Types of Waves: Electromagnetic, Mechanical & Matter Waves | Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) PDF Download
Introduction
In simple terms, a wave can be described as a disturbance that moves through a medium, carrying energy from one place to another without transferring matter. Examples of waves include wind-generated waves and circular water waves.
Water waves consist of two main parts known as the crest and trough, which the wave travels through. Each crest is followed by another crest, and the trough is the lowest point in a wave cycle.
Types of Waves
There are various types of waves that surround us, such as sound waves, radio waves, water waves, and different types of oscillating waves like sine waves and cosine waves. These waves are created by disturbances. Waves can be classified into three main types:
Mechanical Waves:
Mechanical waves propagate through a material medium by causing repeated periodic movements of the medium's particles around their average positions. The disturbance is transferred from one particle to another, carrying momentum and energy. These waves cannot travel through a vacuum as they rely on the inertia and elastic properties of the medium. Examples of mechanical waves include vibrations in a string, tsunami waves, sound waves, ultrasound, oscillations in springs, and waves in a slinky.
Mechanical waves can be further classified into two types:
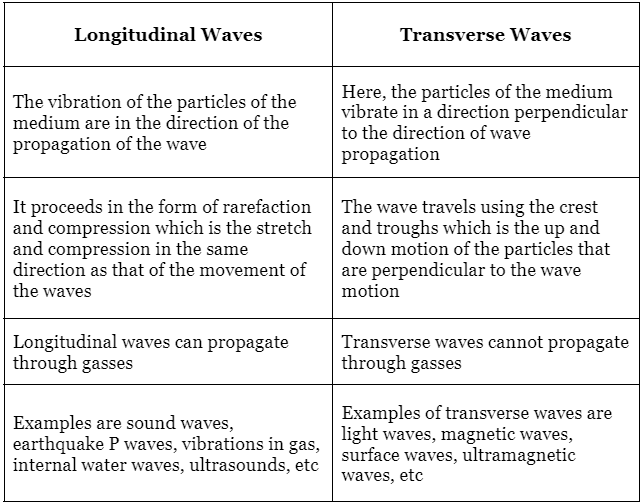
- Transverse Waves:Transverse waves are disturbances in a medium where the particles oscillate perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. The particles move in a cyclical or periodic pattern. Examples of transverse waves include ripples on the water surface and vibrations in strings. The crest represents the highest point of upward displacement in a wave cycle, while the trough is the lowest point. Transverse waves can occur in two independent directions, such as moving a ribbon up and down or sideways.
- Longitudinal Waves: Longitudinal waves are disturbances in a medium where the particles oscillate parallel to the direction of wave propagation. The particles undergo compression and rarefaction, moving in the same direction as the wave. Compression refers to the areas of maximum density and pressure, while rarefaction refers to the areas of minimum density and pressure. Longitudinal waves can only propagate through gases and are also known as compression waves. Examples include sound waves, ultrasound, glass vibrations, waves in a slinky, and spring oscillations.
- S Waves:
S waves are body waves that propagate through the Earth's interior. These waves can be compressional or longitudinal and are known as primary waves. S waves resemble vibrations in a gelatin bowl and are felt as the second wave during earthquakes. They contribute to the changing and evolving structure of the Earth's interior over time, a process called differentiation.
Difference between Transverse Waves and Longitudinal Waves
Electromagnetic Waves:
- Electromagnetic waves arise from the interaction between an electric field and a magnetic field. These waves have perpendicular orientations to both the electric and magnetic fields, as well as to each other.
- Electromagnetic waves occur when there are periodic disturbances in the electric and magnetic fields, and they have frequencies within the electromagnetic spectrum.
- One notable characteristic of electromagnetic waves is that they do not require a medium for their propagation. They are transverse in nature and can be polarized.
Properties of Electromagnetic Waves
Here are the key properties of electromagnetic waves:
- The velocity of electromagnetic waves in a vacuum is 3 × 10^8 m/s.
- They can propagate without the need for a medium.
- Electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum.
- They can be polarized and are transverse waves with momentum.
- Electromagnetic waves exhibit interference and diffraction.
- Electric or magnetic fields do not cause deflection of electromagnetic waves.
Examples and Speed of Electromagnetic Waves:
Examples of electromagnetic waves include radio waves, X-rays, microwaves, gamma rays, and thermal radiation. Together, these waves constitute the electromagnetic spectrum. The specific nature of electromagnetic waves depends on their wavelength and frequency, with the behavior being influenced by the refractive index of the medium.
Electromagnetic Spectrum:
Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy emitted and absorbed by charged particles. These radiations exhibit wave-like behavior as they travel through space. They consist of electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to each other and to the direction of wave propagation.
Electromagnetic Spectrum:
Electromagnetic radiation encompasses various types of waves with different frequencies and wavelengths. The electromagnetic spectrum is used to categorize these waves based on their characteristics, applications, and uses. Examples of electromagnetic spectrum waves include radio waves, infrared rays, visible light, and X-rays.
Matter Waves:
Matter waves, also known as De Broglie waves, demonstrate the wave nature of all matter, including atoms and subatomic particles. These waves are associated with very small particles such as electrons. The De Broglie equations describe the dual nature of matter, with the frequency of matter waves directly related to their kinetic energy.
- Surface Waves:
Surface waves possess both mechanical and electromagnetic characteristics. For example, sea diving creatures can generate surface waves, which are also referred to as Rayleigh waves. - Elastic Waves:
Elastic waves are produced by elastic bodies and are associated with the vibratory motion of particles within those bodies. The particles oscillate and return to their original positions, propagating the elastic wave. These waves can propagate through viscoelastic mediums. The study of elastic waves is known as elastodynamics.
|
743 videos|1444 docs|633 tests
|





















