| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Types of Inductive Effects |

|
| Difference Positive and Negative Inductive effects |

|
| Effects of Inductive effects |

|
Introduction
The inductive effect stems from the partial displacement of covalently bonded electrons towards more electronegative atoms within a carbon chain. Unlike complete electron transfer, the inductive effect involves the transmission of electron density from one end of the chain to the other. As the distance along the chain increases, the intensity of the inductive effect gradually diminishes. This phenomenon plays a pivotal role in various organic reactions and has profound implications for molecular properties.
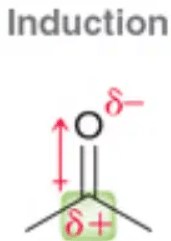
Types of Inductive Effects
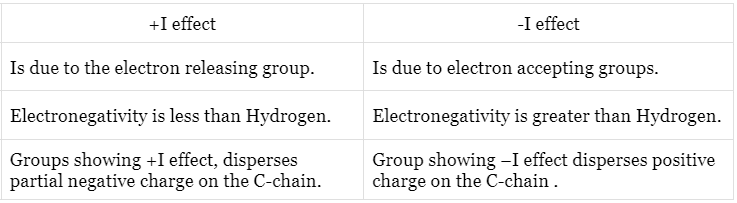
There are two types of inductive effect i.e. – I effect and +I effect.
1. Negative Inductive effect (? I Effect)
When the substituent attached to the end of the carbon chain is electron withdrawing (X), the effect is called negative induction effects (– I effect).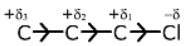
?I effect decreases with distance, as one goes away from groups (electron attracting).
C1(δ+) > C2(δδ+) > C3 (δδδ+) and other third carbon charge is negligible.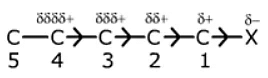
Negative inductive effect (?I effect) of different functional groups in decreasing order:
NO2 > F > COOH > Cl > Br > I > OH > C6 H5
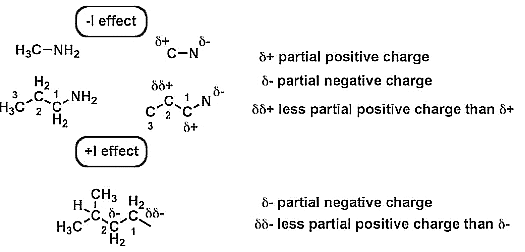
2. Positive inductive effect (+I effect)
When the substituent attached to the end of the carbon chain is electron donating, the effect is called positive inductive effect (+I effect).
This is due to electron releasing of the group, it develops a negative charge on the chain.
Positive inductive effect (+I effect) also decreases as we go away from substitution group (electron releasing nature)
So +I effect is in order of:
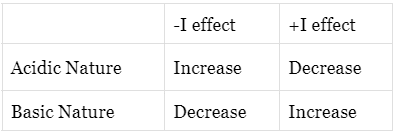
Acidic and Basic Nature due to Inductive effects
- Negative inductive effect (?I effect): Due to electron withdrawing nature of the group, electron density decreases. Thus, basic nature is decreased and acidic nature is increased.
- Positive inductive effects (+I effect): Due to electron releasing of the group electron density is increased. Thus, basic nature is also increased and naturally acidic nature is decreased.
Difference Positive and Negative Inductive effects
 |
Download the notes
Inductive Effect: Types, Nature, Effects & Differences
|
Download as PDF |
Effects of Inductive effects
- Induction effect stabilised carbocation and carbanion.
- Induction effect stabilises free radicals.
- Effects of acidic and basic nature of acids and bases.
Points to Remember
- The phenomenon of inductive effect helps in clarifying the mechanism of many reactions and many other facts.
- Because of the Inductive effect polar compounds have high melting point, boiling point and dipole moment.
- Inductive effect operates via sigma(σ) bonded electrons.
- Inductive effect is distance dependent effect. As distance increases, its effect decreases. Inductive effects can be neglected after the third carbon.
- Inductive effect has a destabilising effect.














