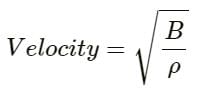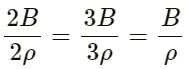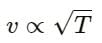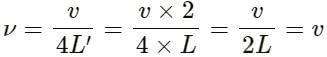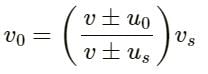Short Answers
Q.1. If you are walking on the moon, can you hear the sound of stones cracking behind you? Can you hear the sound of your own footsteps?
No, we cannot hear the sound of stones. Sound is a mechanical wave and requires a medium to travel; there is no medium on the moon.
No, we cannot hear the sound of our own footsteps because the vibrations of sound waves from the footsteps must travel through our body to reach our ears. By that time however, the sound waves diminish in magnitude.
Q.2. Can you hear your own words if you are standing in a perfect vacuum? Can you hear your friend in the same conditions?
Yes, we can hear ourselves speak. The ear membrane, being a part of our body, vibrates and allows sound to travel through our body.
No, we cannot hear our friend speak as there is no medium (air) through which sound can travel.
Q.3. A vertical rod is hit at one end. What kind of wave propagates in the rod if (a) the hit is made vertically (b) the hit is made horizontally?
(a) The vertical hit will set the particles at that end to vibrate longitudinally, This longitudinal disturbance propagates as a longitudinal wave in the rod.
(b) The horizontal hit will set the particles at that end to vibrate along the perpendicular to the axis of the rod. So the disturbance will propagate as a transverse wave in the rod.
Q.4. Two loudspeakers are arranged facing each other at some distance. Will a person standing behind one of the loudspeakers clearly hear the sound of the other loudspeaker or the clarity will be seriously damaged because of the 'collision' of the two sounds in between?
It depends on the position of the speakers. The placement decides whether the interference so formed is constructive or destructive.
Q.5. The voice of a person, who has inhaled helium, has a remarkably high pitch. Explain on the basis of resonant vibration of vocal cord filled with air and with helium.
The frequency of sound produced by vibration of vocal chords is amplified by resonance in the voice box. Now resonant frequency is directly proportional to the velocity of sound present in the voice box. Now as Helium has less density than air, velocity of sound in Helium is higher than that in air. Higher velocity of sound in Helium implies that the resonant frequency of the sound in voice chamber filled with Helium will be higher than with air. Thus the voice is high pitched in Helium filled voice box.
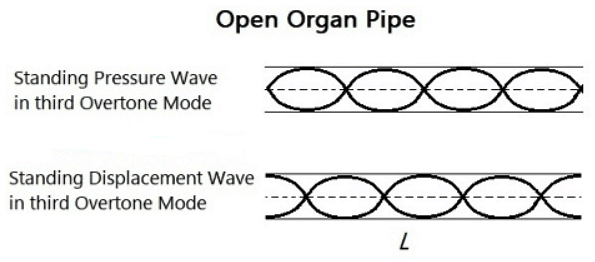
Q.6. Draw a diagram to show the standing pressure wave and standing displacement wave for the 3rd overtone mode of vibration of an open organ pipe.
Frequencies for a standing wave in an open organ pipe is given by, ν = nV/2L, where n = 1, 2, 3, ..... n = 1 is for the fundamental mode of vibration. For the 3rd overtone mode of vibration n = 4, and the corresponding frequency ν = 4V/2L. It will have four pressure antinodes. Corresponding to these antinodes there will be four displacement nodes.
The diagram is the following:
Q.7. Two tuning forks vibrate with the same amplitude but the frequency of the first is double the frequency of the second. Which fork produces more intense sound in air?
We know that: intensity ∝ (amplitude)2.
However, the intensity is independent of frequency. As the amplitude of the vibrating forks is the same, both the forks produce sounds of the same intensity in the air.
Q.8. In discussing Doppler effect, we use the word "apparent frequency". Does it mean that the frequency of the sound is still that of the source and it is some physiological phenomenon in the listener's ear that gives rise to Doppler effect? Think for the observer approaching the source and for the source approaching the observer.
The frequency of the sound is still that of the source. However, the frequency of the vibrations received by the observer changes due to relative motion.
If both (the observer and the source) move towards each other, then the frequency of the vibrations received by the observer will be higher compared to the original frequency.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 16: Sound Waves- 1
Try yourself:Consider the following statements about sound passing through a gas.
(A) The pressure of the gas at a point oscillates in time.
(B) The position of a small layer of the gas oscillates in time.
Explanation
Sound is a longitudinal wave produced by the oscillation of pressure at a point, thus, forming compressions and rarefactions. That portion of gas itself does not move but the pressure variation causes a disturbance.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 16: Sound Waves- 1
Try yourself:When we clap our hands, the sound produced is best described by Here p denotes the change in pressure from the equilibrium value.
Explanation
When we clap, there is a change in pressure, which sets a disturbance and forms a wave. However, this variation is not uniform every time we clap (unlike in the case of a sound wave). Hence, we sum up all the disturbances.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 16: Sound Waves- 1
Try yourself:The bulk modulus and the density of water are greater than those of air. With this much of information, we can say that velocity of sound in air
Explanation
If B is the bulk modulus and ρ is the density, then the velocity of sound is given by:
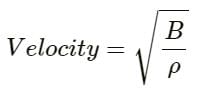
If both B and ρ are greater, then we cannot compare 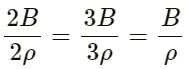
For proper comparison, we need numerical values.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 16: Sound Waves- 1
Try yourself:A tuning fork sends sound waves in air. If the temperature of the air increases, which of the following parameters will change?
Explanation
The velocity of a sound wave varies with temperature as follows:
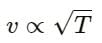
As the temperature increases, the speed also increases. However, since the frequency remains the same, its wavelength changes.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 16: Sound Waves- 1
Try yourself:When sound wave is refracted from air to water, which of the following will remain unchanged?
Explanation
When a sound or light wave undergoes refraction, its frequency remains constant because there is no change in its phase.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 16: Sound Waves- 1
Try yourself:The speed of sound in a medium depends on
Explanation
Propagation of any wave through a medium depends on whether it is elastic and possesses inertia. A wave needs to oscillate (elastic property) for it to be propagated and if it does not have inertia, the oscillations won't keep on moving to and fro about the mean position.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 16: Sound Waves- 1
Try yourself:Two sound waves move in the same direction in the same medium. The pressure amplitudes of the waves are equal but the wavelength of the first wave is double the second. Let the average power transmitted across a cross-section by the first wave be P1 and that by the second wave be P2. Then
Explanation
Since the average power transmitted by a wave is independent of the wavelength, we have P1 = P2
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 16: Sound Waves- 1
Try yourself:When two waves with same frequency and constant phase difference interfere,
Explanation
The energy is redistributed due to the presence of interference. However, as the frequency and phase remain constant, the distribution also remains constant with time.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 16: Sound Waves- 1
Try yourself:An open organ pipe of length L vibrates in its fundamental mode. The pressure variation is maximum
Explanation
In the case of an open organ pipe vibrating in its fundamental mode, antinodes are formed at both ends. An open pipe supports a standing wave pattern that has an antinode (maximum displacement and minimum pressure variation) at each open end. The pressure variation is maximum at the nodes, which occur at the midpoint of the pipe in the fundamental mode. Hence option (b).
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 16: Sound Waves- 1
Try yourself:An organ pipe, open at both ends, contains
Explanation
An open organ pipe has sound waves that are longitudinal. These waves undergo repeated reflections till resonance to form standing waves.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 16: Sound Waves- 1
Try yourself:A cylindrical tube, open at both ends, has a fundamental frequency v. The tube is dipped vertically in water so that half of its length is inside the water. The new fundamental frequency is
Explanation
If v is the velocity of the wave and L is the length of the pipe,
then the fundamental frequency for an open organ pipe is v = v/2L
For a closed organ pipe of length L' = L/2, the fundamental frequency is 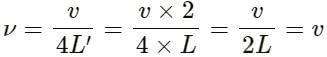
(When the pipe is dipped in water, it behaves like a closed organ pipe that is half the length)
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 16: Sound Waves- 1
Try yourself:The phenomenon of beats can take place
Explanation
When two or more waves of slightly different frequencies (v1 – v2 ≯ 10) travel with the same speed in the same direction, they superimpose to give beats. Thus, the waves may be longitudinal or transverse.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 16: Sound Waves- 1
Try yourself:A tuning fork of frequency 512 Hz is vibrated with a sonometer wire and 6 beats per second are heard. The beat frequency reduces if the tension in the string isslightly increased. The original frequency of vibration of the string is
Explanation
The frequency of beats ν = |ν1 - ν2| = 6 Hz where ν1 = 512 Hz, ν2 = frequency of sonometer. Thus ν2 is either 506 or 518 Hz.
When the tension in the string is slightly increased the frequency of the sonometer slightly increases. Since the beat frequency reduces it means ν2 < ν1 so ν2 is 506 Hz. Option (a).
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 16: Sound Waves- 1
Try yourself:The engine of a train sounds a whistle at frequency v. The frequency heard by a passenger is
Explanation
Since the source and the observer both move with the same speed there is no relative motion. Thus there is no Doppler's effect and no change in apparent frequency.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 16: Sound Waves- 1
Try yourself:The change in frequency due to Doppler effect does not depend on
Explanation
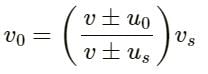
It is clear from the equation that the change in frequency due to Doppler effect depends only on the relative motion and not on the distance between the source and the observer.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 16: Sound Waves- 1
Try yourself:A small source of sound moves on a circle as shown-in figure and an observer is sitting at o. Let v1, v2, v3 be the frequencies heard when the source is at A, B and C respectively.

Explanation
When the source is at C the source speed is perpendicular to the line joining the observer and the source. Thus at this instant, the separation between the two is not changing and the frequency heard ν3 is same as the source. When the source is at A the separation between them is increasing, so due to the Doppler effect ν1 < ν3. But when the source is at B, the separation is decreasing and due to the Doppler effect ν3 < ν2. So ν2 > ν3 > ν1.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 16: Sound Waves- 1
Try yourself:When you speak to your friend, which of the following parameters have a unique value in the sound produced?
Explanation
- The frequency, wavelength and amplitude do not have a unique value in the sound produced.
- The frequency (and wavelength) changes as the pitch of the sound varies, while the amplitude is different as the loudness varies. However, the speed of sound in the air at a particular temperature is constant, i.e., it has a unique value.
Report a problem
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 16: Sound Waves- 1
Try yourself:An electrically maintained tuning fork vibrates with constant frequency and constant amplitude. If the temperature of the surrounding air increases but pressure remains constant, the produced will have
Explanation
The velocity of sound V is directly proportional to the square root of the temperature. So if the temperature increases the velocity of the sound also increases. Option (c). Since the frequency of the sound producing tuning fork is constant hence the frequency of the sound will also be constant. Also, the wavelength = (Sound velocity)/(Frequency). Thus the wavelength will also increase if the temperature increases. Option (a).
Since frequency is constant, Time period will also be constant.
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 16: Sound Waves- 1
Try yourself:The fundamental frequency of a vibrating organ pipe is 200 Hz.
Explanation
The overtone frequencies may be a simple multiple of the fundamental frequency (ν = nν₀) or an odd multiple of the fundamental frequency {ν = (2n + 1)ν₀} depending upon whether it is an open organ pipe or closed organ pipe.
v₀ = Fundamental Frequency
Overtone frequencies for:
Open organ pipe = nv₀
{n = 2, 3, 4, .....]
Closed organ pipe = (2n + 1)ν₀
{n = 1, 2, 3, ....}
Since it is not given whether the pipe is open or closed, we cannot be sure that the first overtone is 400 Hz. So the option (a) is not true.
The first overtone may be 400 Hz if the pipe is open because it is the first even multiple of the fundamental frequency 200 Hz. Option (b) is true.
The first overtone may be 600 Hz if the pipe is closed because it is the first odd multiple of the fundamental frequency 200 Hz (3 * 200 Hz). Option (b) is true.
Since 600 Hz is an even as well as odd multiple of 200 Hz, it is an overtone whether the pipe is open one or closed. Option (d) is true.
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 16: Sound Waves- 1
Try yourself:A source of sound moves towards an observer.
Explanation
Due to Doppler effect, the frequency or wavelength of the sound changes towards the observer only. The actual frequency and wavelength of the source does not change.
Report a problem
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 16: Sound Waves- 1
Try yourself:A listener is at rest with respect to the source of sound. A wind starts blowing along the line joining the source and the observer. Which of the following quantities do not change?
Explanation
The frequency does not change. Hence, the time period (inverse of frequency) also remains the same.
Due to wind, the relative velocity of sound changes. Thus, the wavelength also changes so as to keep the frequency the same. (As v = vλ)