UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Rare Earth Elements (REE): Why are they strategically important?
Rare Earth Elements (REE): Why are they strategically important? - UPSC PDF Download
Introduction to Rare Earth Elements (REE)
Rare Earth Elements (REE) are a group of seventeen chemical elements that occur together in the periodic table, including 15 lanthanides (Z=57 through 71), Scandium (Sc), and Yttrium (Y).
- Similar Properties: All REEs are metals and share several similar properties, leading to their co-occurrence in geologic deposits. This is why they are also known as rare earth metals.
- Alternate Names: They are also referred to as "rare earth oxides" because many of them are sold as oxide compounds.
List of Rare Earth Elements
The seventeen elements included in the Rare Earth Elements (REE) group are:
- Lanthanides (Z=57 through 71): Lanthanum (La), Cerium (Ce), Praseodymium (Pr), Neodymium (Nd), Promethium (Pm), Samarium (Sm), Europium (Eu), Gadolinium (Gd), Terbium (Tb), Dysprosium (Dy), Holmium (Ho), Erbium (Er), Thulium (Tm), Ytterbium (Yb), Lutetium (Lu).
- Scandium (Sc) and 3. Yttrium (Y).
Inclusion of Scandium and Yttrium in REE
- Reason: Scandium and Yttrium are included in the Rare Earth Elements (REE) group because they are commonly found in the same ore deposits as the lanthanides, and they also exhibit similar chemical properties.
Abundance of Rare Earth Elements (REE) as Natural Resources
- Not Rare in Quantity: Contrary to their name, rare earth elements are not scarce in quantity. In fact, some of them are quite abundant in the earth's crust, with cerium being more abundant than copper and lead.
- Extraction Challenges: Despite their abundance, the extraction of rare earth elements is exceptionally difficult due to their occurrence in low concentrations and their complex geological associations.
The Origin of the Term "Rare Earth"
- Historical Naming: The term "rare earth" originated from the 18th and 19th centuries when these elements were first isolated as oxides from "rare minerals."
- Technological Difficulty: Technological limitations in the 20th century made it challenging to extract REEs from their oxide forms, perpetuating the use of the name "rare earth" despite its inaccuracy.
- Abundance Clarification: The term "rare earth" refers to the difficulty in extracting and refining these elements from their natural sources rather than their actual scarcity.
Importance and Strategic Significance
- Growing Global Demand: The global demand for rare earth elements has seen significant growth due to their expanding applications in high-end technology, environmental, and economic sectors.
- High-End Technology: REEs are crucial components in the manufacturing of various high-tech devices such as smartphones, laptops, LED screens, and electric vehicle motors.
- Environmental Applications: Rare earth elements play a vital role in green technologies, including wind turbines, solar panels, and energy-efficient lighting.
- Economic Importance: The strategic significance of REEs is undeniable as they have become essential for industries and national economies worldwide.
- Dependency and Supply Concerns: Their strategic importance is further highlighted by the fact that a few countries dominate the production of rare earth elements, leading to concerns about supply chain vulnerability and geopolitical implications.
The Significance of Rare Earth Elements (REE)
- Rare Earth Elements (REE) possess distinctive properties in electrical, metallurgical, catalytic, nuclear, magnetic, and luminescent fields.
- They are crucial for emerging technologies that address the needs of modern society.
- Usage ranges from everyday items like lighter flints and glass polishing mediums to high-end technologies such as lasers, magnets, batteries, and fiber-optic cables.
- REMs are essential for futuristic technologies like high-temperature superconductivity, safe hydrogen storage, and addressing environmental and energy efficiency issues.
- Their unique properties contribute to reduced weight, emissions, and energy consumption, leading to greater efficiency, performance, miniaturization, speed, durability, and thermal stability.
Uses of Rare Earth Metals (REMs) in Defense
- REMs find applications in various defense technologies due to their unique properties, such as magnetic and luminescent characteristics.
- They contribute to advanced technologies used in communication, clean energy, transportation, healthcare, environmental mitigation, and national defense.
Usage of Rare Earth Elements (REE) in Emerging Technologies
- REMs are utilized in a wide array of innovative products, including consumer electronics like iPhones, TVs, computers, and rechargeable batteries.
- They are integral to technologies like catalytic converters, magnets, fluorescent lighting, and illuminated screens on electronic devices.
- REMs are used for air pollution control and polishing optical-quality glass.
The Rare Earth Dilemma
- REM extraction is one of the most environmentally negative and toxic mining practices.
- Disproportionate rare earth mining leads to landslides, clogged rivers, and environmental pollution, posing risks to people's safety, health, and ecological balance.
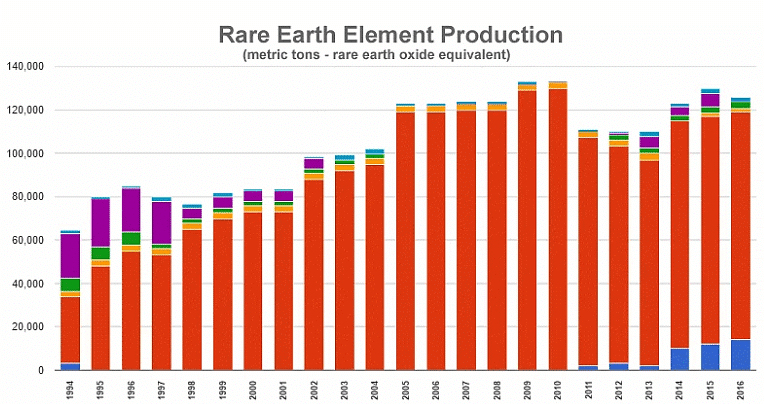
- China dominates the production of REMs, controlling 94% of the market, and has high natural reserves.
- Dependence on China for REMs creates a dilemma for countries like India, which lack sufficient resources and face technological constraints in mining their reserves.
- India considers certain REMs, along with other critical minerals, essential for its manufacturing sector but is mostly import-dependent, leading to concerns about future scarcity.
Global Uses and Production of Rare Earth Elements (REE)
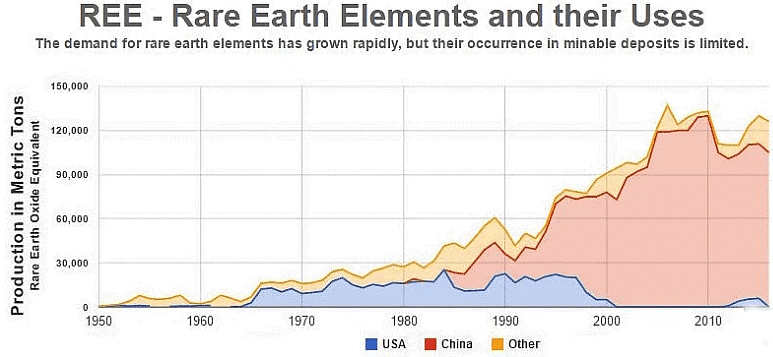
- China's control over 94% of REM production creates a global supply dominance.
- China's acquisition of reserves in other countries further solidifies its monopoly in the REM market.
- India faces challenges due to its limited REM resources and technological limitations in mining.
- A study identifies 12 critical minerals, including rare earth, for India's manufacturing sector, with some being 100% import-dependent.
Future Use of Rare Earth Metals (REMs)
Rising Global Demand in Various Industries
- Automobiles, Consumer Electronics, and Energy-Efficient Lighting: The global demand for automobiles and consumer electronics is projected to increase significantly in the coming decade. REMs play a critical role in various components used in these industries, including electric vehicles (EVs) and energy-efficient lighting systems.
Key Raw Material for Future Technologies and Industries
- Emerging Technologies: REMs are expected to be a vital raw material for the future of emerging technologies. They are indispensable in advanced electronic devices, renewable energy technologies, and high-performance magnets.
Surge in Rare Earth Magnet Demand
- Rechargeable Batteries: The demand for rare earth magnets is anticipated to witness a surge due to the increasing adoption of rechargeable batteries in various applications, such as EVs, portable electronic devices, and renewable energy storage systems.
Advancements in Medical Technology
- Surgical Lasers: With advancements in medical technology, the use of REMs in surgical lasers is expected to grow. REMs enhance the efficiency and precision of surgical procedures, leading to better patient outcomes.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):
- REMs contribute to the development of improved MRI machines, enabling higher-quality medical imaging for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Positron Emission Tomography Scintillation Detectors:
- REMs are crucial in the production of scintillation detectors used in positron emission tomography (PET) scans, which aid in detecting and diagnosing diseases.
Enhanced Efficiency in Future Military and Navy Arsenals
- Defense Applications: REMs are anticipated to find increased use in future military and navy arsenals, contributing to better efficiency and handling of defense technologies.
Related Searches