Plant Tissue | Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) PDF Download
Introduction
- All living organisms whether unicellular or multi-cellular are made up of cells.
- Multi-cellular organisms are in a more advantageous position as compared to unicellular organisms as they exhibit division of labour. Different groups of cell perform different specialised functions. The specialisation is achieved due to differentiation, where cells come to have a definite shape, size and function.
- Group of cells having a common origin, similar structure and which work together to perform a common function is known as Tissue.
 A microscopic view of a Scots pine tree (Pinus sylvestris) showing cells of the xylem tissue
A microscopic view of a Scots pine tree (Pinus sylvestris) showing cells of the xylem tissue - The branch of biology, that deals with the detailed study of tissues, is known as Histology.
Plant Tissue
- Both plants and animals have similar life processes. However, they do not have similar types of tissues because of differences in their organisation, growth patterns, mode of living, lifestyle, movement and locomotion.
Plant tissues are of two types:
(i) Meristematic tissues
(ii) Permanent tissues
Meristematic Tissues
- Meristematic tissues are a thin-walled, compactly arranged group of cells that are preparing to divide or are in the process of multiplication or have the potential to divide.
- They are small, spherical or polygonal cells with dense cytoplasm. The nucleus is large and prominent. Vacuoles are absent or very small in number.
Meristematic tissues can be classified on the basis of their position into:
(i) Apical Meristem (root and shoot apex) occurs at the growing tips of stems and roots and increases the length of the stem and the root.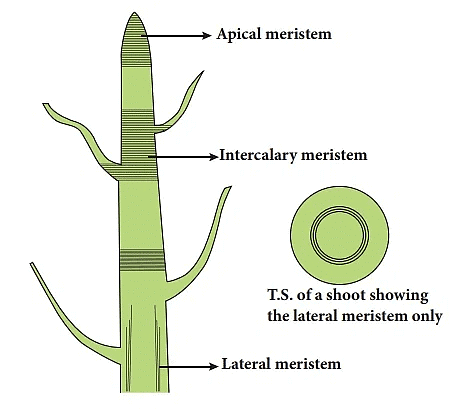 Longitudinal section of shoot apex showing location of meristem and young leaves(ii) Lateral Meristem (cambium, cork cambium) occurs on the sides both in stem and root. It is exclusively present in dicot plants where it increases the girth of stem and root.
Longitudinal section of shoot apex showing location of meristem and young leaves(ii) Lateral Meristem (cambium, cork cambium) occurs on the sides both in stem and root. It is exclusively present in dicot plants where it increases the girth of stem and root.
It is of two main types - Vascular and Cork cambium.
(iii) Intercalary Meristem (internodes) is present at the base of leaves and internodes. It increases the length between the two nodes. It is usually found in monocot plants.
Permanent Tissues
- Permanent tissues are derived from meristematic cells which have lost the ability to divide. They undergo differentiation to perform a particular function.
- Their cells may be living or dead, thin or thick-walled. The thickenings may be regular or irregular.
- There are two main groups of permanent tissues:
(i) Simple Permanent Tissue
(ii) Complex Permanent Tissue
1. Simple Permanent Tissues
A simple tissue is a group of one type of cells which perform the same function.
Simple tissue is classified into three main types:
(a) Parenchyma
- These cells are thin-walled, living, isodiametric cells which form the basic packing tissue of all the plant organs.
- The cells are oval, spherical or polygonal in the outline, that are loosely packed with small and large intercellular spaces in between them. Their primary function is the storage of food.
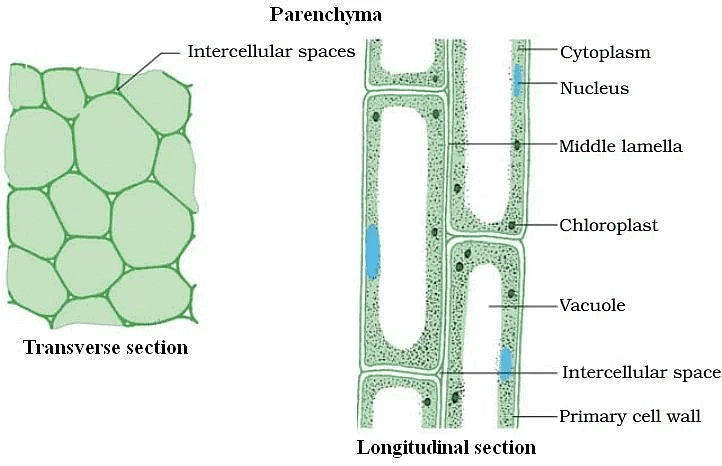 Parenchyma Tissues in Transverse and Longitudinal section
Parenchyma Tissues in Transverse and Longitudinal section - Parenchyma containing chlorophyll is referred to as chlorenchyma which is the seat of photosynthesis.
- In aquatic plants, parenchyma cells are associated walk large air spaces. These air spaces store gases and provide buoyancy to the plants. Such a specialised parenchyma tissue is known as aerenchyma.
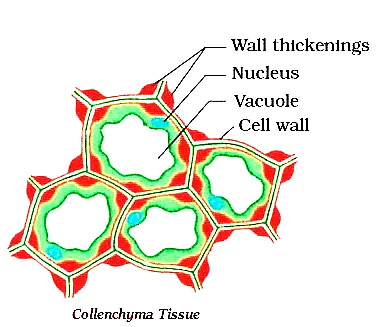
(b) Collenchyma
- These cells are living cells having thickened corners. The uneven thickenings of pectocellulose provide mechanical support and flexibility to plant. Because of collenchyma plant can bend without breaking.
(c) Sclerenchyma
- These cells are usually dead, thick and lignified cells with the narrow lumen.
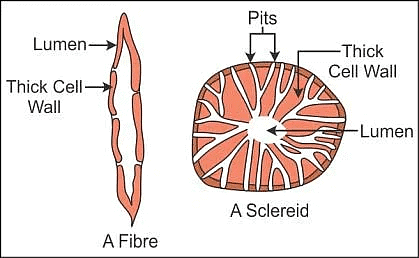 Sclerenchyma Tissue
Sclerenchyma Tissue - Sclerenchyma cells are of two types:
(i) Fibres are elongated spindle-shaped cells pointed at both ends
(ii) Sclereids are short and broad cells which occurs singly or in small groups. - They are also known as stone cells. This tissue provides mechanical support and enables plants to bear various stresses.
Protective tissues constitute an outermost layer of stem, roots, leaves, flowers and fruits. It provides protection against environmental factors and pathogens.
It is of two types namely:
(a) Cork
- Cork is the outer protective tissue of older stem and roots. It is formed by a secondary lateral meristem called cork cambium.
- Cork cambium produces secondary cortex or phelloderm on the inner side and cork or phellem on the outer side.
- Cork cells are rectangular in outline which are compactly arranged and are multilayered. Their walls become impermeable due to the deposition of suberin.
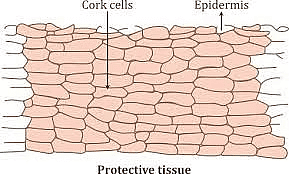
- At certain places they possess small aerating pores called lenticels through which exchange of gases takes place.
- Older cells become dead and are filled with tannins, resins and air.
- Since cork is light, impervious, compressible and non-reactive it is commercially used in the manufacture of sport goods, stoppers for bottles, linoleum, insulation boards and shock absorbers.
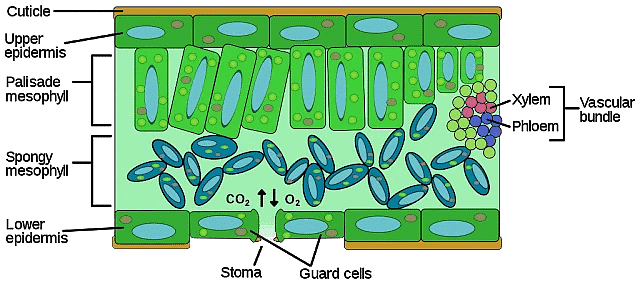
(b) Epidermis
- The epidermis is the outer protective layer of the plant parts that prevent the entry of pathogens and pests.
- Cells of the epidermis are elongated and closely packed. The cells are generally thick on their outer and radial sides and thin-walled on the inner side.
- The outer thick walls are impregnated with an impermeable fatty substance called cutin.
- Generally, the epidermis is single-layered and is discontinuous at certain places as it is interrupted by small pore-like structures called stomata. In xerophytes, the epidermis is multilayered to prevent transpiration.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Transpiration is the process of loss of excess water in the form of vapours through stomata.
- Epidermal cells of root bear long hair-like projections called root hair. Root hairs increase the absorptive surface area thereby facilitates increased absorption of water and minerals from the soil.
- In many plants, the aerial surface also bears cutinised hair over their epidermis. They are called trichomes. Trichomes may be glandular or non-glandular in nature. It produces an insulating stationary layer of air on the surface.
2. Complex Permanent Tissues
Complex permanent tissues are made up of more than one type of cells. All these cells coordinate to perform a common function.
Complex tissue is classified into two main types:
(a) Xylem
- Xylem is a complex permanent plant tissue which plays an important role in the conduction of water and minerals from the soil to the various plant parts via roots.
- Xylem consists of four types of elements:
(i) Tracheids
(ii) Vessels
(iii) Xylem fibres
(iv) Xylem parenchyma.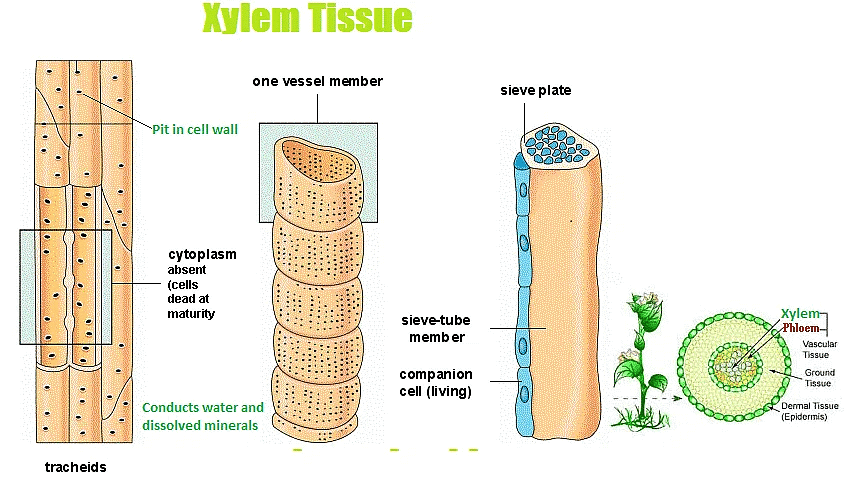
- Tracheids, vessels and xylem fibres are dead cells whereas xylem parenchyma is living.
- Vessels and tracheids are the tracheary elements of xylem which occur in flowering plants. Tracheids are abundant in lower plants (Pteridophytes and Gymnosperms) while vessels are found in angiosperms.
- Tracheids are long tubular dead cells with lignified walls, wide lumen and tapering end. There are certain unthickened areas called pits on the thick lignified walls which help in the movement of water from one tracheid to another.
- Vessels are long tubes which are formed by the end to end union of a large number of dead cells. The walls are lignified and possess pits.
- Xylem parenchyma stores food while xylem fibres provide mechanical support.
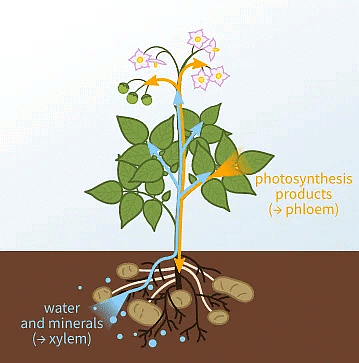 Working of Xylem and Phloem in plant
Working of Xylem and Phloem in plant
(b) Phloem
- Phloem is the conducting tissue which translocates food manufactured in leaves to other parts of the plant.
- Cells of phloem are living and consists of four tracheary elements namely — phloem sieve tubes and sieve cells, companion cells for short-distance transport, parenchyma for storage and phloem fibres for mechanical support.
|
743 videos|1444 docs|633 tests
|
















