Indian History Important Dates | Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) PDF Download
Indus Valley Civilization (2300–1750 BC)
The Indus Valley Civilization, one of the world's oldest urban cultures, flourished in the northwestern regions of South Asia. Known for its advanced architecture, planned cities, and sophisticated drainage systems, this civilization included major cities like Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro. It was characterized by the use of baked bricks, standard weights and measures, and an undeciphered script.
Arrival and Expansion of the Aryans (From 1500 BC - 800 BC)
The Aryans migrated into the Indian subcontinent around 1500 BC. They settled in the region and gradually expanded into the Ganga Valley between 1200 and 800 BC. The Aryans brought with them new cultural practices, including the composition of the Vedas, which are among the oldest sacred texts. 
16 Mahajanapadas and the Emergence of Buddhism and Jainism (600 BC - 468 BC)
The period around 600 BC saw the rise of 16 Mahajanapadas in northern India. This era was marked by significant political, social, and religious transformations. Two major religions, Buddhism and Jainism, were founded during this time. Buddha, born in 563 BC, and Mahavir, born in 540 BC, preached their philosophies, emphasizing non-violence and spiritual liberation. 
The Nanda Dynasty and Alexander's Invasion (362 BC - 326 BC)
The Nanda dynasty ruled over northern India from 362 to 321 BC. Their rule was marked by significant administrative and military advancements. In 327–326 BC, Alexander the Great invaded India, establishing a route between India and Europe and influencing subsequent Indian history. 
The Maurya Empire (322 BC - 232 BC)
Chandragupta Maurya founded the Maurya Empire in 322 BC after defeating the Nanda dynasty. The empire expanded significantly under his rule and that of his successors. Ashoka, one of the greatest Indian emperors, ruled from 273 to 232 BC. His reign is particularly noted for the conquest of Kalinga in 261 BC and his subsequent embrace of Buddhism. 
The Early Tamil Kingdoms (145 BC - 101 BC)
The early Tamil kingdoms, including the Chola dynasty, were significant in the southern part of the Indian subcontinent. Elara, a Chola king, ruled Sri Lanka from 145 to 101 BC. 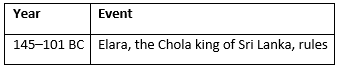
The Vikram and Saka Eras and Kanishka's Reign (58 BC - 101 AD)
The Vikram and Saka eras mark important chronological systems in Indian history. The Vikram era began in 58 BC, while the Saka era started in 78 AD. Kanishka, who reigned from 78 to 101 AD, was a prominent Kushan emperor known for his military conquests and patronage of Buddhism. 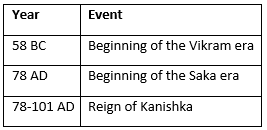
The Gupta Era (319 - 647 AD)
The Gupta Empire, starting in 319 AD, is often referred to as the Golden Age of India due to its extensive achievements in arts, sciences, and culture. Chandragupta II, also known as Vikramaditya, reigned from 380 AD and was succeeded by Kumaragupta I in 415 AD and Skandagupta in 455 AD. The Chinese traveler Fahien visited India during this period, documenting the empire's prosperity. 
The Reign of Harshavardhan (606 - 647 AD)
Harshavardhan ruled northern India from 606 to 647 AD. His reign was marked by the consolidation of territories and the promotion of culture and religion. Harsha was a patron of the arts and Buddhism, and his court attracted scholars from across the world. 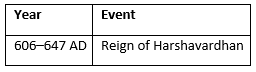
Throughout these periods, ancient India experienced significant developments in politics, culture, and religion, laying the foundation for its rich historical and cultural heritage.
Medieval History: Key Events and Developments
Early Medieval Period (712 - 1206 AD)The early medieval period in India saw the arrival and establishment of various foreign powers and the rise of prominent Indian kingdoms. This era was marked by significant invasions and the establishment of new dynasties.
Year | Event |
712 | Arabs (Mohd. Bin Qasim) make their first invasion in Sindh |
836 | King Bhoja of Kannauj ascends to the throne |
985 | Rajaraja, the Chola ruler, assumes power |
998 | Sultan Mahmud Ghazni becomes the ruler |
1001 | Mahmud Ghazni launches his first invasion of India and defeats Jaipal, the ruler of Punjab |
1025 | Mahmud Ghazni destroys the Somnath Temple |
1191 | The first battle of Tarain takes place |
1192 | The second battle of Tarain occurs |
Establishment of Delhi Sultanate (1206 - 1325 AD)
The Delhi Sultanate was established in 1206 AD with the rule of Qutubuddin Aibak. This period saw the establishment of a centralized Muslim rule in India, leading to significant cultural and political changes.
Year | Event |
1206 | Qutubuddin Aibak becomes the ruler of Delhi |
1210 | Death of Qutubuddin Aibak |
1221 | India is invaded by Chengiz Khan (Mongol invasion) |
1236 | Razia Sultana ascends to the throne of Delhi |
1240 | Death of Razia Sultana |
1296 | Alauddin Khilji becomes the ruler |
1316 | Death of Alauddin Khilji |
1325 | Muhammad-bin-Tughlaq becomes the ruler |
1327 | Muhammad-bin-Tughlaq transfers the capital from Delhi to Devagiri (Daulatabad) in Deccan |
The Vijayanagar Empire and Later Delhi Sultanate (1336 - 1526 AD)
The Vijayanagar Empire in the south and the continued rule of the Delhi Sultanate in the north were significant during this period. The Delhi Sultanate faced numerous invasions and internal conflicts, while the Vijayanagar Empire thrived culturally and economically.
Year | Event |
1336 | The Vijayanagar empire is founded in the South |
1351 | Firoz Shah Tughlaq becomes the ruler |
1398 | Timur invades India |
1469 | Guru Nanak is born |
1494 | Babur ascends to the throne in Farghana |
1497–98 | Vasco da Gama makes his first voyage to India, discovering the sea route via the Cape of Good Hope |
1526 | The first Battle of Panipat takes place, with Babur defeating Ibrahim Lodhi and establishing the Mughal dynasty |
1527 | Battle of Khanwa, where Babur defeats Rana Sanga |
1530 | Death of Babur and accession of Humayun |
Mughal Empire and European Involvement (1539 - 1761 AD)
The Mughal Empire, starting with Babur's victory in 1526, marked a significant period in Indian history. This era saw the establishment of a powerful and culturally rich empire. The arrival of Europeans, starting with the Portuguese and later the British, set the stage for future colonial rule.
Year | Event |
1539 | Sher Shah Suri defeats Humayun in the battle of Chausa and becomes the emperor of India |
1555 | Humayun recaptures the throne of Delhi |
1556 | The second Battle of Panipat occurs, with Bairam Khan defeating Hemu |
1556 | Battle of Talikota (Rakshasa- Tangadi) |
1576 | Battle of Haldighati, where Rana Pratap is defeated by Akbar |
1582 | Din-i-Ilahi is founded by Akbar |
1600 | The English East India Company is established |
1605 | Death of Akbar and accession of Jahangir |
1606 | Execution of Guru Arjun Dev, the 5th Guru of Sikhs |
1611 | Jahangir marries Nurjahan |
1615 | Sir Thomas Roe visits Jahangir |
1627 | Shivaji is born and Jahangir passes away |
1628 | Shahjahan becomes the emperor of India |
1631 | Death of Mumtazmahal |
1634 | The English are granted permission to trade in India (in Bengal) |
1659 | Aurangzeb ascends to the throne, Shahjahan is imprisoned |
1665 | Aurangzeb imprisons Shivaji |
1666 | Death of Shahjahan |
1675 | Execution of Guru Teg Bahadur, the 9th Guru of Sikhs |
1680 | Death of Shivaji |
1707 | Death of Aurangzeb |
1708 | Death of Guru Gobind Singh, the 10th Guru of Sikhs |
1739 | Nadir Shah invades India |
1757 | Battle of Plassey, leading to the establishment of British political rule in India under Lord Clive |
1761 | The third Battle of Panipat takes place |
The medieval period in Indian history was marked by the rise and fall of several dynasties, significant invasions, the establishment of the Delhi Sultanate, the grandeur of the Mughal Empire, and the initial stages of European colonialism, which set the foundation for the modern history of India.
Modern History: Key Events and Developments
British Conquest and Early Colonial Period (1764 - 1833 AD)
The British East India Company consolidated its power in India through a series of battles and administrative reforms. This period was marked by significant conflicts, such as the Anglo-Mysore Wars and the establishment of the Permanent Settlement in Bengal, which restructured land revenue systems.
Year | Event |
1764 | Battle of Buxar |
1765 | Appointment of Clive as Governor of the Company in India |
1767–69 | First Anglo-Mysore War |
1780 | Maharaja Ranjit Singh is born |
1780-84 | Second Anglo-Mysore War |
1784 | Implementation of Pitt's India Act |
1790-92 | Third Anglo-Mysore War |
1793 | Introduction of the Permanent Settlement of Bengal |
1799 | Fourth Anglo-Mysore War; Death of Tipu Sultan |
1802 | Treaty of Bassein |
1809 | Treaty of Amritsar |
1829 | Prohibition of the practice of Sati |
1830 | Raja Rammohan Roy visits England |
1833 | Death of Raja Rammohan Roy in Bristol, England |
Rise of Regional Powers and British Expansion (1839 - 1857 AD)
During this period, the British faced significant resistance from regional powers, leading to conflicts such as the Anglo-Afghan and Anglo-Sikh Wars. Additionally, technological advancements like the introduction of railways and telegraphs began to take root in India.
Socio-Political Awakening and Freedom Struggle (1861 - 1922 AD)
This era saw the birth of prominent leaders and the establishment of key political organizations. The Indian National Congress was formed, and significant movements like the Non-cooperation Movement were launched, marking the beginning of mass participation in the freedom struggle.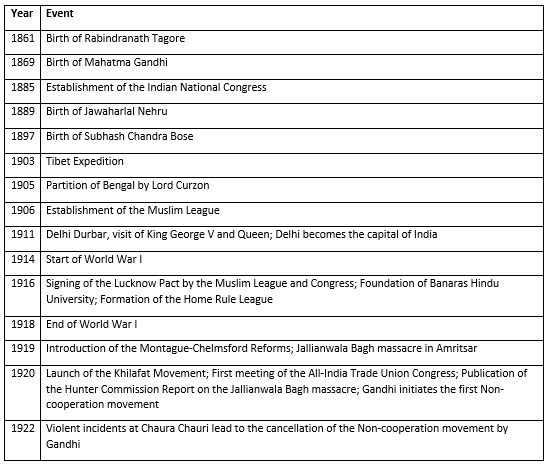
Towards Independence (1925 - 1947 AD)
The period leading up to independence was marked by significant political activities, including the Civil Disobedience Movement, the Quit India Movement, and the formation of the Indian National Army. The end of World War II accelerated the process of India's independence, which was eventually achieved in 1947.
Year | Event |
1925 | Formation of the Communist Party of India in Kanpur |
1927 | Boycott of the Simon Commission; Introduction of broadcasting in India |
1928 | Death of Lala Lajpat Rai; Publication of the Nehru Report |
1929 | Adoption of the resolution of 'Poorna Swaraj' (complete independence) at the Lahore Session of the INC |
1930 | Launch of the Civil Disobedience movement; Gandhi's Dandi March (April 6, 1930); First round table conference held in London |
1931 | Signing of the Gandhi-Irwin Pact; Suspension of the Civil Disobedience movement; Second round table conference held |
1932 | Announcement of the communal award by MacDonald (modified by the Poona Pact on September 24) |
1935 | Implementation of the Government of India Act |
1937 | Granting of Provincial Autonomy; Formation of Congress ministries |
1938 | Formation of the All India Kisan Sabha |
1939 | Start of World War II (September 3); Resignation of Congress Ministries in Provinces |
1941 | Escape of Subhash Chandra Bose from India; Death of Rabindranath Tagore |
1942 | Arrival of the Cripps Mission in India; Launch of the Quit India movement (August 8) |
1943–44 | Formation of Subhash Chandra Bose's Provisional Government of Free India and the Indian National Army in Singapore; Occurrence of the Bengal famine |
1945 | Trial of the Indian National Army at the Red Fort; Shimla Conference; End of World War II |
1946 | Visit of the British Cabinet Mission to India; Formation of the Interim government at the Centre; The Muslim League decides on "Direct Action" to achieve Pakistan |
1947 | Partition of India; Formation of separate independent dominions, India and Pakistan |
The modern period in Indian history is characterized by the rise of British colonialism, the struggle for independence, and the eventual emergence of India and Pakistan as independent nations in 1947. This era witnessed significant socio-political changes and the birth of several prominent leaders who shaped the course of Indian history.
|
1179 videos|2219 docs|849 tests
|
FAQs on Indian History Important Dates - Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests)
| 1. What are the key events and developments in Indian medieval history? |  |
| 2. What are some important dates in Indian history? |  |
| 3. What was the significance of the Indus Valley Civilization? |  |
| 4. How did the Delhi Sultanate impact Indian history? |  |
| 5. What were some key developments in modern Indian history? |  |

















