Electric Field due to Infinite Plane Sheet of Charge | Physics for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Introduction
Electric fields are defined as the force exerted per unit charge. Mathematically, the electric field (E) is given by the equation:
E = F/Q
Where:
- E represents the electric field
- F stands for the electric force
- Q denotes the charge
The electric field is influenced by the distribution of electric charges or changes in the magnetic field. In the SI system, the unit for electric field is volts per meter (V/m).
Definition of Gaussian Surface
A Closed Surface in a three-dimensional space whose flux of a vector field is calculated, which can either be the magnetic field or the electric field or the gravitational field, is known as the Gaussian Surface.
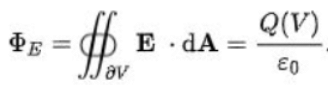
What is Electric Field Due to a Uniformly Charged Infinite Plane Sheet?
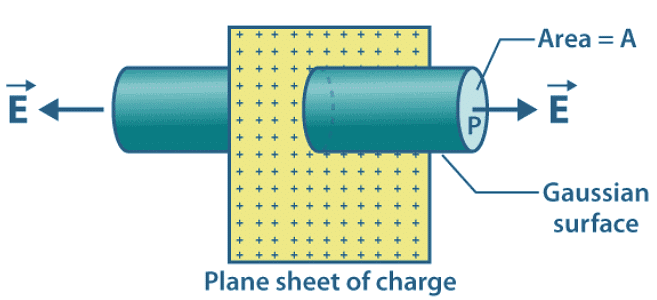
Let us consider an infinitely thin plane sheet that is uniformly charged with a positive charge. Let 𝜎 be the charge density on both sides of the sheet. At point P the electric field is required which is at a distance a from the sheet. Through point P, a Gaussian cylinder is drawn with the cross-sectional area of A.
The following is the electric flux crossing through the Gaussian surface:
Φ = E x area of the circular caps of the cylinder
The electric lines of force and the curved surface of the cylinder are parallel to each other. Therefore, the flux due to the electric field of the plane sheet passes through the two circular caps of the cylinder.
Φ = E x 2A (eq.1)
From the Gauss theorem, we know that,
Φ = q/ε0
The charge enclosed by the Gaussian surface is given as,
q = 𝜎A
Therefore,
Φ = 𝜎A/ε0 (eq.2)
From eq.1 and eq.2,
E x 2A = 𝜎A/ε0
Therefore,
E = 𝜎/2ε0
The direction of an electric field will be in the outward direction when the charge density is positive and perpendicular to the infinite plane sheet.
The direction of an electric field will be in the inward direction when the charge density is negative and perpendicular to the infinite plane sheet.
|
268 videos|740 docs|171 tests
|
















