| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Electronegativity and Ionic Bonding |

|
| Ionic Bond Properties |

|
| Examples of Ionic Bonds |

|
Introduction
An ionic bond, also referred to as an electrovalent bond, is the electrostatic force of attraction that holds two oppositely charged ions together. It occurs when one or more electrons are completely transferred from one atom to another. This transfer allows the atoms to achieve their nearest inert gas configuration. Ionic bonds are formed through the donation or acceptance of electrons, resulting in the combination of atoms and the attainment of stability.
Electronegativity and Ionic Bonding
Ionic bonds are formed between atoms with large differences in electronegativity. Electronegativity refers to an atom's tendency to attract electrons in a chemical bond. When the electronegativity difference between two atoms is significant, an ionic bond is likely to form. In contrast, covalent bonds are formed between atoms with smaller differences in electronegativity. Compounds resulting from the electrostatic attraction between positive and negative ions are called ionic compounds.
Ionic Bond Properties
Ionic bonds possess several distinctive properties due to the strong force of attraction between cations (positively charged ions) and anions (negatively charged ions):
- Strength: Ionic bonds are the strongest type of bond.
- Charge Separation: These bonds exhibit charge separation, making them highly reactive in the appropriate medium.
- High Melting and Boiling Point: Ionic bonded molecules have high melting and boiling points due to the strong electrostatic attraction between ions.
- Electrical Conductivity: Ionic compounds in their aqueous solutions or molten state act as good conductors of electricity. This is because ions present in these compounds act as charge carriers.
Examples of Ionic Bonds
To illustrate the formation of ionic bonds, consider the following examples:
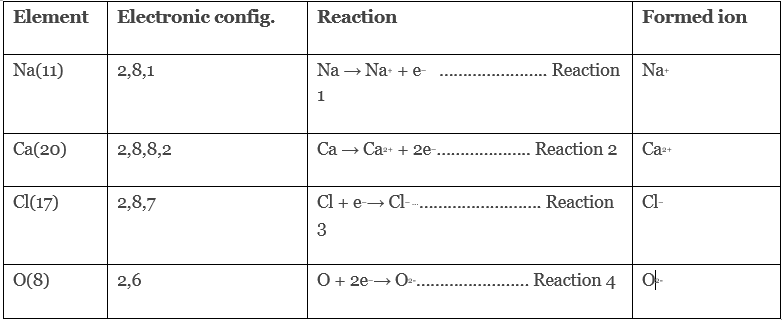
- Now when Na reacts with Cl, reaction 1 and reaction 3 will take place and the resultant compound will be NaCl.
- When Na reacts with O, reaction 1 and reaction 4 will take place and the resultant compound will be Na2
- When Ca reacts with Cl, reaction 2 and reaction 3 will take place and the resultant compound will be CaCl2.
- When Ca reacts with O, reaction 2 and reaction 4 will take place and the resultant compound will be CaO.













