UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Science & Technology for UPSC CSE > Chemistry Basics – Atoms, Molecules, Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures
Chemistry Basics – Atoms, Molecules, Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Fundamentals of Chemistry
Chemistry is a scientific discipline that deals with the study of matter, its composition, structure, properties, and the changes it undergoes. Matter is defined as anything that has rest mass and volume, and it is composed of particles.
Atoms
Atoms are the fundamental units of matter. They are incredibly small and cannot be divided further without losing their essential properties.
- Structure: An atom consists of a central nucleus, which is surrounded by negatively charged electrons.
- Nucleus: The nucleus is the central part of the atom and contains protons and neutrons.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the nucleus in distinct energy levels or orbits.
- Subatomic Particles: Constituent particles of an atom are called subatomic particles, including protons, electrons, and neutrons.
Subatomic Particles:
- Protons: Protons are positively charged subatomic particles found in the nucleus of an atom. They have a relative mass of approximately 1 atomic mass unit (amu) and carry a positive charge of +1.
- Electrons: Electrons are negatively charged subatomic particles that orbit around the nucleus. They have an extremely small mass of about 9.11×10−31 kg and carry a negative charge of -1.
- Neutrons: Neutrons are electrically neutral subatomic particles found in the nucleus. They have a relative mass of approximately 1 amu and do not carry any electrical charge.
Discoveries:
- Proton: Ernest Rutherford discovered the proton in 1918 through his famous gold foil experiment.
- Electron: J.J. Thomson discovered the electron in 1897, identifying it as a fundamental particle with its cathode ray tube experiment.
- Neutron: James Chadwick is credited with the discovery of the neutron in 1932 by conducting experiments with beryllium and paraffin.
Nucleus
The nucleus is the central core of an atom, comprising protons and neutrons.
- Nucleons: Particles present inside the nucleus are called nucleons, and they mainly include protons and neutrons.
- Positive Charge: Due to the presence of protons in the nucleus, it carries a positive charge.
Molecules
Molecules are formed when two or more atoms chemically bond together. They can be composed of atoms from one element (e.g., O2 molecule, where two oxygen atoms bond) or atoms from different elements (e.g., proteins, which consist of atoms from various elements).
Elements
A chemical element is a pure substance consisting of only one type of atom, uniquely identified by its atomic number.
Examples: Carbon, Oxygen, Silicon, Arsenic, Aluminum, Iron, Copper, Gold, Mercury, etc., are all examples of elements.
Abundant Elements
- Hydrogen and Helium: These are the most abundant elements in the universe.
- Iron: Iron is the most abundant element by mass in the Earth.
- Oxygen: Oxygen is the most common element in the Earth's crust.
The Eight Most Abundant Elements in Earth's Crust (by mass)
- 46.6% Oxygen (O)
- 27.7% Silicon (Si)
- 8.1% Aluminum (Al)
- 5.0% Iron (Fe)
- 3.6% Calcium (Ca)
- 2.8% Sodium (Na)
- 2.6% Potassium (K)
- 2.1% Magnesium (Mg)
Periodic Table
- Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev: He is considered the father of the periodic table.
- First Detailed Periodic Table: Mendeleev developed the first detailed form of the periodic table based on mass number.
- Henry Gwyn Jeffrey's Moseley: He later created a new periodic table based on atomic number and is known as the father of the modern periodic table.
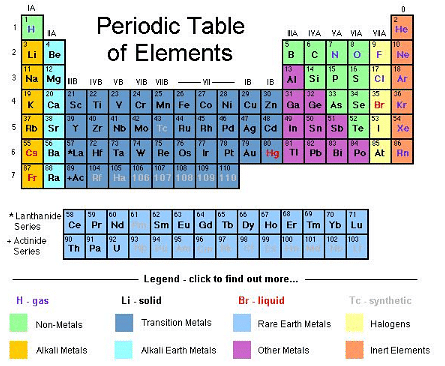
Natural Elements
Natural elements are those elements that occur naturally on Earth.
Synthetic or Man-Made Elements
Synthetic elements are chemical elements that do not occur naturally on Earth. They are prepared artificially and are often unstable.
First Synthetic Element: Technetium was the first synthetic element to be created.
Compounds
Compounds are substances that consist of two or more different kinds of atoms chemically bonded together.
These atoms are held together by chemical bonds to form a stable structure.
Properties
A compound cannot be separated into its constituent atoms by simple physical methods. The chemical properties of compounds differ from those of their individual elements.
Examples:
- Common salt (NaCl) is a compound made up of sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl) atoms.
- Sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) is another example of a compound, composed of sodium (Na), carbon (C), and oxygen (O) atoms.
Mixtures
- Mixtures are formed when two or more substances are physically combined without any chemical bonding between them.
- In mixtures, each substance retains its own chemical identity even after being combined.
Properties
- Mixtures can be separated into their individual components using physical methods like filtration, distillation, or evaporation.
- The physical properties of each substance in the mixture remain unchanged.
Examples:
- A mixture of sand and water represents two distinct substances mixed together without any chemical reaction.
- Another example is a mixture of salt and water, where salt dissolves in water without forming any new compound.
- Sugar and salt can also be combined to form a mixture, with both substances maintaining their properties.
The document Chemistry Basics – Atoms, Molecules, Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Science & Technology for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
90 videos|491 docs|209 tests
|
Related Searches





















