Introduction
The purification of organic compounds is a crucial and intricate step following their extraction from natural sources or synthesis in laboratories. The purification method employed depends primarily on the compound's nature and the impurities present. This article provides an in-depth exploration of various purification techniques for liquids, including sublimation, crystallization, distillation (including fractional, vacuum, and steam distillation), differential extraction, and chromatography. By employing these methods, organic chemists can ensure the removal of unwanted impurities and obtain high-purity compounds.
Determining Purity: Melting and Boiling Points
An easy way to assess the purity of an organic compound is by examining its melting and boiling points. Organic compounds typically exhibit sharp melting and boiling points. Hence, observing deviations or broad ranges can indicate the presence of impurities. Purification involves the elimination of these unwanted impurities from organic compounds, ensuring their integrity and effectiveness.
Methods of Purification
The following methods are commonly employed to purify organic compounds:
1. Sublimation
Sublimation is a purification technique that takes advantage of certain solids' ability to transition directly from the solid to the vapor phase without passing through the liquid phase. This method facilitates the separation of sublimable compounds from non-sublimable ones.
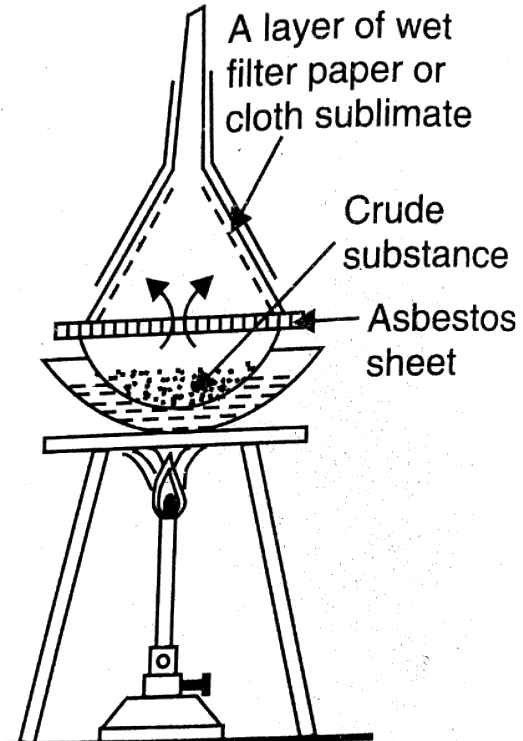
- Heat the substance in a China dish placed above an inverted funnel.
- Keep the funnel cool to expedite the sublimation process.
- The vapors of the substance solidify on the cool funnel.
- Collect the sublimable compounds for purification.
2. Crystallization
Crystallization utilizes the varying solubilities of a compound and its impurities in a chosen solvent. By selecting a solvent where the compound is sparingly soluble at lower temperatures but soluble at higher temperatures, it becomes possible to separate the compound from impurities. The process involves obtaining a saturated solution by heating and subsequently removing the compound's crystals through filtration upon cooling.
- Heat the solution to obtain a saturated solution.
- Allow the solution to cool, causing the compound to crystallize.
- Filter the crystals to separate them from impurities.
- If impurities share the same solubility as the compound, repeated crystallization is performed.
3. Distillation
Distillation, based on the difference in boiling points of liquid mixtures, enables the separation of volatile liquids from non-volatile ones. The boiling point represents the temperature at which a liquid's vapor pressure equals the atmospheric pressure.
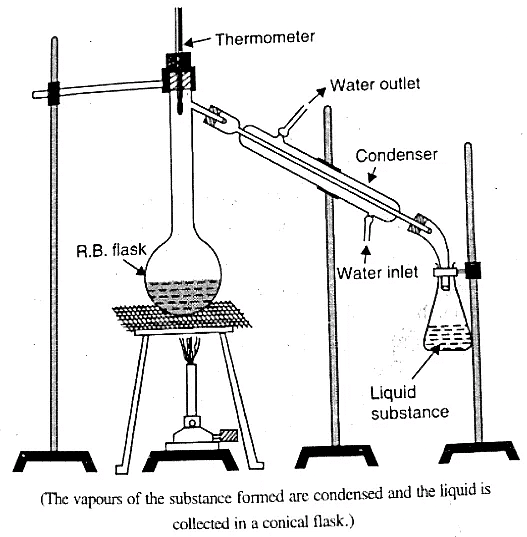
- Take the mixture in a round-bottom flask and heat it.
- The component with the lower boiling point, i.e., the more volatile liquid, evaporates faster and is collected in a separate container.
- A condenser is employed to facilitate the condensation process.
- Distillation can effectively separate mixtures with significantly different boiling points, such as chloroform and aniline.
4. Fractional Distillation
Fractional distillation comes into play when the boiling points of the liquids to be separated are relatively close. To prevent the condensation of their vapors, a fractionating column is added to the round-bottom flask.
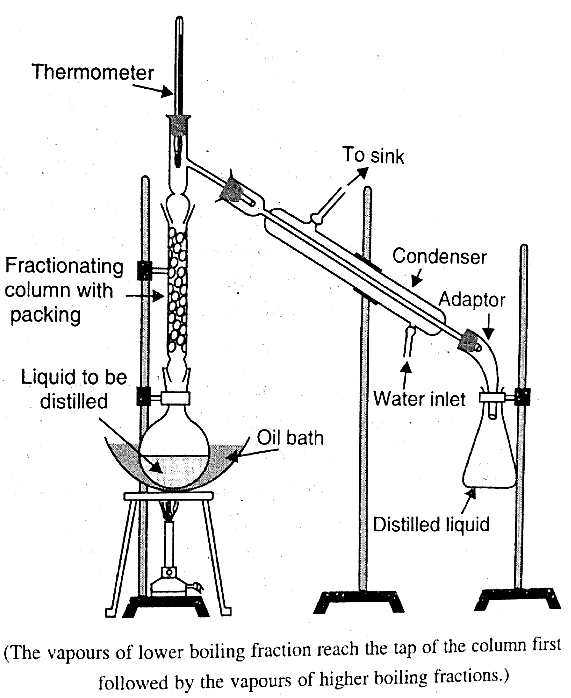
- Introduce a fractionating column to the round-bottom flask.
- The column allows for repeated vaporization and condensation, promoting the separation of liquids with similar boiling points.
- Fractional distillation is particularly useful when dealing with mixtures that exhibit a narrow range of boiling points.
5. Vacuum Distillation
Vacuum distillation involves distilling liquids at temperatures below their regular boiling points. By reducing the atmospheric pressure using a vacuum pump, the boiling points of the liquids are lowered, expediting the distillation process.
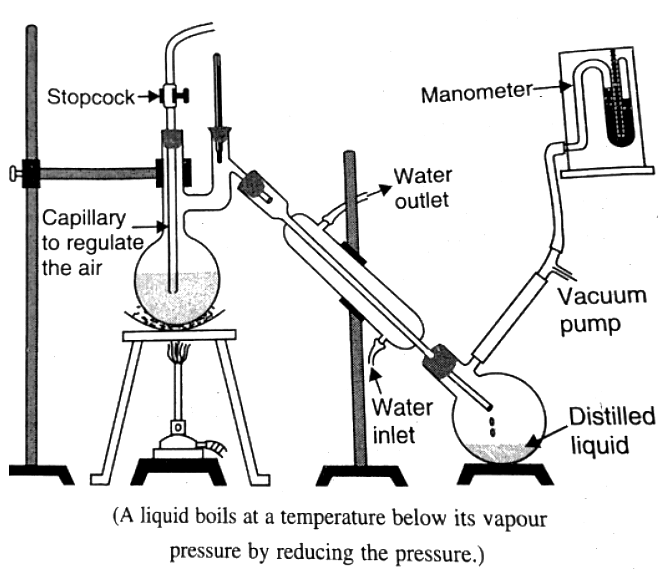
- Employ a vacuum pump to decrease the atmospheric pressure.
- The reduced pressure causes the liquids to boil at lower temperatures than their typical boiling points.
- The lower boiling points result in faster distillation, accelerating the overall purification process.
6. Steam Distillation
Steam distillation utilizes the introduction of steam into the flask containing the liquids to be separated. The presence of steam enhances the boiling process by equalizing the atmospheric pressure through aqueous tension, or the vapor pressure of water.
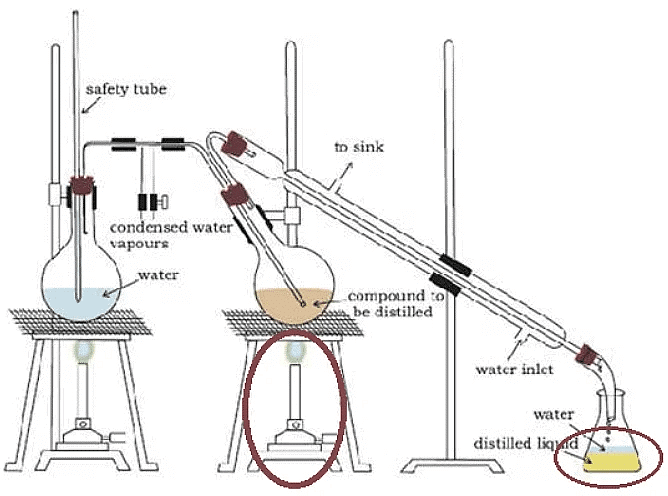
- Pass steam into the flask with the liquid mixture.
- The steam's presence accelerates the boiling process, aiding in equalizing the atmospheric pressure.
- The total pressure is the sum of the aqueous tension and the vapor pressure of the liquid components.
- Steam distillation expedites the boiling process, which would otherwise continue until atmospheric pressure is achieved.
- This method is particularly effective for compounds that require an aqueous environment, such as the extraction of phenol using NaOH solution.
7. Differential Extraction
Differential extraction is employed for immiscible liquids, i.e., liquids that do not mix together, such as oil and water. The immiscible liquids are placed in a separating funnel and left undisturbed, allowing them to separate based on their specific gravities, with the heavier liquid settling at the bottom.
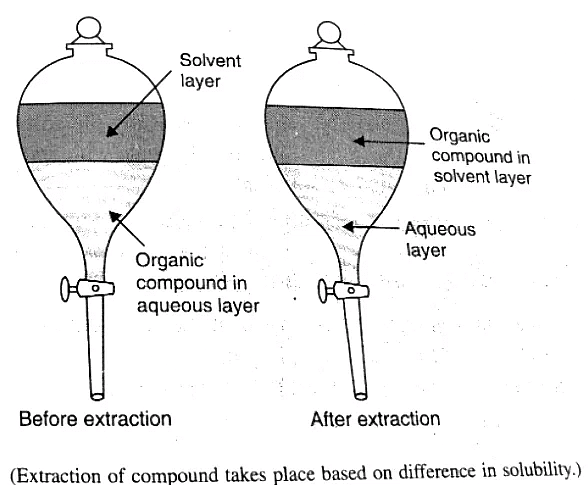
- Pour the immiscible liquids into a separating funnel.
- Allow sufficient time for the liquids to separate based on their specific gravities.
- Collect the separated liquids according to their positions in the funnel.
- Substances can also be separated based on their preferential solubilities in the liquid.
Chromatography
Chromatography is a vital separation technique that aids in the purification and purity assessment of organic compounds. In this method, a mixture of substances is applied to a stationary phase (solid or liquid), while a mobile phase (gas or pure solvent) is allowed to move slowly over it. As a result, the components of the mixture begin to separate from one another.
Chromatography Types
- Adsorption Chromatography: Based on varying degrees of adsorption, with commonly used adsorbents such as silica gel or alumina.
- Partition Chromatography: Relies on the differential partitioning of components between the stationary and mobile phases.
Adsorption Chromatography Process
Apply the mixture of substances to an adsorbent on the stationary phase. As the mobile phase moves over the fixed phase, the constituents get adsorbed at various distances. The separation occurs due to the differential adsorption of the components.
Column Chromatography
- Here, a mixture is separated over a column of either silica gel or alumina, packed in a glass column. The constituent with the most affinity with the fixed phase is adsorbed at the top, and so on. It is then retrieved by using an eluant. The solvent is then evaporated to get the constituent.
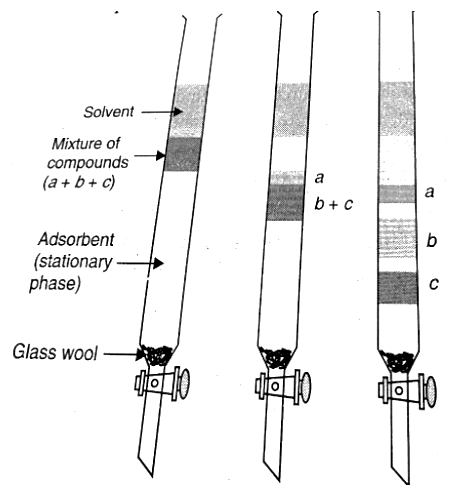
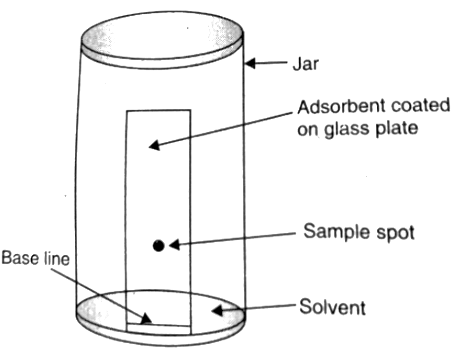
Thin Layer Chromatography
Here, a sheet of alumina is taken (0.2 mm thick), over which a small spot of the mixture is placed, and it is kept in a suitable solvent. The solvent rises due to capillary action, and the constituents also rise with the solvent depending on their differential adsorption, and thereby, they are separated.