UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 23rd July 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| GS-I |

|
| About Cam ranh bay: |

|
| GS-II |

|
| About Section 498A of IPC: |

|
| GS-III |

|
| What is a loan-loss provision? |

|
GS-I
Cam Ranh Bay

Why in News?
Indian Naval Ship Kirpan will soon be handed over to Vietnam People’s Navy (VPN) at the strategic military port of Cam Ranh Bay.
About Cam ranh bay:
- Location: Cam Ranh Bay is a deep-water bay located in Khánh Hòa Province, Vietnam, on the South China Sea.
- Size: It is approximately 20 miles (32 km) long from north to south and up to 10 miles (16 km) wide.
- Depth: The bay is up to 164 feet (50 m) deep, making it one of the deepest natural harbours in Southeast Asia.
- Facilities: The port has two main piers, one for general cargo and one for oil tankers. It also has a number of other facilities, including a repair yard, a fuel depot, and a container terminal.
- It is a major refuelling and repair station for ships in the South China Sea.
- Historical Significance:
- During the colonial era, it was controlled by the Champa Kingdom and later became part of the Vietnamese territories.
- In the 19th century, the French established a major military presence in the bay.
- During the Vietnam War, Cam Ranh Bay gained significant importance as a strategic military base for both the United States and South Vietnam. The United States constructed extensive facilities, including an airbase and a deep-water port, to support its military activities during the war.
- Following the end of the Vietnam War in 1975, Cam Ranh Bay came under the control of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam.
- The Soviet Union subsequently leased the former American facilities and established a major naval base there.
- The Soviet Navy maintained a presence in Cam Ranh Bay throughout the Cold War until the early 2000s.
Key facts about INS Kirpan:
- It is an indigenously-built in-service missile Corvette.
- It is a Khukri class missile corvette commissioned into the Navy on January 12, 1991.
- Features:
- It has a displacing capacity of close to 1,400 tonnes.
- It is capable of a speed of more than 25 knots.
- The Khukri class are equipped with Diesel Engines assembled in India.
- The ship is fitted with a medium-range gun, 30 mm close-range guns, chaff launchers, and surface-to-surface missiles.
- It performs a wide variety of roles, including coastal and offshore patrol, coastal security, surface warfare, anti-piracy, and Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) operations.
Source: The Hindu
GS-II
National Commission for Women

Why in News?
National Commission for Women (NCW) has condemned the incident of Manipur where women were paraded naked.
About NCW:
- It was set up as statutory body in 1992 under the National Commission for Women Act, 1990.
- It aims to review the Constitutional and Legal safeguards for women; recommend remedial legislative measures; facilitate redressal of grievances and advise the Government on all policy matters affecting women.
- The Commission shall consist of:
- A Chairperson, nominated by the Central Government.
- Five Members with expertise in law and issues related to women, nominated by the Central Government.
- At least one Member each shall be from amongst persons belonging to the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes respectively
- Member Secretary must be a central gazetted officer having management and sociological expertise and nominated by the Central Government.
- The National Commission for Women submits all its reports to the Central Government, which is laid before the Parliament during sessions.
- During the investigation of any matter before it, National Commission for Women has all the powers of a civil court.
Functions:
- Inquiry, Investigation and Examination of matters related to safeguards of women.
- Recommendation: to the Union as well State regarding improving the conditions of the women.
- Review different laws related to women and suggest amendments to them.
- Violation Cases: Takes up violation cases pertaining to the provisions of the Constitution and other laws related to women.
- Suo-Moto Notice on matters pertaining to deprivation of women’s rights, non-implementation of laws, non-compliance policy decisions related to women etc.
- Research: Undertake promotional and educational research to find ways to represent women in all spheres of life and improve their efficiency.
- Planning: Participate in the process of planning related to the socio-economic development of women.
- Progress Evaluation: Evaluate the progress related to the development of women in the State and the Union.
- Inspection: Inspect the jail, remand homes etc., where women are kept as prisoners.
- Funding Litigations relating to funds affecting large women body.
Major limitations of National Commission for Women making it toothless:
- Not concrete powers: The NCW is only recommendatory and has no power to enforce its decisions.
- Often it acts only if the issues are brought to light.
- Unreported cases of oppression and suppression of women are not attended to.
- Legal powers: Commission lacks constitutional status, and thus has no legal powers to summon police officers or witnesses.
- In addition, it has no power to take legal actions against the Internal Complaint Committees that prevent grievance redressal of women facing harassment.
- Less funding: NCW’s functions are dependent on the grants offered by the central government.
- Financial assistance provided to the Commission is very less to cater to its needs.
- Political interference: It does not have the power to choose its own members.
- The power-selecting members is vested with the Union government leading to political interference at various levels.
Government efforts for the protection and welfare of women
Constitutional provisions
- Fundamental rights: It guarantees all Indians the right to equality (Article 14), no discrimination by the State based on gender (Article 15(1)), and special provisions to be made by the State in favour of women (Article 15(3)).
- Fundamental Duties: It ensures that practices derogatory to the dignity of women are prohibited under Article 51 (A).
Legislative Framework:
- Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act, 2005
- The Dowry Prohibition Act, 1961
- The Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition, and Redressal) Act, 2013
- The Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO), 2012
Way Forward: Suggestive measures
- Amending NCW Act: Women’s role is continuously expanding in today’s India and the expansion of the role of the NCW is the need of the hour.
- Further, the State Commissions must also widen their ambit.
- Increasing Minimum Age for Marriage: The age of marriage of daughters is being attempted to be raised to 21 years so that marriage at an early age does not hinder the education and career of daughters.
- Addressing Violence against Women (Violence against Women): Women’s violence remains a barrier to attaining equality, development, and peace, as well as the realization of women and girls’ human rights.
- Overall, the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) goal of “leaving no one behind” cannot be realized without ending violence.
Source: The Hindu
Section 498A of IPC

Why in News?
The High Court of Karnataka recently set aside the conviction of a 46-year-old man under Section 498A of the Indian Penal Code (IPC) as the complaint was by his ‘second wife’, which would make the marriage ‘null and void’.
About Section 498A of IPC:
- It deals with the criminal offense of "cruelty by husband or relatives of husband" towards a married woman.
- This section was introduced in 1983 as an amendment to the IPC to address the growing concern of domestic violence and harassment faced by married women in India.
- Under Section 498-A IPC, a husband or his relatives can be sentenced to a jail term of three years for subjecting the wife to cruelty.
- The section applies to married women only.
- Section 498A of IPC reads as “Whoever, being the husband or the relative of the husband of a woman, subjects such woman to cruelty shall be punished with imprisonment for a term which may extend to three years and shall also be liable to fine”.
- For the purposes of this section, 'cruelty' means:—
- any wilful conduct which is of such a nature as is likely to drive the woman to commit suicide or to cause grave injury or danger to life, limb or health (whether mental or physical) of the woman; or
- harassment of the woman where such harassment is with a view to coercing her or any person related to her to meet any unlawful demand for any property or valuable security or is on account of failure by her or any person related to her to meet such demand."
- The term “cruelty” is comprehensive, encompassing various forms of abuse that can be inflicted upon a married woman.
- Bail under Section 498A:
- Section 498A of the Indian Penal Code, enacted in 1860, is a non-compoundable and cognizable offence.
- Bail under Section 498A can only be granted by the Magistrate once a First Information Report (FIR) has been registered by the police based on a complaint filed by the aggrieved party.
- The Supreme Court has ruled that Section 498A should be used sparingly and only in cases where there is genuine evidence of cruelty.
- The court has also ruled that the section should not be used as a tool to settle personal scores.
- Other Indian laws to help curb the instances of violence against women are,
- Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act, 2005 (PWDVA);
- Dowry Prohibition Act, 1961;
- Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition, and Redressal) Act, 2013;
- Indian Penal Code (IPC) Amendments: Various amendments to the IPC have been made to address violence against women, including:
- Section 376: Dealing with punishment for rape, with stricter provisions for different types of rape offenses.
- Section 354: Addressing criminal assault or use of criminal force against women with intent to outrage her modesty.
- Section 354A: Dealing with sexual harassment and punishment for the same.
- Section 354D: Criminalizing stalking and providing punishment for the offense.
- Section 509: Dealing with words, gestures, or acts intended to insult the modesty of a woman.
- Criminal Law (Amendment) Act, 2013: This act was passed in response to the Nirbhaya case and brought significant changes to laws dealing with sexual offenses. It included provisions for stricter punishments for rape, gang rape, and acid attacks, among others.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
DPT3 Vaccine
Why in News?
Recent reports claimed that India recorded all-time high DPT3 immunisation coverage in 2022.
Background:-
- The coverage rate for DPT3 vaccines (diphtheria, pertussis, and tetanus) in India reached an all-time high of 93% in 2022, surpassing the pre-pandemic record of 91% in 2019.
- This significant increase from the 85% coverage in 2021 was reported by the World Health Organization (WHO).
About DPT3 Vaccine:-
- DPT3 vaccines refer to a combination vaccine that provides protection against three infectious diseases: diphtheria, pertussis (whooping cough), and tetanus. (‘ZyCov-D’ vaccine)
- Naming: The “DPT” in DPT3 stands for the initials of these three diseases.
- Diphtheria: a bacterial infection that primarily affects the respiratory system.
- Effects: It can cause severe throat and nose congestion, difficulty breathing, and in severe cases, it can lead to heart and nerve damage.
- Pertussis (Whooping Cough): a highly contagious respiratory infection caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis.
- Symptoms: It is characterized by severe coughing fits, often accompanied by a “whooping” sound when gasping for breath.
- Pertussis can be particularly dangerous for infants and young children.
- Tetanus: a bacterial infection caused by the bacterium Clostridium tetani.
- It enters the body through wounds or cuts and produces a toxin that affects the nervous system, leading to muscle stiffness and spasms, particularly in the jaw and neck muscles.(Nation’s first mRNA-based vaccine)
Dosage of DPT3 vaccines:–
- The primary dose of DPT is provided as part of the pentavalent vaccine.
- Pentavalent vaccine: a combination vaccine with five individual vaccines conjugated into one.
- Two booster doses are given at 16 -24 months and 5-6 years, respectively.
Source: The Hindu
Expected Credit Loss (ECL) Framework
Why in News?
Private sector lender ICICI Bank recently said the bank is ready to move to an expected credit loss (ECL) framework for provisioning.
What is a loan-loss provision?
- The RBI defines a loan loss provision as an expense that banks set aside for defaulted loans.
- Banks set aside a portion of the expected loan repayments from all loans in their portfolio to cover the losses either completely or partially.
- In the event of a loss, instead of taking a loss in its cash flows, the bank can use its loan loss reserves to cover the loss.
- The level of loan loss provision is determined based on the level expected to protect the safety and soundness of the bank.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently proposed to move the banking system to an expected credit loss-based provisioning approach from an “incurred loss” approach.
What is the Expected Credit Loss (ECL) regime?
- Under this practice, a bank is required to estimate expected credit losses based on forward-looking estimations rather than wait for credit losses to be actually incurred before making corresponding loss provisions.
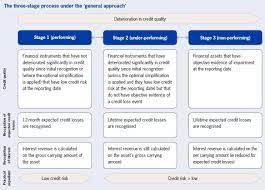
- As per the proposed framework, banks will need to classify financial assets (primarily loans) as Stage 1, 2, or 3, depending on their credit risk profile, with Stage 2 and 3 loans having higher provisions based on the historical credit loss patterns observed by banks.
- Thus, through ECL, banks can estimate the forward-looking probability of default for each loan, and then by multiplying that probability by the likely loss given default, the bank gets the percentage loss that is expected to occur if the borrower defaults.
- This will be in contrast to the existing approach of incurred loss provisioning, whereby step-up provisions are made based on the time the account has remained in the Non-Performing Asser (NPA) category.
- Benefits of the ECL regime:
- It will result in excess provisions as compared to a shortfall in provisions, as seen in the incurred loss approach.
- It will further enhance the resilience of the banking system in line with globally accepted norms.
What is the problem with the incurred loss-based approach?
- It requires banks to provide for losses that have already occurred or been incurred.
- The delay in recognizing loan losses resulted in banks having to make higher levels of provisions which affected the bank's capital. This affected banks’ resilience and posed systemic risks.
- The delays in recognizing loan losses overstated the income generated by the banks, which, coupled with dividend payouts, impacted their capital base.
Source: PIB
Airbus C295 aircraft
Why in News?
As per recent announcements, the first C-295 transport aircraft manufactured by Airbus for the Indian Air Force is scheduled to be delivered in September 2023.
Background:-
- 16 aircraft would come in fly-away condition, manufactured at the Airbus facility in Seville, Spain, and 40 would be manufactured in India by Airbus jointly with Tata.
About Airbus C-295 aircraft:-
- Airbus C295 is a new-generation tactical airlifter in the light and medium segment. (U C-295 aircraft deal)
- It conducts multi-role operations worldwide under all weather conditions.
- It is fully certified and routinely operates day and night in combat missions in all weather extremes, from desert to maritime environments, from extremely hot to extremely cold temperatures.
- Missions and operations: The robustness and versatility of the C295 make it the ideal platform for any type of military or civic operations for the benefit of society.
Features Airbus C-295 aircraft:-
- The aircraft, with a flight endurance of up to 11 hours.
- It can carry out multi-role operations under all weather conditions. ( Induction of C-295MW in Indian Air Force (IAF))
- It can routinely operate day as well as night combat missions from desert to maritime environments.
- It has a rear ramp door for quick reaction and para-dropping of troops and cargo.
- Short take-off/land from semi-prepared surfaces is another of its features.
Replacement:-
- It will replace the Indian Air Force’s ageing fleet of Avro-748 planes.
- Avro-748 planes: are a British-origin twin-engine turboprop, military transport and freighter.
Source: The Hindu
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|