| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Power of i |

|
| Square of Iota |

|
| Square Root of Iota |

|
| Higher Power of i |

|
| Value of Iota for Negative Power |

|
Introduction
Iota is an imaginary unit number that is denoted by i and the value of iota is √-1 i.e., i = √−1. While solving quadratic equations, you might have come across situations where the discriminant is negative. For example, consider the quadratic equation x2 + x + 1 = 0. If we use the quadratic formula to solve this, we get the discriminant (the part inside the square root) as a negative value.
In such cases, we write √−3 as √−3 = √−1 × √3. This would give the solution of the above quadratic equation to be: x = (−1 ± √3i)/2. Hence, the value of iota is helpful in solving square roots with negative values.
Thus, the value of iota is, i = √−1.
Power of i
The powers of i, i repeat in a certain pattern in a cycle. Let us start with calculating the value of powers of i for general cases and try to figure out the pattern.
Square of Iota
We know that the value of iota, i is defined as, i = √−1. If we square both sides of the above equation, we get: i2 = -1 i.e., the value of the square of iota is -1. Therefore, the square of iota is, i2 = −1.
Square Root of Iota
Iota has two square roots, just like all non-zero complex numbers. The value of the square root of iota, given as √i, can be calculated using De Moivre's Theorem.
We know that, i = cos(π/2) + isin(π/2)
= cos(π/2 + 2nπ) + isin(π/2 + 2nπ), n = 0, 1
= cos[(π + 4nπ)/2] + i sin[(π + 4nπ)/2]
Here, we took n = 0, 1 as we need 2 solutions. But we have to find √i = (i)1/2. Let us raise the exponent to 1/2 on both sides. So we get: √i = [cos{(π + 4nπ)/2} + isin{(π + 4nπ)/2}]1/2 = cos[(π + 4nπ)/4] + isin[(π + 4nπ)/4], n = 0, 1
- When n = 0, √i = cos(π/4) + isin(π/4) = √2/2 + i√2/2
- When n = 1, √i = cos(5π/4) + isin(5π/4) = −√2/2 − i√2/2
√i = √2/2 + i√2/2 = −√2/2 − i√2/2
Let us see how to calculate some other powers of i.
- i3 = i × i2 = i × −1 = −i
- i4 = i2 × i2 = −1×−1 = 1
- i5 = i × i4 = i × 1 = i
- i6 = i × i5 = i × i = i2 = −1
- i7 = i × i6 = i × −1 = -i
- i8 = ((i)2)4 = (−1)4 =1
- i9 = i × i8 = i × 1 = i
- i10 = i × i9 = i × i = i2 = −1
From the above calculations, we can observe that the values of iota repeat in certain pattern. The following figure represents the values for various powers of i in the form of a continuous circle.
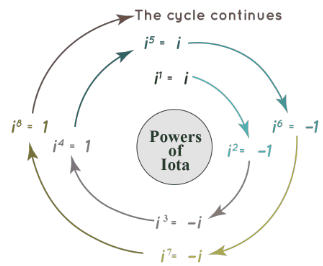
This signifies that i repeats its values after every 4th power. We can generalize this fact to represent this pattern (where n is any integer), as,
- i4n = 1
- i4n+1 = i
- i4n+2 = -1
- i4n+3 = -i
Higher Power of i
Higher powers of iota can be calculated by decomposing the higher exponents i into smaller ones and thus evaluating the expression. Finding value if the power of i is a larger number using the previous procedure, will take quite some time and effort. If we observe all the powers of i and the pattern in which it repeats its values in the above equations, we can calculate the value of iota for higher powers as given below,
- Step 1: Divide the given power by 4.
- Step 2: Note the remainder for the division in Step 1, and use it as the new exponent/power of i.
- Step 3: Calculate the value of iota for this new exponent/power using the previously known values, i = √−1; i2 = -1 and i3 = -i.
Example: Find the value of i20296.
- We first divide 20296 by 4 and find the remainder.
- The remainder is 0 (by divisibility rules, we can just divide the number formed by the last two digits which is 96 in this case, to find the remainder).
- Thus, using the above rules, i20296 = i0 = 1
- Therefore, i20296 = 1
We just have to remember that i2 = -1 and i3 = -i. We will find some other higher powers of i using these and the above rules.
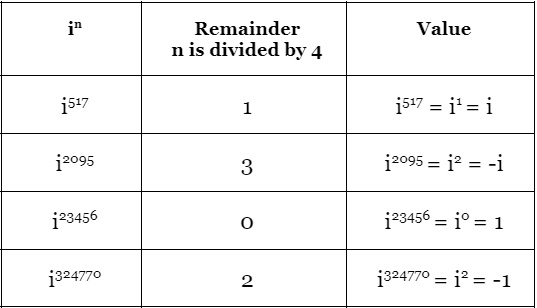
Value of Iota for Negative Power
The value of iota for negative power can be calculated following few steps. We first convert it into a positive exponent using the negative exponent law and then we apply the rule: 1/i = -i. This is because:1/i = 1/i • i/i = i/i2 = i/(-1) = -i
Example: Find the value of i-3927
i-3927 = 1/i3927
∵ a-m = 1/am
= 1/i3
∵ Remainder of 3927 divided by 4 is 3
= 1/-i
∵ i3 = -i
= --i
∵ 1/i = -i
= i













