Introduction
In the realm of linear algebra, the Cayley-Hamilton theorem, named after mathematicians Arthur Cayley and William Rowan Hamilton, establishes that every square matrix belonging to a commutative ring (such as the real or complex field) satisfies its own characteristic equation. If we have a given n×n matrix A and In represents the n×n identity matrix, the unique polynomial of A can be expressed as:
p(x) = det(xIn – A)
Here, the determinant operation is denoted by 'det', and x represents the scalar element of the base ring. Since the entries of the matrix are polynomials in x (either linear or constant), the determinant itself becomes an nth-order monic polynomial in x.
What is Cayley–Hamilton theorem?
The Cayley-Hamilton theorem can be restated as follows: When we substitute the matrix A for x in the polynomial p(x) = det(xIn - A), the result is the zero matrix, expressed as
p(A) = 0.
This theorem asserts that an n x n matrix A is annihilated by its characteristic polynomial, det(tI - A), which is a monic polynomial of degree n. The powers of A, obtained by substituting powers of x, are determined through repeated matrix multiplication. The constant term of p(x) yields a multiple of the power A0, where the power corresponds to the identity matrix. The theorem allows us to express An as a linear combination of the lower powers of A. If the ring under consideration is a field, the Cayley-Hamilton theorem is equivalent to the statement that the minimal polynomial of a square matrix divides its characteristic polynomial.
Example of Cayley-Hamilton Theorem
1. 1 x 1 Matrices
For 1 x 1 matrix A(a1,1) the characteristic polynomial is given by
p(λ) = λ - α
So, p(A) = (α) – (a1,1) = 0 is obvious.
2. 2 x 2 Matrices
Let us look this through an example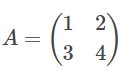

The Cayley-Hamilton claims that if, we define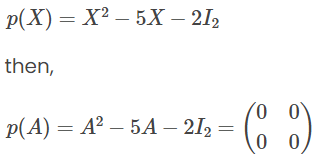
We can verify this result by computation
For a generic 2 x 2 matrix,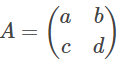
The resultant polynomial is given by:
So the Cayley-Hamilton theorem states that
it is always the case, which is evident by working out on A2.