| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Types of Pulleys |

|
| Understanding Mechanical Advantage |

|
| Pulley Formula |

|
| Advantages of Pulleys |

|
| Disadvantages of Pulleys |

|
| Key Points to Remember |

|
Introduction
A pulley is a mechanical device comprising a wheel and a rope or belt that enables the lifting of objects. Pulleys come in various sizes and can freely rotate around an axis passing through their center. One of the simplest examples of a pulley is the mechanism used to raise a flag. By understanding the workings of a pulley, we can harness its power for our benefit, simplifying our tasks and accomplishing more.
Types of Pulleys
In today's world, three types of pulleys are most commonly used:
1. Fixed Pulley:
- Fixed pulleys are attached to rigid structures and are immovable.
- These pulleys can be found on ceilings, walls, or floors, providing a stationary system.
- While the pulley itself remains fixed, the rope can move freely.
- Fixed pulleys change the direction of force and reduce the effort required to lift heavy objects.

2. Movable Pulley:
- Movable pulleys are not connected to rigid structures.
- One end of the rope is attached to a fixed structure, while the wheels carry the load.
- When one end of the rope is pulled, the load shifts to a different position.
- Movable pulleys require less work to operate and provide mechanical advantage.
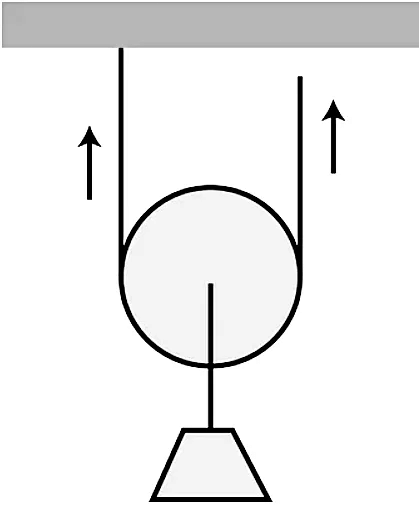
3. Compound Pulley:
- Compound pulleys combine the functions of fixed and movable pulleys.
- In this type, a movable pulley is connected to a rope attached to a fixed pulley.
- By manipulating the movable wheel, the weight can be shifted to alter the overall workload and redirect force.
- Compound pulleys offer versatility in adjusting the mechanical advantage according to requirements.

Understanding Mechanical Advantage
- The concept of mechanical advantage allows us to measure the effectiveness of pulleys. In an ideal scenario without friction, the mechanical advantage of a machine can be calculated. However, in real-world applications, some friction exists, resulting in a mechanical advantage slightly higher than the theoretical value. When calculating the mechanical advantage of a pulley system, we assume that the weight of the pulley and ropes is negligible, there is no energy loss due to friction, and the ropes do not elongate during operation.
- The mechanical advantage of a pulley is directly proportional to the number of loops in the rope. In a system with a single loop, the effort required to lift the weight is equal to the weight itself. By adding more loops, the effort decreases proportionally. For example, with two loops, the effort becomes half, and with three loops, it reduces to one-third. Beyond a certain number of pulleys, the mechanical advantage remains constant.
Pulley Formula
To determine the mechanical advantage and other parameters related to pulleys, we can use the following formulas:
Mechanical Advantage (MA):
- The mechanical advantage of a pulley system is the ratio of the load lifted to the effort applied.
- For a pulley system without friction, the mechanical advantage is equal to the number of supporting ropes or strands.
- Formula: MA = Load / Effort
Ideal Mechanical Advantage (IMA):
- The ideal mechanical advantage of a pulley system is calculated based on the number of pulleys or sheaves.
- Formula: IMA = Number of Pulleys
Actual Mechanical Advantage (AMA):
- The actual mechanical advantage takes into account the effects of friction in the pulley system.
- AMA is always less than or equal to the ideal mechanical advantage.
- Formula: AMA = Load / Effort
Efficiency (η):
- Efficiency measures the effectiveness of a pulley system by comparing the output work to the input work.
- Efficiency is always less than or equal to 1 (or 100%).
- Formula: η = (Output Work / Input Work) * 100%
Advantages of Pulleys
- Mechanical Advantage: Pulleys provide mechanical advantage, allowing us to lift heavy objects with less effort.
- Directional Change: Pulleys change the direction of the force applied, making it easier to lift loads vertically or at an angle.
- Versatility: Pulley systems can be designed in various configurations, providing flexibility and adaptability for different tasks.
- Safety: By using pulleys, heavy loads can be lifted and moved safely, minimizing the risk of injury.
- Increased Efficiency: Pulleys reduce the amount of effort required, making work more efficient and saving time and energy.
 |
Download the notes
What is Pulley: Types, Formula, Working & Examples
|
Download as PDF |
Disadvantages of Pulleys
- Friction: Friction between the pulley and the rope reduces the mechanical advantage and efficiency of the system.
- Complex Configurations: Some pulley systems with multiple pulleys can be complicated to set up and operate.
- Space Requirements: Pulley systems may require adequate space for installation, especially when using compound pulleys or large loads.
- Weight Limitations: Pulleys have weight limitations based on their design and materials used, and exceeding these limits can lead to failure or accidents.
Key Points to Remember
Pulleys are mechanical devices used to lift and move heavy objects efficiently.
There are three main types of pulleys: fixed pulley, movable pulley, and compound pulley.
- Mechanical advantage (MA) measures the effectiveness of a pulley system in reducing the effort required to lift a load.
- The ideal mechanical advantage (IMA) is based on the number of pulleys, while the actual mechanical advantage (AMA) considers the effects of friction.
- Pulley formulas include MA = Load / Effort, IMA = Number of Pulleys, AMA = Load / Effort, and Efficiency = (Output Work / Input Work) * 100%.
Pulleys offer advantages such as mechanical advantage, directional change, versatility, safety, and increased efficiency.
Disadvantages of pulleys include friction, complex configurations, space requirements, and weight limitations.