UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 17th July 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Shelf cloud

Why in News?
Massive ‘shelf cloud’ formation was spotted in Haridwar, Uttarakhand recently.
Background:-
- Video featuring clouds that resemble a majestic snow-covered mountain has sparked curiosity about this extraordinary weather phenomenon.
About Shelf Cloud:-
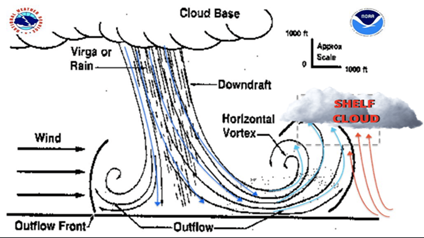
- Shelf clouds are a type of Arcus cloud characterized by a low-lying, horizontal formation.
- Arcus cloud: a low, horizontal cloud formation, usually appearing as an accessory cloud to a cumulonimbus.
- They appear as a wedge-shaped structure beneath the main cloud base and typically form on the leading edge of a storm.
- They resemble a shelf hanging from the sky.
- It is a wide, low cloud that appears before a big storm.
- They are usually dark and ominous-looking due to the condensation and the presence of rain or hail within the storm.
- Shelf clouds produced by thunderstorms are always preceded by a rush of dry and cold air ahead of the cloud, with rain arriving after the shelf cloud has passed overhead.
Formation of shelf clouds:-
- Shelf clouds are formed when a mass of cold, dense air forcefully interacts with a warmer air mass.
- When warm, moist air is lifted rapidly by an advancing thunderstorm or cold front Shelf clouds are formed.
Safety concerns:-
- Shelf clouds are typically found in conjunction with thunderstorms, which can bring strong winds, heavy rainfall, and lightning.
- Their presence often suggests the potential for severe weather conditions, prompting the need for caution and preparedness.
Source: The Hindu
What is Namda Art?

Why in News?
The Namda craft of Kashmir is being successfully revived under a Skill India’s Pilot Project as part of the Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY), with nearly 2,200 candidates from across six districts of the state, receiving training in the dying art form.
About Namda Art:
- It is said to have begun in the 16th century when Mughal Emperor Akbar wanted to get a covering for his horses to protect them from the cold.
- It was introduced by a Sufi saint named Shah-e-Hamdan to Kashmiris.
- Namda is a type of traditional Kashmiri felted carpet that is created using sheep wool and has colourful hand embroidery.
- The distinct feature of this Kashmiri craft is that wool is felted and not woven.
- How it is made?
- It is usually a sandwich of many layers of wool flattened over each other.
- After a layer is spread, it is sprinkled homogeneously with water and pressed with a tool known as ‘pinjra’ (woven willow wicker).
- Unique themes and floral patterns provide the themes for these masterpieces and flowers and leaves, buds and fruits are the essence of the designs.
- It is practised as a craft in several cultures, especially in the countries throughout Asia, viz. Iran, Afghanistan and India.
Source: PIB
GS-II
UN Human Rights Council (UNHRC)

Why in News?
Recently, India voted in favour of a draft resolution tabled in the UN Human Rights Council (UNHRC) condemning “public and premeditated” acts of desecration of the Holy Quran.
Background:-
- UN Human Rights Council adopted the draft resolution ‘Countering religious hatred constituting incitement to discrimination, hostility or violence’, with 28 members voting in favour, seven abstentions and 12 nations voting against.
- The resolution was strongly opposed by the United States and the European Union, who say it conflicts with their view on human rights and freedom of expression.
About UN Human Rights Council (UNHRC):-
- It is an inter-governmental body within the United Nations system.
- Objective: it is responsible for strengthening the promotion and protection of human rights around the world.
- Establishment: 2006.
- The Council was created by the United Nations General Assembly in 2006.
- It replaced the former United Nations Commission on Human Rights.
- HQ: Geneva, Switzerland.
Membership:-
- Current members: 47 Member States.
- These are elected by the majority of members of the General Assembly of the United Nations through direct and secret ballots.
- The Council’s Membership is based on equitable geographical distribution.
- Seats are distributed as follows:
- African States: 13 seats
- Asia-Pacific States: 13 seats
- Latin American and Caribbean States: 8 seats
- Western European and other States: 7 seats
- Eastern European States: 6 seats
- The term of each seat is three years.
- No member may occupy a seat for more than two consecutive terms.
India and UN Human Rights Council:-
- 2019: India was elected to the Council for a period of three years.
- 2020: India’s National Human Rights Commission submitted its mid-term report to the Council as a part of the third round of the Universal Periodic Review (UPR) process.
- 2021: India was re-elected to the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC) for the 2022-24 term.
- It vowed to continue to work for the promotion and protection of human rights through “Samman, Samvad and Sahyog”.
Source: The Hindu
UK signs CPTPP Trade Deal
Why in News?
The UK has formally signed the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP), a major Indo-Pacific trade deal.
- Joining the bloc is seen as the UK’s biggest trade deal since leaving the European Union.
What is CPTPP?
- The CPTPP, established in 2018, reduces trade barriers among 11 countries, including Australia, Canada, Japan, Mexico, and Vietnam.
- Objectives of CPRPP include-
- Tariff Reduction and Market Opening: The agreement requires countries to eliminate or significantly reduce tariffs and make commitments to open services and investment markets.
- Addressing Competition and Intellectual Property: The CPTPP includes rules on competition, intellectual property rights, and protections for foreign companies.
- Expanding Membership: While the CPTPP aims to counter China’s regional dominance, China and other countries such as Taiwan, Ukraine, Costa Rica, Uruguay, and Ecuador have applied to join.
Importance of CPTPP for the UK
- Cutting Tariffs and Expanding Trade: The UK government anticipates reduced tariffs for UK exports to Asia Pacific countries. Joining the CPTPP expands trade opportunities, as the bloc represents 15% of global trade and a combined GDP of £12 trillion.
- Post-Brexit Trade Strategy: After leaving the EU, the UK seeks to deepen trade ties with the Pacific region through its “Global Britain” strategy.
- Seeking Faster-Growing Economies: The UK aims to establish trade deals with countries and blocs with faster-growing economies than the EU, given limitations in achieving agreements with major powers like China and the United States.
Challenges and Criticisms
- Economic Impact of Brexit: Critics argue that trade deals like the CPTPP will struggle to compensate for the economic damage caused by leaving the EU, which remains the UK’s largest trading bloc.
- Long-Term Productivity Forecast: Brexit is projected to reduce the UK’s long-term productivity by 4%, according to the Office for Budget Responsibility.
- Existing Trade Deals and Economic Boost: The UK already has trade deals with most CPTPP members, and the projected economic boost from joining the agreement is relatively modest at 0.08% annually.
Recent Developments
- Information Gathering Process: CPTPP members are assessing aspiring economies’ ability to meet the bloc’s high standards as part of the decision-making process for future membership.
- Collective Decision-Making: The decision on new members and the timeline for their inclusion will be made collectively by existing CPTPP participants.
Source: Indian Express
Black Sea Grain Initiative
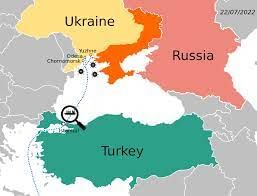
Why in News?
The Black Sea grain deal is set to expire on July 17.
- Russia has not agreed to renew the deal, citing unmet promises and difficulties in its own agricultural exports due to Western sanctions.
Black Sea Grain Initiative
- The Initiative eased Russia’s naval blockade and saw the reopening of three key Ukrainian ports.
- The UN and Turkey brokered the deal in July 2022, allowing cargo ships to travel between Ukrainian ports and undergo inspections to ensure they were not carrying arms.
- The deal has been extended twice but is set to expire on July 17, 2023.
- The agreement created procedures to safely export grain from certain ports to attempt to address the 2022 food crisis.
- It provides a safe maritime humanitarian corridor for Ukrainian exports (particularly for food grains) from three of its key ports, namely, Chornomorsk, Odesa and Yuzhny/Pivdennyi in the Black Sea.
Outcomes of this deal
- Approximately 9.8 million tonnes of grains have been shipped so far since the deal was brokered.
- People hoarding the grain in the hope of selling it for a sizable profit owing to the supply crunch were now obligated to sell.
- The initiative has also been credited for having made a huge difference to the global cost of living crisis.
Why was this deal launched?
- Ukraine’s Role: Ukraine is a significant exporter of foodgrains, including wheat and corn, and contributes to the UN’s food aid programs.
- Impact of Russian Invasion: Russia’s invasion and blockade of Ukrainian ports raised concerns about food security and soaring prices globally.
Russia’s Opposition and Reasons
- Claims of Unmet Promises: Russia argues that promises made under the deal have not been fulfilled, affecting its own agricultural exports and fertilizers due to Western sanctions.
- Obstacles to Agricultural Exports: Russia faces challenges with payment platforms, insurance, shipping, and logistics, even though there are no direct restrictions on its agricultural products.
- Frustration and Goodwill: Russian President expressed frustration and stated that Russia has shown goodwill in extending the deal but feels enough is enough.
- Shift in Grain Destinations: Russia claims the deal was meant to ensure global food security, but Ukraine has mainly exported to high- and middle-income countries, while the UN notes that food prices have cooled down, benefiting poorer nations.
Impact on Grain Exports and Production
- Russian Wheat Export Dominance: Russia remains the world’s top wheat exporter, primarily targeting the Middle East, North Africa, and Central Asia.
- Ukraine’s Declining Shipments: Ukraine’s grain shipments are projected to more than halve, with production at an 11-year low.
- Shifting Markets: Ukraine’s grain markets have shifted from Asia and North Africa to Europe, driven by ease of shipment, causing a glut of Ukrainian grain and protests from farmers in Eastern European countries.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
What is Measles?
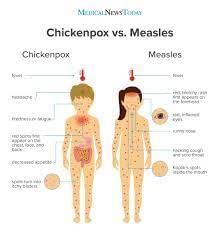
Why in News?
Recently, the UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) warned that London is standing at risk of a major measles outbreak.
About Measles:
- It is a highly contagious and serious airborne disease.
- It is caused by a virus in the paramyxovirus family, and is normally passed through direct contact and the air.
- The virus infects the respiratory tract, then spreads throughout the body, causing severe disease, complications and even death.
- Symptoms
- The first sign of measles is usually high fever, beginning about 10 to 14 days after exposure to the virus and lasting four to seven days.
- A runny nose, cough, red and watery eyes, and small white spots inside the cheeks can develop in the initial stage.
- A rash erupts after several days, usually on the face and upper neck. The rash spreads over about three days, eventually reaching the hands and feet, and lasts five to six days before fading.
- Who is at risk?
- Any non-immune person (not vaccinated or vaccinated but did not develop immunity) can become infected.
- Unvaccinated young children and pregnant persons are at highest risk of severe measles complications.
- Treatment: No specific antiviral treatment exists for measles.
- Criteria for Measles elimination:
- Measles elimination is defined as the absence of endemic measles virus transmission in a region or other defined geographical area for more than 12 months.
- Conversely, a country is no longer considered to be measles free if the virus returns and transmission is sustained continuously for more than a year.
- Measles & Rubella Initiative (M&RI):
- M&RI is a partnership formed in 2001 of the American Red Cross, CDC, the United Nations Foundation, UNICEF and World Health Organization (WHO)
- It is committed to achieving the Global Vaccine Action Plan goal of measles and rubella elimination in at least five WHO regions by 2020.
Source: Hindustan Times
India Government Mint

Why in News?
Recently, the 120th anniversary of the Indian Government Mint was celebrated in Hyderabad with commemorative souvenir coins.
Background:-
- These souvenir coins were crafted of silver, copper, and serve as a tribute to the rich legacy and contributions of the Indian Government Mint in the field of coinage and minting.
- Security Printing and Minting Corporation of India Ltd (SPMCIL) Chairman and Managing Director SK Sinha released the commemorative coins.
About Security Printing and Minting Corporation of India Ltd (SPMCIL)
- It is a wholly owned Schedule ‘A’ Miniratna Category-I company of t Government of India.
- Establishment: 2006.
- Ministry: Ministry of Finance.
- Objectives To be a leader in the manufacturing of currency, coins and security products through process excellence and innovation.
- Functions::-
- Conducting printing and minting activities of the Government of India.
- Developing state-of-art currency, coins and diversified security products in a transparent, cost-effective and efficient manner.
- Constantly focusing on benchmarking, process automation, applied R & D, indigenization and the triple bottom line people, planet and profit.
- Ensuring Employees, Customers and Stakeholders’ delight.
- Production of Currency and Bank Notes, Security Paper, Non-Judicial Stamp Papers, Postal Stamps & Stationery.
- It also includes producing Travel Documents viz. Passport and Visa, Security certificates, Cheques, Bonds, Warrants, Special Certificates with security features, Security Inks, Circulation & Commemorative Coins, Medallions, Refining of Gold & Silver, and Assay of Precious Metals.
About India Government Mint:-
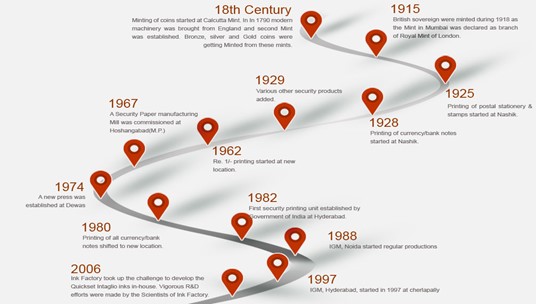
- India Government Mints (IGM) the units of Security Printing and Minting Corporation of India Ltd (SPMCIL).
- There are four such units:-
- India Government Mints (IGM) Mumbai: it was established in 1829, and is one of the oldest mints in India.
- India Government Mints (IGM) Hyderabad: The present mint started in 1997 at Cherlapally.
- India Government Mints (IGM) Kolkata: The new mint was established in 1952 and became a unit of SPMCIL during corporatization in 2006.
- India Government Mints (IGM) Noida: it is the only Mint established in the post-independence era.
- IGMs offer a comprehensive range of services covering every stage of the minting process – from planning to the finished products.
- They utilize advanced technology, innovation, quality and reliable delivery methods.
- They strictly follow global laboratory standards.
Source: PIB
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|

















