States & their Folk Dances | Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) PDF Download
Introduction
Dance Forms in India can be broadly categorized into classical and folk dance, each having distinct origins.
- Classical dance, deeply rooted in the Natya Shastra, comprises a set of dance forms, each with its unique features.
- On the other hand, Folk dance evolved from the local traditions of various states, ethnicities, and geographical regions.
Classical Dance in India
India boasts 8 classical dance forms initially, as stated by scholars. However, with the inclusion of Chhau by the Cultural Ministry, the count extends to 9 classical dance forms. The classical dance forms express 8 fundamental emotions, as follows:
- Shringar - Love
- Hasya - Humor
- Karuna - Sorrow
- Raudra - Anger
- Veer - Heroism
- Bhayanak - Fear
- Bibhats - Disgust
- Adbhoot - Wonder
The list of classical dances in India is given below:
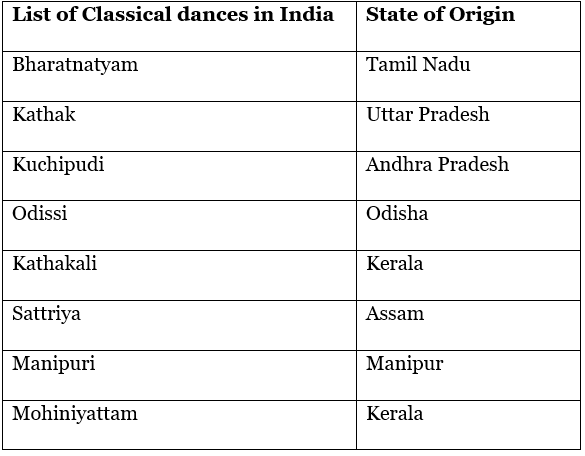
- Bharatanatyam is a classical dance form that finds its artistic foundation in ancient texts like Bharata's Natyashastra. This expressive dance style includes a diverse repertoire of songs in languages like Telugu, Tamil, and Sanskrit, encompassing themes of human and divine love, categorized as shringara (romantic love) and Bhakti (devotion). The music for Bharatanatyam is closely tied to the Carnatic system of music from southern India.
- Kathak, the predominant dance of northern India, continues to thrive in regions such as Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, Delhi, Madhya Pradesh, and parts of western and eastern India. Rooted in the storytelling tradition of Kathakaras, who have for generations narrated scriptures, the epics Ramayana and Mahabharata, and puranic literature to the masses, Kathak stands as a captivating form of art.
- Kuchipudi, another prominent classical dance genre, emerged in Andhra Pradesh during the 7th century AD and flourished through the Bhakti movement. It incorporates elements of Nritta (pure dance), Nritya (expressive dance), and Natya (dramatic representation). Nritta features intricate footwork and rhythmic patterns, Nritya involves expressive movements known as Sabdams, and Natya entails acting with Mudras to depict the song's essence.
- Odissi dance originated in the eastern state of Orissa and was initially performed by female temple employees known as 'maharis.' Evolving into a theatrical art form in the mid-twentieth century, Odissi draws inspiration not only from existing dance traditions but also from depictions in Orissa's medieval sculpture, painting, and literature.
- Kathakali, meaning 'story play,' developed in the seventeenth century under the patronage of the prince of Karnataka in Kerala. It involved the creation of plays based on the epic Ramayana in the local Malayalam language. Over three centuries, a rich repertoire of Kathakali plays, mostly centered around stories from the Ramayana and Mahabharata, has been passed down.
- Sattriya dance emerged in the sixteenth century within Assam's monasteries as the Vaishnava faith spread, thanks to the influence of saint and reformer Shankaradeva. It stands as a distinct genre within classical Indian dance, showcasing a sophisticated vocabulary of hand gestures (hasta), footwork (pada karma), movement and emotion (Nritta and Abhinaya), with a focus on devotion to Lord Krishna.
- Manipuri dance, originating in Manipur in north-eastern India, is deeply rooted in the Vaishnava beliefs of the Meitei community. It consists of two main sections: jagoi and cholom, which correspond to the lasya (graceful) and tandava (vigorous) aspects mentioned in Sanskrit literature. Each form within this spectrum offers unique characteristics and nuances.
- Mohiniattam, derived from Kerala in southern India, derives its name from the mythical enchantress Mohini. This dance exudes feminine grace and finds its origins in performances associated with Kerala's temples. Mohiniattam incorporates rhythmic patterns distinct to Kerala, with the Maddalam drum's syllables accompanying female characters in Kathakali theatre, and the Edakka as a primary percussion instrument in the performance.
Folk Dances in India
Folk dances in India serve as vibrant reflections of the culture and traditions of the communities from which they originate. These dances are typically performed during various community celebrations, such as childbirth, festivals, and weddings, preserving the essence of local customs.
State of Origin | List of Folk Dances |
Andhra Pradesh | Vilasini Natyam, Bhamakalpam, Veeranatyam, Dappu, Tappeta Gullu |
Arunachal Pradesh | Buiya, Chalo, Wancho, Pasi Kongki, Ponung |
Assam | Bihu, Bichhua, Bagurumba, Jhumur |
Bihar | Jata-Jatin, Bakho-Bakhain, Domkach |
Chhattisgarh | Gaur Maria, Panthi, Raut Nacha |
Gujarat | Garba, Dandiya Ras, Tippani, Bhavai |
Goa | Dekhnni, Fugdi, Shigmo, Dhalo |
Haryana | Jhumar, Phag, Daph, Loor, Gugga |
Himachal Pradesh | Nati, Jhora, Chharhi, Dhaman |
Jammu & Kashmir | Rouf, Hikat, Kud, Dumhal |
Jharkhand | Karma, Chhau, Paika, Jhumair |
Karnataka | Yakshagana, Huttari, Suggi, Dollu Kunitha |
Kerala | Thiruvathira, Kolkali, Kaikottikali |
Maharashtra | Lavani, Powada, Koli, Tamasha |
Madhya Pradesh | Jawara, Matki, Aada, Grida, Phulpati |
Manipur | Lai Haraoba, Thang-Ta, Manipuri Dance |
Meghalaya | Shad Suk Mynsiem, Nongkrem, Wangala |
Mizoram | Cheraw, Khuallam, Chailam, Sarlamkai |
Nagaland | Chang Lo, Zeliang, Konyak Dance |
Odisha | Ghumura, Chhau, Gotipua, Dalkhai |
Punjab | Bhangra, Giddha, Luddi, Julli |
Rajasthan | Ghoomar, Kalbeliya, Bhavai, Chari |
Sikkim | Maruni, Tamang Selo, Singhi Chaam |
Tamil Nadu | Kummi, Kolattam, Karagattam |
Tripura | Hojagiri, Garia, Lebang Boomani |
Uttar Pradesh | Nautanki, Raslila, Kajri, Mayur |
Uttarakhand | Chancheri, Chholiya, Barada Nati |
|
744 videos|1444 docs|633 tests
|
FAQs on States & their Folk Dances - Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests)
| 1. What are the main characteristics of folk dances in India? |  |
| 2. Can you name some popular folk dances from different states in India? |  |
| 3. How do folk dances contribute to the cultural heritage of India? |  |
| 4. Are there any significant festivals associated with folk dances in India? |  |
| 5. How can one learn about different folk dances in India? |  |





















