Plants Morphology | Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Types of Roots |

|
| Stem |

|
| Leaf Morphology |

|
| Fruit and seeds |

|
Introduction
Morphology is a biological field concerned with studying the forms and characteristics of different plant parts. It focuses on the external structures of plants, such as stems, roots, and leaves.
Roots and Their Functions:
- Roots always grow downward into the soil, away from sunlight.
- They lack green coloration.
- They do not bear leaves, flowers, or fruits.
- The tips of roots are protected by root caps.
Types of Roots
Roots can generally be classified into two categories.
- True or tap root system
- Adventitious roots.
Modification of Tap roots
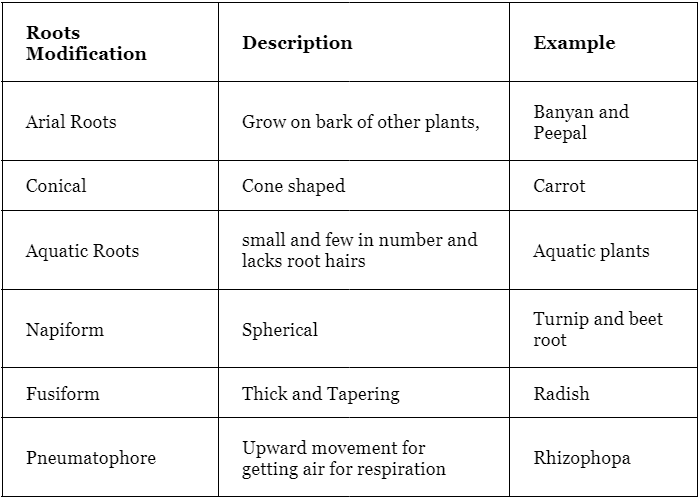
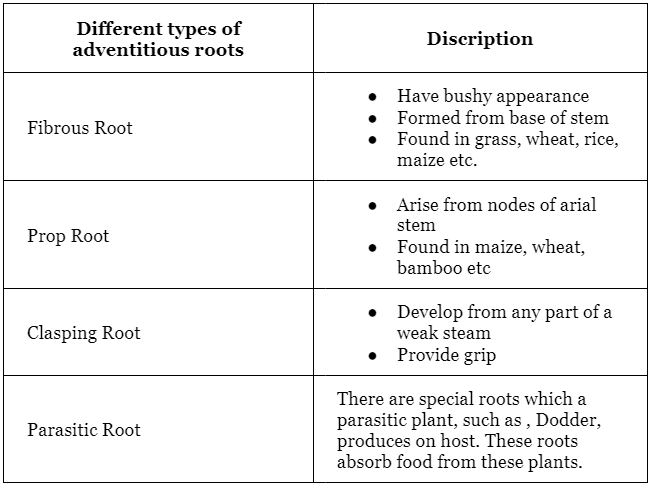
Modification of Adventitious Roots
Stem
- The stem is the part of a plant that grows upward. It can be either herbaceous or woody.
- A herbaceous stem is soft, green, and commonly found in herbaceous plants.
- It develops from the plumule.
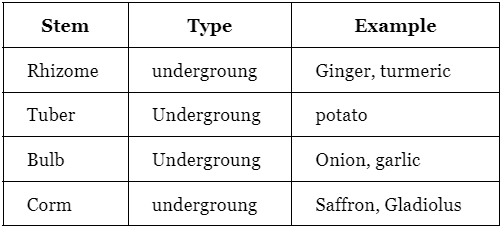
Various Forms of Stems
The stem can undergo different forms of modification, including:
- Suckers.
- Runners.
- Climbers.
- Tubers.
- Rhizomes.
- Tendrils.
- Thorns.
- Cladodes.
Modification of the Stem:
Leaf Morphology
The primary function of leaves is to facilitate photosynthesis. A leaf consists of a leaf base, petiole, and lamina.
- Small leaf-like structures called stipules are present at the base of the leaf.
Leaf Modifications:
Leaves can undergo modifications based on the specific functions they perform. These modifications include:
- Leaf tendrils.
- Spines.
- Storage leaves.
- Insect-catching leaves.
Leaf Functions:
Leaves carry out several important functions, including:
- Photosynthesis.
- Transpiration.
- Storage.
- Guttation.
- Defense.
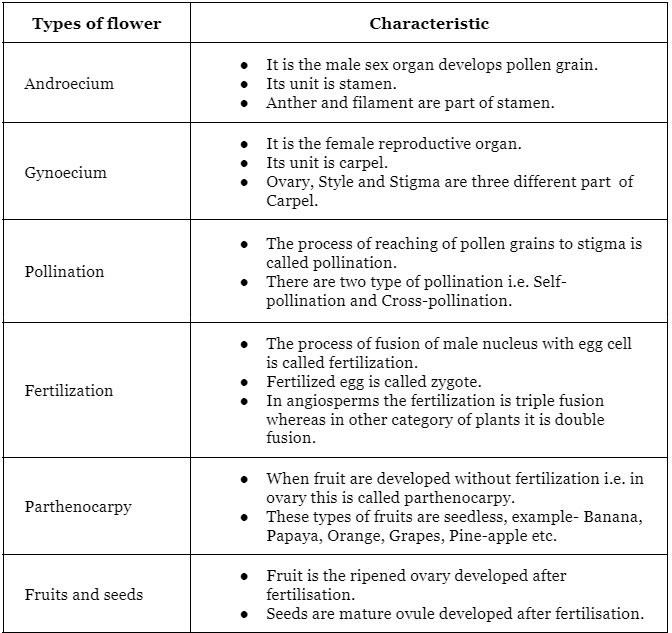
Flower Morphology:
- Flowers serve as the reproductive structures of plants.
- Flowers are typically modified shoots.
The various parts of a flower are as follows:
Fruit and seeds
Fruits are divided into three parts:
- Simple fruits like Banana, Guava etc.
- Aggregate fruits like strawberry, custard apple etc.
- Composite fruits like jackfruit and mulberry
Some fruit and their edible parts: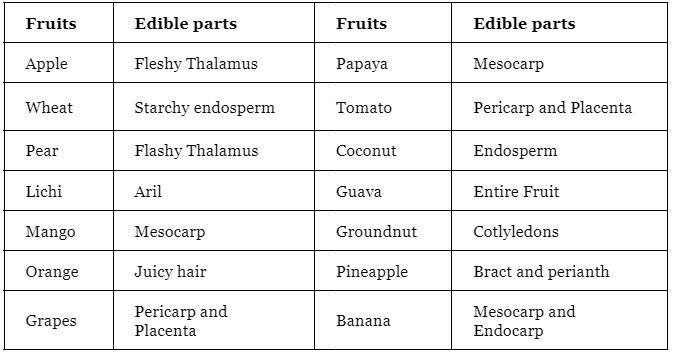
|
744 videos|1444 docs|633 tests
|















