Egyptian Civilization | General Knowledge Encyclopedia - Class 8 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Daily Life in Ancient Egypt |

|
| Medicine in Ancient Egypt |

|
| Introduction to Ancient Egypt |

|
| Old, Middle, and New Kingdoms |

|
Introduction
- Ancient Egypt, one of the earliest and most famous civilisations in history, began around 5,000 years ago in the Nile River valley of northeastern Africa. The Nile River was crucial for agriculture and trade, enabling the growth and prosperity of this civilisation.
- The ancient Egyptians were known for their impressive architectural skills, evident in the enormous pyramids, temples, palaces, and tombs they built. These structures are a testament to their advanced knowledge and capabilities in construction.

- In addition to architecture, ancient Egyptians excelled in art. Their paintings and carvings are regarded as some of the most beautiful art ever created. They depicted scenes of everyday life, work, and leisure with great attention to detail, providing valuable insights into their daily routines and activities.
- The dry climate of Egypt played a significant role in preserving many artifacts from this ancient civilisation. These well-preserved items have been uncovered by archaeologists since the late 1700s, offering historians valuable information about ancient Egyptian life and culture.
- Ancient Egypt is of great importance in world history, as its culture and society have influenced many others for thousands of years.
Daily Life in Ancient Egypt
- Archaeological findings from ancient Egypt, including artifacts such as clothing, leather, wood, and food items, offer valuable insights into the daily lives of the ancient Egyptians. Tombs have played a crucial role in uncovering details about their lifestyle, as they feature intricate paintings depicting scenes of everyday activities. The ancient Egyptians held a strong belief in the afterlife, which is why they included various items in tombs that they thought would be necessary in the next life.

- For instance, the tomb of Queen Hatshepsut revealed her loyal dog's burial, and in the tomb of another nobleman, a complete meal was found, consisting of barley porridge, quail, kidneys, pigeon stew, fish, bread, and cakes. Initially, tombs contained models of essential items like houses, granaries, boats, cattle, and servants to aid the deceased in the afterlife.
- Over time, these scenes were painted on the walls of tombs for the same purpose. Wealthy tombs also held treasures such as jewellery and other valuable objects.
- The ancient Egyptians practiced mummification to preserve the dead, a process involving the removal of internal organs and the use of natron to maintain the body's integrity. In addition to human mummies, many mummies of sacred animals like cats, ibises, and crocodiles have been found. Prominent individuals were often placed in elaborate coffins called sarcophagi, some of which featured a likeness of the deceased. For example, the renowned pharaoh Tutankhamun was laid to rest in a solid gold coffin.
Medicine in Ancient Egypt
- Deep Understanding of Anatomy: The ancient Egyptians possessed a profound knowledge of the human body, which enabled them to train skilled doctors.
- Medical Texts: Their detailed study of anatomy and medicine is evident in the oldest medical and surgical texts found in Egypt.
- Ebers Papyrus: One of these texts, the Ebers Papyrus, dating back to around 1550 BCE, contains a compilation of 700 remedies for common diseases.
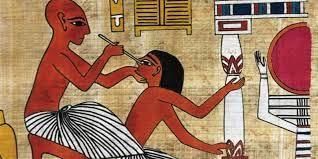
These practices laid the foundation for future medical knowledge.
Writing
- The ancient Egyptians developed a distinctive form of writing known as hieroglyphics, which originated as a pictorial system. These symbols represented the sounds of words and were meticulously carved or painted onto the walls of tombs and temples, using vibrant colors such as red, yellow, green, black, and blue. Hieroglyphics have been in use since approximately 3100 BCE.

- Around 2900 BCE,. cursive writing style emerged, but hieroglyphics continued to be used. This cursive script was written with ink and a reed pen, primarily on papyrus, a paper made from the papyrus plant. Additionally, a script called demotic emerged around 500 BCE for everyday writing, while hieratic was used mainly for administrative and religious documents.
- A significant breakthrough in understanding Egyptian writing came with the discovery of the Rosetta Stone in 1799. This stone, dating to around 200 BCE, featured text in Greek alongside hieroglyphics and demotic script. By comparing the Egyptian writing to the Greek text, a scholar familiar with Greek was able to decipher hieroglyphics and demotic script.
Daily Life in Ancient Egypt
- Villages and towns in ancient Egypt were situated along the Nile River, which was essential for trade and the only source of water. Houses in these areas were constructed from mud bricks. To shield against the harsh sun and heat, windows were small, positioned high up, and covered with loosely woven mats. The walls were adorned with vibrant frescoes, while the floors were covered with straw mats and rugs.

- Wall paintings offer valuable glimpses into the everyday lives of ordinary people, depicting scenes of child-rearing, hunting, farming, and various daily activities. They also reveal details about clothing, jewellery, and hairstyles across different social classes. Egyptians were known for their use of perfumes and cosmetics; both men and women applied green eyeshadow and black kohl around their eyes, while women also coloured their lips and nails. Containers for cosmetics and grinding tools were placed in tombs for use in the afterlife.
- Due to the hot climate, clothing in ancient Egypt was typically simple. Young children, servants, and labourers often wore minimal clothing. The most common fabric was white linen, while wool was used for cloaks when extra warmth was needed. Early garments were draped and tied around the body or secured with pins and belts. Men usually wore linen skirts and sometimes vests, while women wore straight, ankle-length dresses with shoulder straps. Necklaces and wide collars adorned with gemstones were popular accessories. Over time, Egyptian clothing became more intricate. Wigs gained popularity, and rulers, including female rulers, wore false beards made of metal. Men also frequently donned beards.
Religion in Ancient Egypt
- The ancient Egyptians had a polytheistic belief system, worshipping a multitude of gods and goddesses. The most important deity was the sun god, Ra (or Re ), who was revered across the land. Each city in ancient Egypt had its own set of local gods, who were central to the community's religious practices.

- As the city of Thebes rose to prominence, its patron god, Amon, gained greater importance. Over time, Amon was merged with Ra, creating the composite deity Amon-Re, who became regarded as the supreme god of the Egyptian pantheon.
- The ancient Egyptians held a profound belief in an afterlife, which made the god Osiris, ruler of the afterlife, extremely significant in their religion. Osiris's wife, Isis, and their son, Horus, were also widely venerated and played crucial roles in the Egyptian mythological framework.
Ancient Egyptian Inventions
- The ancient Egyptians were remarkably innovative, even without the use of pulleys. They devised ingenious methods to transport and lift heavy stone blocks using tools such as sledges, rollers, and ramps.

- In addition to their engineering feats, the Egyptians were keen observers of the stars, which led them to develop calendars based on both the lunar and solar cycles. This was crucial for their agricultural practices, especially in relation to the flooding of the Nile River, which was vital for their advanced irrigation system.
Introduction to Ancient Egypt
The history of Ancient Egypt is a fascinating journey that begins along the banks of the Nile River, where human settlements emerged over 10,000 years ago. Initially, this narrow valley was covered with swamps and various plants, but as the river's flow brought in nutrient-rich silt, it transformed into a fertile delta. Over time, people cleared the swamps, built villages, and developed agriculture, giving rise to two distinct kingdoms: Upper Egypt in the south and Lower Egypt in the north. Around 2900 BCE, Narmer, also known as Menes, unified these kingdoms, establishing Memphis as the capital and laying the foundation for the remarkable civilization that would follow.
The Nile River's Role
- The Nile River was crucial for the development of Ancient Egypt. Its annual floods deposited fertile silt, making the land ideal for agriculture.
- This natural bounty allowed the Egyptians to grow surplus crops, which supported a growing population and led to the development of complex societies.
Kingdoms of Upper and Lower Egypt
- Upper Egypt was known for its narrow, fertile valley and was the site of many early agricultural communities.
- Lower Egypt, with its expansive delta, became a hub for trade and agriculture due to its rich soil and access to waterways.
Narmer's Unification
- Narmer's unification of Upper and Lower Egypt around 2900 BCE was a pivotal moment in history.
- It marked the beginning of a centralized state, with Memphis as the capital.
- This unification laid the groundwork for the development of one of history's most iconic civilizations, known for its advancements in writing, architecture, and governance.
Old, Middle, and New Kingdoms
- After Menes, more than 30 dynasties governed ancient Egypt. The history of Egypt is categorized into three primary eras: the Old Kingdom, the Middle Kingdom, and the New Kingdom.
- The Old Kingdom 2575 to 2130 BCE. is renowned for the construction of the great pyramids, especially the Pyramids of Giza, built during the 4th dynasty by Pharaohs Khufu, Khafra, and Menkaure. The methods used by the ancient Egyptians to build these massive stone structures with limited technology remain a subject of fascination. The Great Sphinx, with its lion-like body and human face, is located near the second pyramid and is another marvel of this era.

- Following a period of civil war and division until around 2055 BCE, the Middle Kingdom began and lasted until 1630 BCE. This era saw the expansion of Egyptian rule into regions like Nubia, Syria, and Palestine. The capital was moved to Thebes, marking a time of great artistic and architectural achievement, although few structures from this period have survived.
- A phase of weakness ensued, marked by the invasion of Egypt by the Hyksos, an Asian group. By 1539 BCE, the Egyptians expelled the Hyksos, ushering in the New Kingdom, which lasted until 1075 BCE.
- Thutmose III, a formidable pharaoh of the New Kingdom ( 1479 to 1426 BCE ), led Egypt to its peak of power and prosperity. He expanded the empire into Syria and initiated the construction of numerous tombs and temples, including the famous tombs in the Valley of the Kings, located west of Thebes.
- During the 19th dynasty, Egypt was ruled by strong kings. Ramses II ( 1279 to 1213 BCE. initiated an extensive building program. However, after Ramses' reign, internal conflict arose, leading to a divided Egypt characterized by riots, strikes, and chaos.
Alexander and the Ptolemies
- Throughout history, various Asian groups, starting with the Assyrians and then the Persians, took control of Egypt. In 332 BCE, Alexander the Great from Macedonia, near Greece, conquered Egypt and founded Alexandria at the Nile's mouth.

- After Alexander's death, his general Ptolemy took the throne in 323 BCE, starting the Ptolemaic dynasty. The Ptolemies, Macedonians who spoke Greek, introduced Greek culture and governance in Egypt, sometimes causing friction with the locals.
- Despite this, Egypt thrived under Ptolemaic rule, experiencing cultural growth. They built the Pharos, a massive lighthouse in Alexandria, considered one of the ancient world's seven wonders. They also created a famous library in Alexandria, attracting scholars from the Greek-speaking world.
Overall, the Ptolemaic period was significant for its contributions to Egyptian culture and the blending of Greek and Egyptian traditions.
Roman and Muslim Conquests
- The Ptolemaic dynasty in Egypt came to an end with Queen Cleopatra. In 31 BCE, Roman forces defeated her navy at the Battle of Actium, leading to Egypt becoming a province of the Roman Empire in 30 BCE.

- When the Roman Empire split into two parts in the 300s CE, Egypt was included in the eastern half, known as the Byzantine Empire.
- In the 600s CE, Muslim Arabs conquered Egypt, marking a significant change in its history. Since then, Egypt has predominantly remained a Muslim country.
|
30 videos|108 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on Egyptian Civilization - General Knowledge Encyclopedia - Class 8
| 1. What were the main achievements of ancient Egyptian civilization? |  |
| 2. How did religion influence daily life in ancient Egypt? |  |
| 3. What was the significance of the Nile River to ancient Egyptians? |  |
| 4. What were the roles of pharaohs in ancient Egypt? |  |
| 5. How did ancient Egyptians contribute to the field of medicine? |  |















