UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 18th June 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| GS-I |

|
| Pandharpur Wari |

|
| GS-II |

|
| GS-III |

|
GS-I
One Nation One Anganwadi Program

Why in News?
More than 57,000 migrant workers have registered for the special one nation one Anganwadi program on Poshan Tracker App.
- Poshan app will allow migrant workers to access nurseries at their respective locations by using the Poshan Tracker App on mobile phones.
What is Poshan Tracker App?
- The Ministry of Women and Child Development (MoWCD) has launched an application called Poshan Tracker.
- The Poshan Tracker management application provides a 360-degree view of the activities of the Anganwadi Centre.
- The app facilitates efficient service delivery by digitizing and automating the tasks performed by Anganwadi Workers.
- To support their work, smartphones procured through Government e-Market (GeM) have been provided to the workers.
- Additionally, a designated individual has been appointed in each state to offer technical support and resolve any issues related to downloading and using the new Poshan Tracker application.
- Migrant workers who have registered in their original state can visit the nearest Anganwadi in their current place of residence to access the schemes and services provided through the app.
What are the Achievements of the App?
- Since the launch of the Poshan Abhiyan in 2018, a total of 10 crore 6 lakh beneficiaries have been registered on App.
- There has been a significant decline over the years in the numbers of girls dropping out in the age group of 11-14 years.
- In the Northeast and in aspirational districts, as many as 22.40 lakh adolescent girls have been identified, who will be covered under this new scheme which now falls under the ambit of the Poshan 2.0.
- An age-appropriate take-home ration is being designed for children up to six years of age.
What is Poshan Abhiyan?
- About:
- POSHAN Abhiyaan (Prime Minister's Overarching Scheme for Holistic Nutrition) was launched the Prime Minister on 8th March 2018 in Jhunjhunu district of Rajasthan.
- Objectives:
- Prevent and reduce Stunting in children (0- 6 years)
- Prevent and reduce under-nutrition (underweight prevalence) in children (0-6 years)
- Reduce the prevalence of anemia among young Children (6-59 months)
- Reduce the prevalence of anemia among Women and Adolescent Girls in the age group of 15-49 years
- Reduce Low Birth Weight (LBW).
What is Anganwadi?
- Anganwadi Services (Now renamed as Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0) is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme implemented by States/UTs.
- It provides a package of six services, namely, (i) Supplementary Nutrition; (ii) Pre-school Non-formal Education; (iii) Nutrition & Health Education; (iv) Immunization; (v) Health Check-up; and (vi) Referral Services.
- It provides services to all eligible beneficiaries, namely, children in the age group of 0-6 years, pregnant women and lactating mothers through the platform of Anganwadi Centres across the country.
- Three of the services viz. Immunization, Health Check-up and Referral Services are related to health and are provided through NRHM & Public Health Infrastructure.
What are the other related Initiatives?
- Anemia Mukt Bharat Abhiyan
- The National Food Security Act (NFSA), 2013
- Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY)
- PM POshan SHAkti Nirman (PM-POSHAN).
Source: The Hindu
Festivals in news: Pandharpur Wari
Why in News?
The Sant Tukaram and Sant Dyaneshwar Palkhi processions started their three-week-long journeys from the temple towns of Dehu and Alandi in Pune.
Pandharpur Wari
- Tradition: The Wari tradition is an 800-year-old pilgrimage in Maharashtra, where devotees, known as Warkaris, undertake a foot journey to the Vithoba temple (Incarnation of Vishnu) in Pandharpur.
- Largest walking event: The event is said to be one of the world’s largest and oldest movements where people gather on one day each year and walk a distance of around 250 km.
- Guinness Record: The Wari has been classified by the World Book of Records as “one of the most visited places in a day”
- Essence of Wakari Panth: The Wari is a ritualistic practice and a distinctive part of Maharashtrian culture, representing the essence of the Wakari Panth, which is a sect within the Bhakti tradition.
- Four Processions: The Wari takes place in four months – Chaitra, Ashadh, Kartik, and Magh. The Ashadhi Ekadashi Wari is the most popular and significant among these processions.
Historical Evolution
- Changed over time: Over the years, the Wari procession has evolved with changing practices, associated legends, and unique systems of organization and management.
- Influence of Sant Dyaneshwar: The Wari tradition can be traced back to Sant Dyaneshwar, the father of Sant Dyaneshwar, who played a pivotal role in promoting the pilgrimage to Pandharpur.
- Legacy of Sant Namdev: Sant Namdev (whose verses find mention in Guru Granth Sahib), a contemporary of Sant Dyaneshwar, also followed the tradition and composed devotional compositions expressing his devotion to Lord Vitthala.
Rituals and Cultural Aspects
- Dindi and Musical Fervor: Dindis, comprising groups of devotees, accompany the palkis during the Wari, singing, chanting, and dancing. Musical instruments like the veena and mridangam enhance the devotional fervor.
- Seva Dindis and Social Initiatives: Seva Dindis perform selfless service along the Wari route, including annadana (donation of food), medical assistance, and rural infrastructure development.
- Social Messaging and Initiatives: The Wari has been utilized as a platform for social messaging and initiatives such as promoting cleanliness through the ‘Nirmal Wari’ campaign and women-centric drives like ‘Wari Nari Shakti’ focusing on menstrual hygiene.
Source: AIR
GS-II
Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)
Why in News?
According to the Food Outlook report of the Food and Agriculture Organization, food imports by vulnerable countries are expected to decline in 2023.
About the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO):
- It is a specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition and food security.
- Its goal is to achieve food security for all and make sure that people have regular access to enough high-quality food to lead active, healthy lives.
- Head Quarter: Rome (Italy).
- Member countries: With 195 members - 194 countries and the European Union, FAO works in over 130 countries worldwide.
- Its sister bodies are the World Food Programme (WFP) and the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD).
- Reports published by the FAO: The State of the World's Forests (SOFO), The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture (SOFIA), The State of Agricultural Commodity Markets (SOCO), The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World (SOFI)
Initiatives are taken by the FAO
- The Codex Alimentarius Commission is in charge of overseeing the implementation of the Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme.
- Agricultural Heritage Systems of Global Importance (GIAHS).
- Monitors the status of Desert Locusts all over the world.
- The International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture was adopted by the Thirty-First Session of the Conference of the FAO in 2001.
Source: DTE
VAIBHAV Scheme

Why in News?
The Government of India has introduced a new fellowship programme called Vaishvik Bhartiya Vaigyanik (VAIBHAV) to facilitate collaboration between the Indian diaspora in Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics and Medicine (STEMM) and Indian academic and research institutions.
- VAIBHAV Summit was also organised as an event dedicated to connecting the Indian STEMM diaspora with Indian institutions.
What is the VAIBHAV Fellowship Scheme?
- About:
- The VAIBHAV Fellowship aims at improving the research ecosystem of India’s Higher Educational and Scientific Institutions by facilitating academic and research collaborations between Indian Institutions and the best institutions in the world through mobility of faculty/researchers from overseas institutions to India.
- It is implemented by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Ministry of Science and Technology.
- Key Features of the VAIBHAV Fellowship Programme:
- Knowledge Verticals: The programme will focus on 18 identified knowledge verticals, including quantum technology, health, pharmaceuticals, electronics, agriculture, energy, computer sciences, and material sciences, among others.
- Eligibility: The fellowship is open to outstanding scientists and technologists of Indian origin (Non-resident Indians (NRI)/ Persons of Indian Origin (PIO)/Overseas Citizen of India (OCI) who are actively engaged in research activities in their respective countries.
- Collaboration Duration: Selected fellows will have the opportunity to work in collaboration with Indian Higher Educational Institutions (HEIs), universities, and public-funded scientific institutions.
- They may spend up to two months per year, for a maximum of three years, at an Indian institution of their choice.
- Fellowship Grant: VAIBHAV fellows will receive a monthly fellowship grant of INR 4,00,000, which will support their research activities during the collaboration period.
- Travel, Accommodation, and Contingencies: The fellowship will cover international and domestic travel expenses, accommodation, and contingencies, ensuring a conducive research environment for the fellows.
What are the Other Government Initiatives involving Overseas Indian?
- Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD) is celebrated on 9th January every year to mark the contribution of the Overseas Indian community in the development of India.
- Know India Program (KIP) is a flagship initiative of the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) for diaspora engagement which familiarises Indian-origin youth (18-30 years) with their Indian roots and contemporary India.
- VAJRA (Visiting Advanced Joint Research) Faculty Scheme of the Department of S&T enables NRIs and overseas scientific communities to participate and contribute to research and development in India.
Source: PIB
Dugdh Sankalan Sathi App for Dairy Sector
Why in News?
The Union Minister of Heavy Industries Dr Mahendra Nath Pandey unveiled the "Dugdh Sanakalan Sathi Mobile App" at Mussoorie, Uttarakhand.
About the App
- Objective: Improve the quality of milk, foster transparency among stakeholders, and streamline operations at the grassroots village level, including Milk Cooperative Societies.
- Designed and Developed by: Rajasthan Electronics and Instruments Limited (REIL), Jaipur, a 'Mini Ratna" Central Public Sector Enterprises under the Ministry of Heavy Industries
Significance
- The app would benefit the milk producers and contribute to the growth of the dairy sector.
- This improves operations at the grassroots level across all partnerships including milk producers, milk co-operative societies, milk organizations and state federations.
- This would facilitate the digitizing processes and facilitating direct beneficiary transfers of the government subsidies to milk producers.
Dairy Sector in India: Key Facts
- India is the largest Milk Producer: India is the highest milk producer and ranks first position in the world contributing 24% of global milk production in the year 2021-22.
- Top 5 milk-producing states are: Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat and Andhra Pradesh.
- Export of dairy products: India’s export of dairy products has witnessed a steady rise over the last three years. In 2021-22, India exported 108,711 MT of dairy products to the world for a total of Rs. 2,928.79 crore (US$ 391.59 million), with key export destinations being Bangladesh, UAE, Bahrain, Malaysia, Saudi Arabia and Qatar.
Evolution of the Dairy Sector in India
- From a milk-deficit nation to a milk-products exporter: During the 1950s and 1960s, India was a milk-deficit nation dependent on imports, and the annual production growth was negative for several years.
- In 1950-51, per capita consumption of milk in the country was only 124 grams per day. By 1970, this figure had dropped to 107 grams per day, one of the lowest in the world .
- The country produced less than 21 million tonnes of milk per annum despite having the largest cattle population in the world.
- The National Dairy Development Board (NDDB) was created in 1965 with a mandate to support the creation of the ‘Anand Pattern’ of dairy cooperatives across the country through the Operation Flood (OF) programme which was to be implemented in phases.
- Starting in 1970, NDDB replicated the Anand Pattern cooperatives through the Operation Flood programme all over India. Dr. Verghese Kurien, widely renowned as the “Father of White Revolution” in India, was the first chairman of NDDB.
Operation Flood
- It was implemented in the following phases:
- Phase I (1970–1980) was financed by the sale of skimmed milk powder and butter oil donated by the European Union (then the European Economic Community) through the World Food Programme.
- Phase II (1981–1985) increased the number of milk sheds from 18 to 136; urban markets expanded the outlets for milk to 290. By the end of 1985, a self-sustaining system of 43,000 village cooperatives with 42,50,000 milk producers had been covered.
- Phase III (1985–1996) enabled dairy cooperatives to expand and strengthen the infrastructure required to procure and market increasing volumes of milk. This phase added 30,000 new dairy cooperatives, which led to a total of 73,000.
- Operation Flood helped quality milk reach consumers across 700 towns and cities through a National Milk Grid. The programme also helped remove the need for middlemen, thereby reducing seasonal price variations.
- In 1968-69, prior to the launch of Operation Flood, milk production was only 21.2 MT which increased to 30.4 MT by 1979-80 and 51.4 MT by 1989-90. Now it has increased to 210 million tonnes in 2020-21.
Significance of the Dairy Sector in India
- India's dairy industry has played a crucial role in the country's economic development.
- The sector has demonstrated an important part in achieving food security, reducing poverty, generating employment opportunities, and providing a regular source of income for rural households.
- The Operation Flood has reduced the import bill, converted India from a milk importer to the world’s largest producer.
Government Initiatives to Boost Dairy Industry
- Rashtriya Gokul Mission: Aims to genetically improve the cattle population and promote and conserve indigenous cattle breeds. Under the mission, farmers now have access to several cutting-edge technologies at their doorstep, including sex-sorted semen, IVF technique and genomic selection.
- National Programme for Dairy Development (NPDD): Aims to build or strengthen infrastructure for the production of high-quality milk as well as for the procurement, processing, and marketing of milk and milk products through the State Implementing Agency or State Cooperative Dairy Federation.
- Dairy Entrepreneurship Development Scheme (DEDS): DEDS is being implemented by the Department of Animal Husbandry, Dairying, and Fisheries to create self-employment opportunities in the dairy industry. The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development is carrying out the programme.
- e-GOPALA: The web version of the e-GOPALA application developed by the National Dairy Development Board (NDDB) has been launched to aid dairy farmers.
- Launching of Dairy mark: The National Dairy Development Board (NDDB) and Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) together developed a dedicated ‘Dairy Mark’ logo as a unified quality mark across India to boost the confidence of consumers in milk and milk products.
Way Ahead
- Cooperatives revolutionized dairying, but due to a variety of factors their success has not gone beyond Gujarat and Karnataka.
- Forming new cooperatives of farmers to more formalization of the dairy sector.
- Ensuring more prices to farmers as they are the actual producers of the milk.
- Improve cold storage and transportation.
Source: Live Mint
GS-III
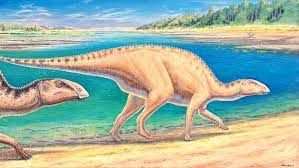
Duck-billed dinosaur
Why in News?
Recently, scientists from Chile have discovered a new species of duck-billed dinosaur in the far south of Chile.
About Duck-billed dinosaur:
- It is a species of herbivorous dinosaur previously unknown in the southern hemisphere.
- These were slender-looking dinosaurs, which could easily adopt a bipedal and quadrupedal posture to reach the vegetation at height and ground level.
- This type of duck-billed dinosaur was common in North America, Asia and Europe during the Cretaceous period.
Key Facts about Cretaceous Period
- The Cretaceous Period, in geologic time, is the last of the three periods of the Mesozoic Era.
- The Cretaceous began 145.0 million years ago and ended 66 million years ago.
- It followed the Jurassic Period and was succeeded by the Paleogene Period.
Source: The Hindu
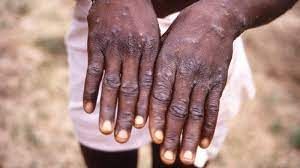
Monkeypox
Why in News?
Recently, there has been an increase in reported cases of Monkeypox from some countries, particularly in Southeast Asia and the Western Pacific Region.
About Monkeypox:
- What it is? It is a viral disease that primarily spread to the human population through zoonotic spillovers, with rodents and primates serving as potential reservoirs.
- The first case in humans was reported in 1970 in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
- Transmission: It can be transmitted between humans through close contact and exposure to infected bodily fluids or lesions.
- Incubation period: The incubation period (the period between exposure to an infection and the appearance of the first symptoms) of monkeypox is usually from 6 to 13 days but can range from 5 to 21 days.
- Symptoms: Common symptoms of mpox are a skin rash or mucosal lesions, Fever, rash and swollen lymph nodes which may lead to a range of medical complications.
- There is no effective vaccine available for Monkeypox infection.
Source: The Hindu
Predator Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)
Why in News?
The Defence Acquisition Council (DAC) headed by the Defence minister, approved the procurement of 31 armed Predator UAV (MQ-9 Reaper) from General Atomics Aeronautical Systems (GA-ASI), for the Indian Armed Forces.
What is an UAV?
- Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), also known as drones, are aircraft either controlled by ‘pilots’ from the ground or increasingly, autonomously following a pre-programmed mission.
Features of Predator UAV:
- The MQ-9 UAV has an endurance of over 27 hours, speeds of 240 KTAS, can operate up to 50,000 feet, and has a 1,746 kilograms payload capacity that includes 1,361 kilograms of external stores.
- It can carry 500 per cent more payload and has nine times the horsepower in comparison to the earlier MQ-1 Predator.
- MQ-9 UAV provides long-endurance, persistent surveillance,and strike capability for the warfighter.
- Sea Guardian is the maritime variant of the MQ-9 UAV and has an endurance of over 30 hours.
Capabilities of Predator UAV:
- These High-Altitude Long Endurance drones can carry out and boost the Indian Armed Forces Intelligence-Surveillance-Reconnaissance (ISR) capabilities.
- Armed with payloads, the weaponized UAV will be able to strike strategic targets in mountains and the maritime domain during long-endurance missions.
- Given its significant loiter time, wide-range sensors, multi-mode communications suite,it provides a unique capability to perform strike, coordination, and reconnaissance against high-value, fleeting, and time-sensitive targets.
Countries using the MQ-9 UAV
- The MQ-9 UAV has been acquired by the US Air Force, the US Department of Homeland Security, NASA, the Royal Air Force (U K), the Italian Air Force, the French Air Force and the Spanish Air Force.
Why does India need Predator drones?
- Counterterrorism operations: Predator drones can play a crucial role in counterterrorism operations by conducting surveillance, gathering intelligence, and providing real time situational awareness to security forces.
- Maritime security:Predator drones equipped with maritime surveillance capabilities can monitor coastal areas, detect illegal activities such as smuggling and piracy, and support search and rescue operations.
- Disaster management: Predator drones can be utilised for assessing damage, monitoring affected areas, and facilitating relief and rescue operations during disasters
- Strategic deterrence: To enhance India's overall defence capabilities and serve as a deterrent to potential adversaries like Pakistan and China..
Source: Indian Express
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|