in India |
| Sea surface temperature in the equatorial Pacific Ocean rises above normal levels | Sea surface temperature in the equatorial Pacific Ocean drops below normal levels |
| Changes in the atmospheric circulation patterns | Changes in the atmospheric circulation patterns |
| Shift in the location of the jet stream, affecting the strength and direction of the monsoon winds | Increase in the strength of the monsoon winds, bringing more moisture and rainfall to India |
| Results in reduced rainfall, dry spells, and heatwaves, leading to crop failures and water scarcity | Excessive rainfall can also lead to floods and landslides, causing damage to crops and infrastructure |
El Nino and Indian Monsoon
- El Nino and its impact on Indian monsoon: El Nino refers to abnormal warming of surface waters in the equatorial Pacific Ocean, which tends to suppress monsoon rainfall in India.
- Phases of El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO): ENSO consists of three phases in the Pacific Ocean: El Nino, La Nina (abnormal cooling), and a neutral phase with sea surface temperatures close to long-term averages.
- Ocean and atmospheric conditions: ENSO involves not only temperature abnormalities of sea surface waters but also atmospheric conditions, including differences in sea-level air pressure and wind strength and direction.
- Southern oscillation and the role of winds: Southern Oscillation Index measures the difference in sea-level air pressure over the western and eastern sides of the Pacific Ocean, while wind patterns play a crucial role in ENSO.
Factors triggering El Nino
- Weakening trade winds: When the trade winds in the tropical Pacific weaken, it contributes to the occurrence of El Nino by reducing the movement of warm surface waters.
- Changes in ocean currents: Alterations in the normal patterns of ocean currents can trigger El Nino events as they affect the distribution and accumulation of warm water in the central and eastern Pacific.
- Variations in atmospheric pressure: Fluctuations in atmospheric pressure patterns disrupt the typical circulation associated with trade winds, which can initiate the onset of El Nino conditions.
- Influence of oceanic Kelvin waves: The presence and behavior of oceanic Kelvin waves, large-scale waves that transport warm water eastward, play a role in the development and intensification of El Nino events.
- Interactions with other climate modes: El Nino can be influenced by the interactions and connections with other climate phenomena such as the Indian Ocean Dipole and the Madden-Julian Oscillation, which can impact the oceanic and atmospheric conditions in the Pacific region.
Measuring the Cycle
(1) Oceanic Nino Index (ONI)
- Measures the oceanic component of El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO).
- Tracks the departure from average sea surface temperatures in the tropical Pacific Ocean.
- Helps quantify the intensity and duration of El Nino or La Nina events.
- Typically based on a rolling three-month average of sea surface temperature anomalies in specific regions.
(2) Southern Oscillation Index (SOI)
- Measures the atmospheric component of ENSO.
- Quantifies the difference in air pressure between two locations: Tahiti and Darwin.
- Positive SOI values indicate higher pressure in the eastern Pacific and lower pressure in the western Pacific.
- Negative SOI values indicate lower pressure in the eastern Pacific and higher pressure in the western Pacific.
- Reflects the strength and changes in the atmospheric circulation patterns associated with ENSO.
- Used to assess the phase and strength of ENSO and its impact on global weather and climate patterns.
Economic impact of El Nino on Indian Agriculture
- Drought and reduced rainfall: El Nino events often lead to below-average monsoon rainfall in India, resulting in drought conditions in various regions.
- Crop failure and lower yields: Lack of adequate water availability can lead to crop failure or lower yields for major crops such as rice, wheat, pulses, and oilseeds.
- Increased input costs: During El Nino-induced droughts, farmers may need to invest in additional irrigation, water management, and supplementary feeding for livestock, leading to increased input costs.
- Price fluctuations: Reduced crop production due to El Nino can affect market supply, leading to price fluctuations and potential inflation in food prices.
- Livestock and fisheries: Water scarcity and changes in marine ecosystems can negatively affect animal husbandry and fishing activities, disrupting the livelihoods of those dependent on these sectors.
- Rural livelihoods and migration: The economic stress created can impact rural livelihoods, leading to increased migration from rural to urban areas in search of alternative employment opportunities.
Source: Indian Express
GS-II
Hiroshima AI Process (HAP)
Why in News?
Recently, in the annual Group of Seven (G7) Summit the G7 Hiroshima Leaders’ Communiqué initiated the Hiroshima AI Process (HAP)
About Hiroshima AI Process (HAP):
- It is an effort by the G7 bloc to determine a way forward to regulate artificial intelligence (AI).
- It also encourages international organisations such as the OECD to consider the analysis of the impact of policy developments and the Global Partnership on AI (GPAI) to conduct practical projects.
What is Global Partnership on AI (GPAI)?
- It is a multi-stakeholder initiative which aims to bridge the gap between theory and practice on AI by supporting cutting-edge research and applied activities on AI-related priorities.
- Launched in June 2020 with 15 members, GPAI is the fruition of an idea developed within the G7.
- At present, it has 29 members and India is also a member of this initiative.
- Its secretariat is at the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)
Source: The Hindu
North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)

Why in News?
In the recent aftermath of the escalation of tensions between Kosovo and Serbia, the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) sent 700 more of its peacekeeping troops to Kosovo.
Kosovo -Serbia Conflict
- Kosovo: is a small, landlocked country in the Balkans.
- Bordering countries: Albania, North Macedonia, Montenegro and Serbia.
- Many Serbs consider it the birthplace of their nation
- Historical Background:-
- After the break-up of Yugoslavia in the 1990s, Kosovo which was a province of the former country sought independence.
- Serbia responded with a brutal crackdown against ethnic Albanians seeking independence.
- This ended in 1999, with a NATO bombing campaign against Serbia.
- Serbian forces withdrew from Kosovo but for many Kosovo Albanians and Serbs, the conflict has never been resolved.
- The NATO-led Kosovo Force (KFor) is still based in Kosovo.
- In 2008, Kosovo unilaterally declared independence.
- UN Members who recognize Kosovo’s independence:-
- A total of 99 out of 193 United Nations countries now recognize Kosovo’s independence.
- These include the US, the UK and 22 out of 27 EU countries.
- Russia, India & China do not recognize Kosovo as an independent state
- Current Situation:-
- The relationship between the Albanian-dominated government and the Serb minority has been strained for years.
- In 2022, tensions led to civil disobedience.
- In the summer, ethnic Serbs in the northern region of Kosovo, barricaded roads and some men reportedly fired shots in protest against a new law.
- EU-mediated talks to resolve the dispute
India’s Stand on Kosovo-Serbia Conflict:-
- India has refused to recognize Kosovo as a separate state since it declared independence from Serbia in 2008.
- Further, India has, on Serbia’s request, opposed Kosovo’s membership of international bodies, UNESCO, Apostille Convention, Convention for the Pacific Settlement of International Disputes, and Egmont Group of Financial Intelligence Units.
- India and Serbia are co-founders of the Non-Aligned Movement and have traditionally enjoyed a close partnership for decades.
About North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO):-
- NATO is a Western defensive military alliance led by the United States.
- It is also called the Washington Treaty.
- Historical Background: It came into being after World War II as a counter to the Soviet Union’s possible expansion attempts in Europe.
- Then-US President Harry S Truman signed the 12-member treaty in 1949.
- After the collapse of the USSR in 1991, several eastern European nations previously members of the Soviet Union joined NATO.
- HQ: Brussels, Belgium.
- Headquarters of Allied Command Operations: Mons, Belgium.
- NATO Secretary General: Jens Stoltenberg.
- Funding: The U.S. contributes roughly three-fourths of NATO’s budget.
- 30 Members: Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, the United Kingdom, the United States, Greece, Turkey, Germany, Spain, Czech, Hungary, Poland, Bulgaria, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Albania, Croatia, Montenegro, and North Macedonia.
- India is not a member of NATO.
Objectives of NATO:-
- To safeguard the freedom and security of all its members by political and military means.
- Political objectives: NATO promotes democratic values and enables members to consult and cooperate on defense and security-related issues to solve problems.
- Military Objectives: NATO is committed to the peaceful resolution of disputes but if diplomatic efforts fail, it has the military power to undertake crisis-management operations.
- These are carried out under the collective defense clause of NATO’s founding treaty – Article 5 of the Washington Treaty or under a United Nations mandate, alone or in cooperation with other countries and international organizations.
- NATO has only once invoked Article 5, in 2001 following the 9/11 attacks on the World Trade Centre in the US.
Functions of NATO:-
- NATO has an integrated military command structure but very few forces or assets are exclusively its own.
- Most forces remain under full national command and control until member countries agree to undertake NATO-related tasks.
- All 30 allies have an equal say, the Alliance’s decisions must be unanimous and consensual.
- Its members must respect the basic values that underpin the Alliance, namely democracy, individual liberty and the rule of law.
- NATO’s protection does not extend to members’ civil wars or internal coups.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
Anjadip Shallow Water Craft

Why in News?
‘Anjadip’, the 3rd of eight ships of the Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft (SWC) Project being built by Kolkata-based Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE) for the Indian Navy, was recently launched.
About Anjadip Shallow Water Craft:
- It is an anti-submarine warfare shallow watercraft vessel built for the Indian Navy.
- It was built by the Kolkata-based Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE).
- Anjadip is the third of the eight ships of the contract that was signed between Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers, Kolkata and the Ministry of Defence in April 2019.
- The vessel was named after the island of Anjadip, located off Karwar Port, Karnataka, signifying its strategic maritime importance.
- It is designed to undertake anti-submarine operations in coastal waters, low intensity maritime operations and subsurface surveillance among others.
- Features:
- The ship is a 900-ton, 77-metre-long vessel powered by water-jet propulsion.
- It can achieve a maximum speed of 25 knots (46 km/h) and has an endurance of 1,800 nautical miles (3,300 km) at 14 knots (26 km/h).
- The crew consists of 57 members, including seven officers and 50 sailors.
- It is equipped with an Anti-submarine Combat Suite, potentially the DRDO-developed IAC MOD'C', a Hull Mounted Sonar, and a Low-frequency Variable depth Sonar.
- It also features a fire control system (FCS), an integrated Platform Management system, an Atomic Power Management system, and a Battle Damage control system.
Source: Indian Express
Sea Lettuce

Why in News?
Researchers have recently discovered 20 new species of Sea lettuce along the Baltic and Scandinavian coasts.
About Sea Lettuce:
- Sea lettuce (Ulva lactuca) is commonly referred to as seaweed.
- It is a genus of green algae usually found growing on rocky shores of seas and oceans around the world.
- Some species of Sea lettuce also grow in brackish water rich in organic matter or sewage and can accumulate heavy metals.
- It usually grows attached by a small discoid holdfast to rocks and shells, but it can also grow in a free-floating, non-attached form, sometimes in prolific masses.
- It needs a lot of sunlight to flourish.
- It is perennial, and grows all year, although the largest blooms occur during the summer.
- Large masses of sea lettuce are often an indicator of nutrient pollution in the water.
- In some parts of the world, people eat sea lettuce in soups and salads.
- Features:
- It resembles leaves of green lettuce. The color is often bright green but can range from dark green to almost yellow.
- The leaves can be narrow or broad and single or multi-lobed. They’re often rounded or oval with ruffled edges and riddled with holes or perforations.
- They are rich in iodine and vitamins A, B, and C.
Source: Newsonair
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|