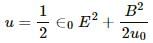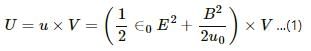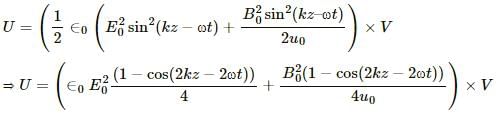Short Answers
Q.1. In a microwave oven, the food is kept in a plastic container and the microwaves is directed towards the food. The food is cooked without melting or igniting the plastic container. Explain.
The natural frequency of water matches the frequency of microwave. This is the reason that food containing water gets cooked. The natural frequency of the plastic container does not match the frequency of microwave. So, the plastic container is not damaged.
Q.2. A metal rod is placed along the axis of a solenoid carrying a high-frequency alternating current. It is found that the rod gets heated. Explain why the rod gets heated.
The magnetic field along the axis of a solenoid carrying a high-frequency alternating current changes continuously. Due to the change in the magnetic field, e.m.f (or eddy current) is induced in the metal rod. There will be flow of charge due to the induced e.m.f. The direction of the induced e.m.f changes very frequently due to the high-frequency alternating current in the solenoid. Thus, the rod gets heated up due to the flow of charge in it.
Q.3. Can an electromagnetic wave be deflected by an electric field or a magnetic field?
No, an electromagnetic wave cannot be deflected by an electric field or a magnetic field. This is because according to Maxwell's theory, an electromagnetic wave does not interact with the static electric field and magnetic field. Even if we consider the particle nature of the wave, the photon is electrically neutral. So, it is not affected by the static magnetic and electric fields.
Q.4. A wire carries an alternating current i = i0 sin ωt. Is there an electric field in the vicinity of the wire?
When an alternating current passes through a conductor, the changing magnetic field create a changing electric field outside it. An electromagnetic field is radiated from the surface of the conductor. There is a time-varying electric field outside the conductor. Hence, there is a time-varying electric field in the vicinity of the wire.
Q.5. A capacitor is connected to an alternating-current source. Is there a magnetic field between the plates?
When an alternating-current source is connected to a capacitor, the electric field between the plates of the capacitor keeps on changing with the applied voltage. Due to the changing electric field, a magnetic field exists in between the plates of the capacitor.
Q.6. Can an electromagnetic wave be polarised?
An electromagnetic wave is a transverse wave; thus, it can be polarised. An unpolarised wave consists of many independent waves, whose planes of vibrations of electric and magnetic fields are randomly oriented. They are polarised by restricting the vibrations of the electric field vector or magnetic field vector in one direction only.
Q.7. A plane electromagnetic wave is passing through a region. Consider (a) electric field (b) magnetic field (c) electrical energy in a small volume and (d) magnetic energy in a small volume. Construct the pairs of the quantities that oscillate with equal frequencies.
Let the electromagnetic wave be propagating in the z-direction. The vibrations of the electric and magnetic fields are given by:
Ex= E0 sin (kz – ωt)
By= B0 sin (kz – ωt)
Let the volume of the region be V.
The angular frequency of the vibrations of the electric and magnetic fields are same and are equal to ω. Therefore, their frequency,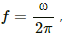 is same.
is same.
The electrical energy in the region,
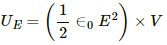
It can be written as :
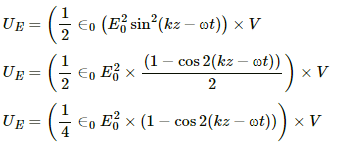
The magnetic energy in the region,
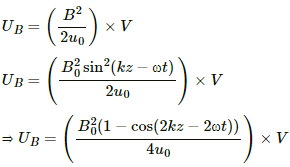
The angular frequency of the electric and magnetic energies is same and is equal to 2ω.Therefore, their frequency, 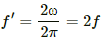 , will be same.
, will be same.
Thus, the electric and magnetic fields have same frequencies and the electrical and magnetic energies will have same frequencies.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 40: Electromagnetic Waves- 1
Try yourself:A magnetic field can be produced by
Explanation
According to Ampere-Maxwell's Law, a magnetic field is produced due to the conduction current in a conductor and the displacement current. The conduction current is actually the motion of the charge. The displacement current is due to the changing electric field. The displacement current is given by 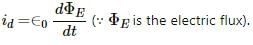
Thus, the magnetic field is produced by the moving charge as well as the changing electric field.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 40: Electromagnetic Waves- 1
Try yourself:A compass needle is placed in the gap of a parallel plate capacitor. The capacitor is connected to a battery through a resistance. The compass needle
Explanation
The compass needle deflects due to the presence of the magnetic field. Inside the capacitor, a magnetic field is produced when there is a changing electric field inside it. As the capacitor is connected across the battery, the charge on its plates at a certain time t is given by :
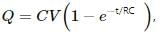
where
Q = charge developed on the plates of the capacitor
R = resistance of the resistor connected in series with the capacitor
C = capacitance of the capacitor
V = potential difference of the battery
The time constant of the capacitor is given, τ = RC
The capacitor keeps on charging up to the time τ. The development of charge on the plates will be gradual after t = RC. The change in electric field will be up to the time the charge is developing on the plates of the capacitor. Thus, the compass needle deflects and gradually comes to the original position in a time that is large compared to the time constant.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 40: Electromagnetic Waves- 1
Try yourself:Dimensions of 1/(µ0ϵ0) is
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 40: Electromagnetic Waves- 1
Try yourself:Electromagnetic waves are produced by
Explanation
A static charge produces an electrostatic field. A moving charge produces a magnetic field. Electromagnetic waves are produced by an accelerating charge.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 40: Electromagnetic Waves- 1
Try yourself:An electromagnetic wave going through vacuum is described by
E = E0 sin (kx − ωt); B = B0 sin (kx − ωt).
Which of the following equations is true?
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 40: Electromagnetic Waves- 1
Try yourself:An electric field  and a magnetic field
and a magnetic field  exist in a region. The fields are not perpendicular to each other.
exist in a region. The fields are not perpendicular to each other.
Explanation
For an electromagnetic wave,electric field ,magnetic field and direction of propagation are mutually perpendicular to each other.We can have a region in which electric and magnetic fields are applied at an angle with each other.In transmission lines Different modes exist. In transverse electric (TE) mode-no electric field exist in the direction of propagation. These are sometimes called H modes because there is only a magnetic field along the direction of propagation (H is the conventional symbol for magnetic field).
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 40: Electromagnetic Waves- 1
Try yourself:Consider the following two statements regarding a linearly polarised, plane electromagnetic wave :
(A) The electric field and the magnetic field have equal average values.
(B) The electric energy and the magnetic energy have equal average values.
Explanation
For a linearly polarised, plane electromagnetic wave
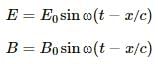
The average value of either E or B over a cycle is zero ( average of sin(θ) over a cycle is zero).
Also the electric energy density (uE) and magnetic energy density (uB) are equal .
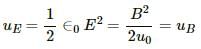
Energy can be found out by integrating energy density over the entire volume of full space.
As the energy of the electromagnetic wave is equally shared between electric and magnetic field so their average values will also be equal.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 40: Electromagnetic Waves- 1
Try yourself:A free electron is placed in the path of a plane electromagnetic wave. The electron will start moving
Explanation
As the electron is at rest initially, only the electric field will exert force on it. There will be no magnetic force on the electron in the stating. Hence, the electron will start moving along the electric field.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 40: Electromagnetic Waves- 1
Try yourself:A plane electromagnetic wave is incident on a material surface. The wave delivers momentum p and energy E.
Explanation
When an electromagnetic wave strikes a material surface, it transports the momentum, as well as the energy, to the surface. The striking electromagnetic wave exerts pressure on the surface. The total energy transferred to the surface by the electromagnetic wave is given by E = pc. Therefore, p ≠ 0, E ≠ 0.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 40: Electromagnetic Waves- 1
Try yourself:An electromagnetic wave going through vacuum is described by
E = E0 sin (kx − ωt).
Which of the following is/are independent of the wavelength?
Explanation
Report a problem
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 40: Electromagnetic Waves- 1
Try yourself:Displacement current goes through the gap between the plates of a capacitor when the charge of the capacitor
Explanation
Displacement current inside a capacitor,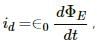 Where
Where 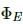 is the electric flux inside the capacitor.
is the electric flux inside the capacitor.
Up to the time the electric flux changes, there will be a displacement current. This is possible when the charge on a capacitor changes. Therefore, the displacement current goes through the gap between the plates of a capacitor when the charge of the capacitor or electric field increases or decreases inside the capacitor.
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 40: Electromagnetic Waves- 1
Try yourself:Speed of electromagnetic waves is the same
Explanation
In a vacuum, the speed of electromagnetic waves is constant for all intensities.
Report a problem
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 40: Electromagnetic Waves- 1
Try yourself:Which of the following have zero average value in a plane electromagnetic wave?
Explanation
In a plane electromagnetic wave, the electric and the magnetic fields oscillate sinusoidally. For an electromagnetic wave propagating in the z-direction, the electric and magnetic fields are given by:
Ex = E0 sin (kz – ωt)
By = B0 sin (kz – ωt)
These are sinusoidal functions. Therefore, for a fixed value of z, the average value of the electric and magnetic fields are zero.
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 40: Electromagnetic Waves- 1
Try yourself:The energy contained in a small volume through which an electromagnetic wave is passing oscillates with
Explanation
Report a problem
is same.
, will be same.
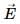 and a magnetic field
and a magnetic field 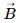 exist in a region. The fields are not perpendicular to each other.
exist in a region. The fields are not perpendicular to each other.

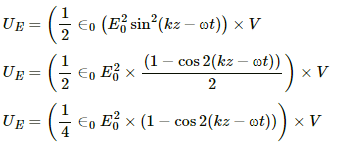
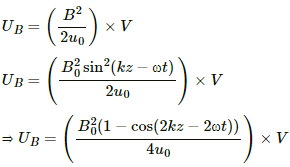
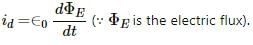
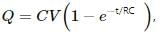
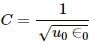
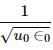 are of velocity, i.e L/T .
are of velocity, i.e L/T .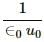 will have dimension L2/T2.
will have dimension L2/T2.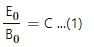
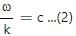
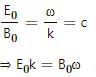
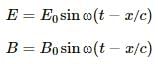
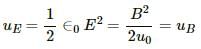
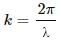
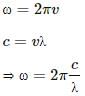
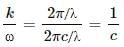
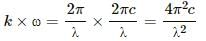
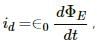 Where
Where 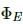 is the electric flux inside the capacitor.
is the electric flux inside the capacitor.