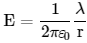| Table of contents |

|
| Gauss's Law: Unveiling the Formula and Derivation |

|
| What is Linear Charge Density? |

|
| Electric Field due to a Linear Charge Distribution |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Gauss's Law: Unveiling the Formula and Derivation
Gauss's Law serves as a salvation when it comes to calculating the electric field of a symmetric charge distribution. This law takes into account the charge and the electric flux through a surface and is widely applicable, especially for symmetric charge distributions. Its significance is such that it has been integrated into Maxwell's equations of electromagnetism. The law states that the total electric flux magnitude through a symmetric surface is equal to the total enclosed charge divided by the material permittivity. Electric flux, the product of the electric field and the area of the surface, represents the field lines passing through a given surface.
Mathematical representation of Gauss's Law: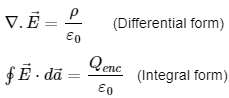
In the case of calculating the electric field using Gauss’s law, one has to assume a hypothetical Gaussian surface around the charge to enclose it completely. If the field is uniform, then the calculation is easier. We only have to find the area of the symmetric figure.
What is Linear Charge Density?
Charge density can be of different nature depending on the surface on which charge is getting distributed. The charge density is the measure of how much charge is contained in that particular field. So, based on this argument, charge density can be linear, surface, and volume. Linear means anything that is in a line. So, linear charge density is the charge distributed in a line per unit length of the line.
Mathematically,
λ = Q/L
Here, Q is the total charge distributed on the line and L is the total length of the line.
Therefore, λ denotes the charge per unit length or linear charge density. The S.I. the unit of λ is coulomb/(metre)2.
Electric Field due to a Linear Charge Distribution
Consider a straight infinite conducting wire with linear charge density of λ. Consider a point P at a distance r from the wire in space measured perpendicularly. The wire cross-section is cylindrical in nature, so the Gaussian surface drawn is also cylindrical in nature. The area of a cylindrical surface is equal to S = 2πrL.
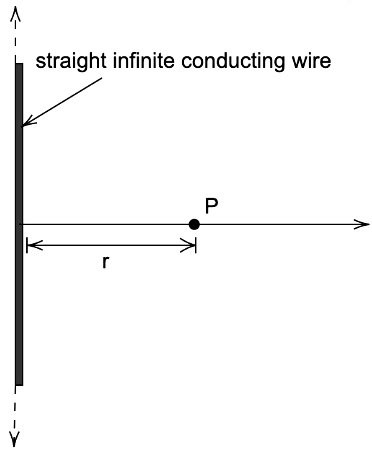
The total amount of positive charge enclosed in a cylinder is Q = λL
Our goal is to calculate the total flux coming out of the curved surface and the two flat end surfaces numbered 1, 2, and 3.
Flux through surface 1 is
φ1 = 0
Flux through surface 2 is
φ2 = 0
Flux through surface 3 is
φ3 = Ecosθ × S
The field is uniform and its magnitude is E, so, the flux becomes,
φ3 = E × 1 × 2πrL
Therefore, the total electric flux is calculated as
φ = φ1 + φ2 + φ3
φ = 2πrLE
Now, from Gauss’s Law, this flux is equal to the net closed charge divided by the permittivity of the material. So,
φ = λL/ε0
Substitute the value of the flux in the above equation and solving for the electric field E, we get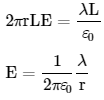
This is the electric field intensity (magnitude) due to a line charge density using a cylindrical symmetry.
Conclusion
The following points can be concluded for the topic:
- The density of electric field lines tells us about the electric field intensity at that point.
- Electric field is the space where charged particles experience force of attraction or repulsion due to a source charge.
- Linear charge density is the charge distributed per unit length along a line.
- According to Gauss’s Law, the total flux due to a charge through a surface is equal to the total charge enclosed in the closed surface divided by the permittivity of the medium.
- The electric field due to a line charge distribution makes use of a cylindrical Gaussian surface. The magnitude of the electric field at a point in space which is at a distance r from the wire is