Quadratic Equation: Practice Questions | CSAT Preparation - UPSC PDF Download
Q1: If (p – x)(p – y) = 1 and (x – y = √5), then, the value of 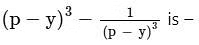
(a) 4√5
(b) 8√5
(c) 6√7
(d) 10√5
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (b)
Sol:
Given:
(p – x)(p – y) = 1
Also, (x - y)=√5
Formula Used:
(x – y)3 = x3 – y3 – 3xy(x – y)
Calculation:
(p – x)(p – y) = 1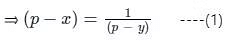
⇒ x - y = √5 ----(2)Add and subtract 'p' in left side of eq. (2)
⇒ -p + x + p – y = √5⇒ (p − y) − (p − x) = √5 ----(3)
Put the value of (p - x) from eq. (1) to eq. (3)
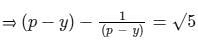
Taking cube both sides, we have –
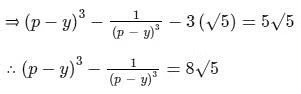
Q2: What is the sum of the reciprocals of the values of zeroes of the polynomial 6x2 + 3x2 – 5x + 1?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (d)
Sol: Given:
6x2 + 3x2 – 5x + 1
Calculation:
6x2 + 3x2 – 5x + 1
⇒ 9x2 – 5x + 1
Let 'a' and 'b' be two roots of the equations
As we know,
Sum of roots (α + β) = (-b)/a = 5/9
Product of roots (αβ) = c/a = 1/9
According to the question
⇒ 1/α + 1/β
⇒ (α + β)/αβ
⇒ [5/9] / [1/9] = 5
Q3: One of the roots of the equation x2 – 12x + k = 0 is x = 3. The other root is:
(a) x = -4
(b) x = 9
(c) x = 4
(d) x = -9
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (b)
Sol: Concept:
Roots of a quadratic equation satisfy the equation, so by putting the value of one root,
One can find the unknown variable and hence the other root.
Calculation:
Let us put x = 3 in the equation x2 – 12x + k = 0,
⇒ 9 – 36 + k = 0
⇒ k = 27
Putting the value of k in the equation,
we get: x2 – 12x + 27 = 0
⇒ x2 – 9x – 3x + 27 = 0
⇒ x(x – 9) – 3 (x – 9) = 0
⇒ (x – 3)(x – 9) = 0
⇒ x = 3 and 9
∴ Other root of the equation is 9
Q4: If x6 + x5 + x4 + x3 + x2 + x + 1 = 0, then, find the value of x42 + x84.
(a) -1
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) -2
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (c)
Sol: Given:
x6 + x5 + x4 + x3 + x2 + x + 1 = 0 ----(1)
Calculation:
Multiplying by x, we have –
⇒ x7 +x6 + x5 + x4 + x3 + x2 + x = 0 ----(2)
Equation (2) – (1), we have –
⇒ x7 – 1 = 0
⇒ x7 = 1
According to question –
The value of x42 + x84 = 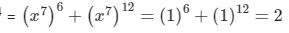
Q5: Find the quadratic equation whose one root is 5 = 2√5
(a) x2 + 10x + 5 = 0
(b) x2 - 5x + 10 = 0
(c) x2 - 10x + 5 = 0
(d) x2 + 5x - 10 = 0
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (c)
Sol: Given:
One root of the equation is 5 = 2√5
Concept:
If one root of the quadratic equation is in this form (a + √b) then the other roots must be conjugate (a - √b) and vice-versa.
Quadratic equation: x2 - (sum of root) + (product of root) = 0
Calculation:
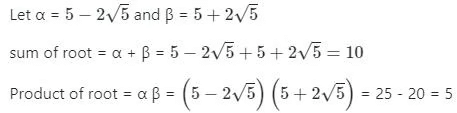
Quadratic equation = x2 - (α + β)x + α β = 0
Now, Quadratic equation = x2 - 10x + 5 = 0
Hence, required quadratic equation is x2 - 10x + 5 = 0
Q6: The roots of the equation ax2 + x + b = 0 are equal if
(a) b2 = 4a
(b) b2 < 4a
(c) b2 > 4a
(d) ab = 1/4
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (d)
Sol: Given: The given equation is ax2 + x + b = 0
Concept used:
General form of the quadratic equation is ax2 + x + b = 0
Condition for roots,
For equal and real roots, b2 – 4ac = 0
For unequal and real roots, b2 – 4ac > 0
For imaginary roots, b2 – 4ac < 0
Calculation:
For equal and real roots, b2 – 4ac = 0
⇒ b2 = 4ac
After comparing with the general form of the quadratic equation we'll get
b = 1, a = a and c = b
Then, b2 = 4ac
⇒ 1 = 4ab
⇒ ab = 1/4
∴ The correct relation is ab = 1/4
Q7: One root of the equation 5x2 + 2x + Q = 2 is reciprocal of another. What is the value of Q2?
(a) 25
(b) 1
(c) 49
(d) 4
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (c)
Sol: Given:
5x2 + 2x + Q = 2
Given α = 1/β ⇒ α.β = 1 ----(i)
Concept:
Let us consider the standard form of a quadratic equation, ax2 + bx + c =0
Let α and β be the two roots of the above quadratic equation.
The sum of the roots is given by:
α + β = − b/a = −(coefficient of x/coefficient of x2)
The product of the roots is given by:
α × β = c/a = (constant term /coefficient of x2)
Calculation:
Let the roots of 5x2 + 2x + Q - 2 = 0 are α and β
According to the question,
α = 1/β
⇒ α.β = 1
Compare with general equation ax2 + bx + c = 0
a = 5, b = 2, c = Q - 2
⇒ (Q – 2)/5 = 1
⇒ Q - 2 = 5
⇒ Q = 7
Hence, Q2 = 72 = 49.
Q8: If 3x2 – ax + 6 = ax2 + 2x + 2 has only one (repeated) solution, then the positive integral solution of a is:
(a) 3
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) 5
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (b)
Sol: Given:
3x2 – ax + 6 = ax2 + 2x + 2
⇒ 3x2 – ax2 – ax – 2x + 6 – 2 = 0
⇒ (3 – a)x2 – (a + 2)x + 4 = 0
Concept Used:
If a quadratic equation (ax2 + bx + c=0) has equal roots, then discriminant should be zero i.e. b2 – 4ac = 0
Calculation:
⇒ D = B2 – 4AC = 0
⇒ (a + 2)2 – 4(3 – a)4 = 0
⇒ a2 + 4a + 4 – 48 + 16a = 0
⇒ a2 + 20a – 44 = 0
⇒ a2 + 22a – 2a – 44 = 0
⇒ a(a + 22) – 2(a + 22) = 0
⇒ a = 2, -22
∴ Positive integral solution of a = 2
Q9: Quadratic equation corresponding to the roots 2 + √5 and 2 − √5 is
(a) x2 - 4x - 1 = 0
(b) x2 + 4x - 1 = 0
(c) x2 - 4x + 1 = 0
(d) x2 + 4x + 1 = 0
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (a)
Sol: Given:
Two roots are 2 + √5 and 2 - √5.
Concept used:
The quadratic equation is:
x2 - (Sum of roots)x + Product of roots = 0
Calculation:
Let the roots of the equation be A and B.
A = 2 + √5 and B = 2 - √5
⇒ A + B = 2 + √5 + 2 - √5 = 4
⇒ A × B = (2 + √5)(2 - √5) = 4 - 5 = -1
Then equation is
∴ x2 - 4x - 1 = 0
Mistake Points:
For a quadratic equation, ax2 + bx + c = 0,
Sum of the roots = (-b/a) = 4/1
Product of the roots = c/a = -1/1
Then, b = -4
So, the sign of coefficient of x is negative.
Q10: If α and β are roots of the equation x2 – x – 1 = 0, then the equation whose roots are α/β and β/α is:
(a) x2 + 3x – 1 = 0
(b) x2 + x – 1 = 0
(c) x2 – x + 1 = 0
(d) x2 + 3x + 1 = 0
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (d)
Sol: Given:
x2 – x – 1 = 0
Formula used:
If the given equation is ax2 + bx + c = 0
Then Sum of roots = -b/a
And Product of roots = c/a
Calculation:
As α and β are roots of x2 – x – 1 = 0, then
⇒ α + β = -(-1) = 1
⇒ αβ = -1
Now, if (α/β) and (β/α) are roots then,
⇒ Sum of roots = (α/β) + (β/α)
⇒ Sum of roots = (α2 + β2)/αβ
⇒ Sum of roots = [(α + β)2 – 2αβ]/αβ
⇒ Sum of roots = (1)2 – 2(-1)]/(-1) = -3
⇒ Product of roots = (α/β) × (β/α) = 1
Now, then the equation is,
⇒ x2 – (Sum of roots)x + Product of roots = 0
⇒ x2 – (-3)x + (1) = 0
⇒ x2 + 3x + 1 = 0
Q11: In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. x2 – 2x – 80 = 0
II. y2 – 10y – 171 = 0
(a) x > y
(b) x < y
(c) x ≥ y
(d) x = y or relation between x and y can not be established.
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (d)
Sol: For I:
x2 – 2x – 80 = 0
⇒ x2 – 10x + 8x – 80 = 0
⇒ x(x – 10) + 8(x – 10) = 0
⇒ (x + 8) (x – 10) = 0
⇒ x = -8, 10
For II:
y2 – 10y – 171 = 0
⇒ y2 – 19y + 9y – 171 = 0
⇒ y(y – 19) + 9(y – 19) = 0
⇒ (y – 19) (y + 9) = 0
⇒ y = 19, -9
Comparison between x and y (via Tabulation):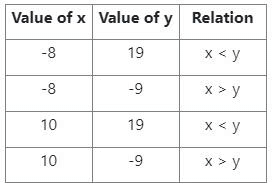
So x = y or the relationship cannot be established.
Q12: In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. x2 + 8x – 48 = 0
II. y2 – 8y – 105 = 0
(a) x = y or relation between x and y can not be established.
(b) x > y
(c) x < y
(d) x ≤ y
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (a)
Sol: For I:
x2 + 8x – 48 = 0
⇒ x2 + 12x – 4x – 48 = 0
⇒ x(x + 12) – 4(x + 12) = 0
⇒ (x + 12) – 4(x + 12) = 0
⇒ x = -12, 4
For II:
y2 – 8y – 105 = 0
⇒ y2 – 15y + 7y – 105 = 0
⇒ y(y – 15) + 7(y – 15) = 0
⇒ (y – 15)(y + 7) = 0
⇒ y = 15, -7
Comparison between x and y (via Tabulation):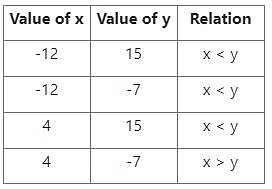
So x = y or relation between x and y can not be established.
Q13: In the given question, two equations numbered l and II are given. Solve both equations and mark the appropriate answer.
I. x2 + x – 90 = 0
II. y2 + 4y – 96 = 0
(a) x < y
(b) x ≤ y
(c) x = y or relation between x and y can not be established.
(d) x ≥ y
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (c)
Sol: For I:
x2 + x – 90 = 0
⇒ x2 + 10x – 9x – 90 = 0
⇒ x(x + 10) – 9(x + 10) = 0
⇒ (x – 9) (x + 10) = 0
⇒ x = 9, -10
For II:
y2 + 4y – 96 = 0
⇒ y2 + 12y – 8y – 96 = 0
⇒ y(y + 12) – 8(y + 12) = 0
⇒ (y + 12) (y – 8) = 0
⇒ y = -12, 8
Comparison between x and y (via Tabulation):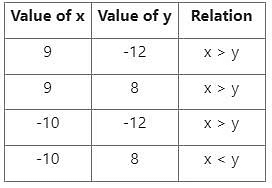
So x = y or relation between x and y can not be established.
Q14: If roots of quadratic equation ax2 + 2bx + c = 0 are equal then
(a) a, b, c in A.P
(b) a, b, c in G.P
(c) a, b, c in H.P
(d) None of these
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (b)
Sol: Concept:
If roots of ax2 + bx + c = 0 are equal then
D = b2 - 4ac = 0
Calculation:
Given the quadratic equation ax2 + 2bx + c = 0,
the roots are equal if the discriminant is zero:
(2b)2 - 4ac = 0
⇒ 4b2 = 4ac
⇒ b2 = ac
⇒ b = √ac
So, the correct answer is (2) a, b, c are in Geometric Progression (GP).
Q15: If x = -2/3, then 9x2 – 3x – 11 is equal to
(a) -13
(b) 13
(c) -5
(d) -17
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (c)
Sol: Given:
x = -2/3
Calculation:
9x2 – 3x – 11 = ?
⇒ 9 × (-2/3)2 – 3(-2/3) – 11 = ?
⇒ 9 × (4/9) – (-2) – 11 = ?
⇒ 4 + 2 – 11 = ?
⇒ 6 – 11 = ?
⇒ -5 = ?
∴ The required value is -5
|
209 videos|138 docs|138 tests
|
FAQs on Quadratic Equation: Practice Questions - CSAT Preparation - UPSC
| 1. What is the standard form of a quadratic equation? |  |
| 2. How can I find the roots of a quadratic equation? |  |
| 3. What does the discriminant tell us about the roots of a quadratic equation? |  |
| 4. Can a quadratic equation have complex roots? |  |
| 5. How do I graph a quadratic function? |  |