Major Landforms Class 5 Notes SST
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Mountains |

|
| What are Plateaus? |

|
| Understanding Plains |

|
| What are Deserts? |

|
| Rivers |

|
Introduction
- Have you ever wondered what makes our Earth so unique?
- From tall mountains that touch the sky to flat plains where animals roam, our planet is filled with amazing landforms!
- Today, we will explore different types of landforms, like plateaus that rise high above the ground, deserts that are dry and sandy, and much more.
- Each landform has its own special features and secrets.
- Get ready to discover how these natural wonders shape our world and create the beautiful landscapes we see around us!
Mountains
A mountain is defined as a geographical feature that elevates more than 900 meters above the average sea level.

- Mountains cover about 20 per cent of the Earth's land area and are important landforms known for their significant height compared to sea level.
- The elevation and shape of mountains vary, and they are often recognized by their steep slopes.
- The top of a mountain, called the summit or peak, is the highest point, usually shaped like a cone.
- One of the highest peaks in the world is Mount Everest.
- The height and shape of mountains are affected by their age:
1. Younger mountains, such as the Himalayas and the Alps, tend to be tall with pointed peaks.
Older mountains, like the Aravallis and the Appalachians, are generally shorter with rounded tops. - Mountains can connect to form chains or ranges, which are often made up of parallel series extending over long distances.
- Examples of such formations include the Andes in South America and the Rockies in North America.
 Chains of Mountains
Chains of Mountains
Importance of Mountains
Mountains have thin soil and steep slopes, making it hard to farm and leading to fewer people living in these areas. This is mainly because of bad weather, not much flat land, and difficulty getting around. However, mountains also provide many benefits:
- They act as natural barriers against harsh weather, like strong cold and hot winds.
- Rivers that come from mountains provide important water for farming.
- The slopes have rich pasturelands and useful forests.
- Some mountains have plenty of valuable minerals.
What are Plateaus?
A plateau, also known as a tableland, is an elevated area characterized by a level or gently sloping flat top, which sharply ascends from the surrounding terrain.
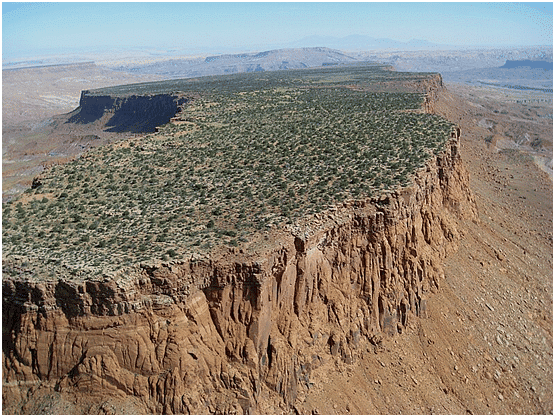 Plateaus represent highland areas characterized by flat surfaces, often dissected by rivers and streams.
Plateaus represent highland areas characterized by flat surfaces, often dissected by rivers and streams.- These elevated landforms can exhibit steep slopes on one or more sides.
- The height of plateaus varies widely, ranging from a few hundred meters to several thousand meters.
- Plateaus are predominantly found in arid regions and are commonly located on the sheltered side of mountain ranges.
- Because of their elevated altitudes, plateaus typically experience cold climates and have short growing seasons.
- Many plateaus feature extensive canyons etched into their surfaces, such as the renowned Grand Canyon situated within the Colorado Plateau.
Types of Plateaus
(a) Deccan Plateau
Located in India, the Deccan Plateau extends for hundreds of kilometres and is renowned for its size and geographical significance.
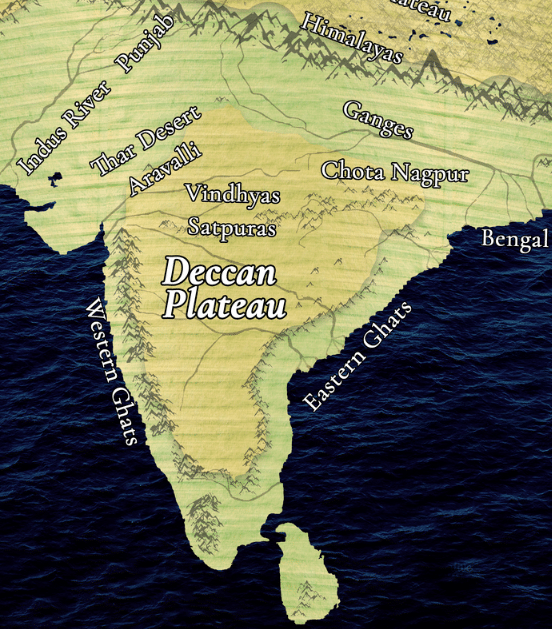 The Deccan Plateau
The Deccan Plateau
(b) Plateau of Tibet
Known as the "roof of the world," the Plateau of Tibet is the highest plateau globally and It is surrounded by mountain ranges on all sides.
(c) East African Plateau
Spanning Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda, the East African Plateau is prominent in the African continent. Australia's Western Plateau is another notable example of a plateau.
Importance of Plateaus
- Plateaus provide grasslands suitable for raising livestock like cattle and sheep.
- Certain plateaus boast abundant mineral deposits, offering opportunities for mining activities.
Understanding Plains
A plain, also known as lowlands, refers to a flat or gently rising land surface that lies at a low elevation. It may exhibit slight hills or remain entirely level, characterized by a gentle slope across the terrain.
 Plains are expansive, flat, and low-lying landforms found across the globe.
Plains are expansive, flat, and low-lying landforms found across the globe.- They are often formed by river deposits, with examples such as the northern plains of India.
- Rivers transport sand, mud, and silt, which gradually settle on their banks, leading to the formation of plains.
Importance of Plains
- Plains have good soil for farming, which is why many ancient civilizations settled near rivers on plains.
- Most big cities and towns are found on plains.
- Building roads, railways, airports, and canals is easier in plains.
What are Deserts?
Deserts are vast areas of land characterized by extremely low levels of rainfall, resulting in a dry climate and very limited vegetation.

- Deserts experience very hot temperatures during the day and significantly cooler temperatures at night.
- They are prone to frequent dust storms, which can affect visibility and impact local ecosystems.
- Sand dunes, hills formed by wind-blown sand, are common features of deserts.
- Due to the scarcity of water, deserts typically have limited vegetation.
Importance of Deserts
- Deserts play a crucial role in maintaining global ecosystems and biodiversity.
- They offer unique habitats for specialized flora and fauna adapted to arid conditions.
- Deserts have cultural significance for indigenous communities that have adapted their lifestyles to thrive in these environments.
- Some deserts contain valuable natural resources, such as minerals and fossil fuels, which contribute to economic activities such as mining.
Rivers
Rivers are natural pathways that transport rainwater or melted ice and snow from mountains to plains, lakes, and seas. They originate as small streams that merge together to form larger watercourses.
 Rivers are natural freshwater channels that flow towards oceans, lakes, seas, or other rivers.
Rivers are natural freshwater channels that flow towards oceans, lakes, seas, or other rivers. - Originating from mountainous regions, rivers carry rainwater, melted ice, and snow as they journey through mountains, plains, and other landscapes.
- They play a vital role in shaping the land.
The journey of a river can be divided into three stages
1. Upper Course
- The river begins in the mountains, where the slopes are steep and the water flow is low.
- As it moves down, it speeds up, creating deep valleys and waterfalls.
- For example, the River Ganga starts at Gangotri and flows all the way to Haridwar.
2. Middle Course
- The river enters the plains, resulting in reduced speed as it flows on a relatively flat surface.
- Meandering and the formation of loops become prominent in this stage.
- River Ganga exemplifies this course between Kanpur and Prayagraj.
3. Lower Course
- The river reaches its lower course, merging with a larger water body, such as a sea.
- The river's speed decreases significantly, causing it to divide into multiple channels.
- The accumulation of sediment forms a triangular-shaped landmass called a delta.
- River Ganga forms a delta as it flows into the Bay of Bengal.
Conclusion
- Understanding major landforms is essential for recognizing the different features of the Earth's surface.
- Mountains, plateaus, plains, deserts, and rivers all play a role in shaping our landscapes.
- Each landform has its own unique characteristics and resources.
- Mountains act as a protective barrier, providing shelter and influencing weather patterns.
- Plains are important for agriculture, offering fertile land for growing crops.
- Plateaus are known for their scenic beauty, often featuring stunning views and unique ecosystems.
- Deserts are characterized by their harsh conditions, which make survival challenging for plants and animals.
- Rivers are vital as they provide water and support life, serving as a resource for drinking, farming, and transportation.
- By exploring and studying these landforms, we can appreciate the amazing variety and complexity of our planet.
|
33 videos|264 docs|50 tests
|
FAQs on Major Landforms Class 5 Notes SST
| 1. What are the main characteristics of mountains? |  |
| 2. How are plateaus different from mountains? |  |
| 3. What defines a desert, and how do they form? |  |
| 4. What are the different types of plains, and how are they created? |  |
| 5. How do rivers contribute to the formation of landforms? |  |
















