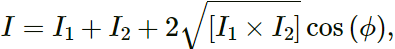HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 17: Light Waves - 1 | HC Verma Solutions - JEE PDF Download
Short Answers
Q.1. Is the colour of 620 nm light and 780 nm light same? Is the colour of 620 nm light and 621 nm light same? How many colours are there in white light?
White light is a composition of seven colours. These are violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red, collectively known as VIBGYOR. Spectrum of white light consists of sever colour bands. Each band consists of some range of wavelengths or frequencies.
- For orange colour : (590 nm to 620 nm)
- For red colour: (620 nm to 780 nm)
So, the colour of 620 nm and 780 nm lights may be different. But the colour of 620 nm light and 621 nm light is same.
Q.2. The wavelength of light in a medium is λ = λ0/μ, where λ is the wavelength in vacuum. A beam of red light (λ0 = 720 nm ) enters water. The wavelength in water is λ = λ0/μ = 540 nm. To a person under water, does this light appear green?
Colour of light will depend only on the frequency of light and not on the wavelength of the light. So, light will appear red to an observer under water.
Q.3. Will the diffraction effects from a slit be more or less clearly visible if the slit-width is increased?
The width of the central band is inversely proportional to the slit width. So, as the width of the slit is increased, the central band will become less wider and further bands will start merging in them. Hence, diffraction effects will be visible less clearly.
Q.4. If we put a cardboard (say 20 cm × 20 cm) between a light source and our eyes, we can't see the light. But when we put the same cardboard between a sound source and out ear, we hear the sound almost clearly. Explain.
Light waves have the property of travelling in a straight line, unlike sound waves. When we put a cardboard between the light source and our eyes, the light waves are obstructed by the cardboard and cannot reach our eyes, which doesn't happen when the cardboard is inserted between sound source and our ear.
Q.5. TV signals broadcast by a Delhi studio cannot be directly received at Patna, which is about 1000 km away. But the same signal goes some 36000 km away to a satellite, gets reflected and is then received at Patna. Explain.
To receive TV signals transmitted from Delhi in Patna directly, one has to use antennas of great height, which will cost much. On the other hand, transmission of signals with the help of satellites requires only high frequency waves and can be done easily.
Q.6. Can we perform Young's double slit experiment with sound waves? To get a reasonable "fringe pattern", what should be the order of separation between the slits? How can the bright fringes and the dark fringes be detected in this case?
Young's double slit experiment can be performed with sound waves, as the sound waves also show interference pattern. To get a reasonable "fringe pattern", the separation of the slits should be of the order of the wavelength of the sound waves used.
In this experiment, the bright and dark fringes can be detected by measuring the intensity of sound using a microphone or any other detector.
Q.7. Is it necessary to have two waves of equal intensity to study interference pattern? Will there be an effect on clarity if the waves have unequal intensity?
Interference pattern can be studied with waves of unequal intensity.
where
∅ = phase difference
In case of waves of unequal intensities, the contrast will not be clear, as the minima will not be completely dark.
Q.8. Can we conclude from the interference phenomenon whether light is a transverse wave or a longitudinal wave?
The interference pattern can be produced by any two coherent waves moving in the same direction. It cannot be concluded from the interference phenomenon that light is a transverse wave, as sound waves that are longitudinal in nature also interfere.
Q.9. Why don't we have interference when two candles are placed close to each other and the intensity is seen on a distant screen? What happens if the candles are replaced by laser sources?
In order to get interference, the sources should be coherent, i.e. they should emit wave of the same frequency and a stable phase difference. Two candles that are placed close to each other are distinct and cannot be considered as coherent sources. Two independent sources cannot be coherent. So, two different laser sources will also not serve the purpose.
|
134 docs
|