Transport in India - 2 | Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) PDF Download
Water Transport in India
- Most efficient, least costly and environment friendly means of transportation.
- Water transport is of two types:
- Inland waterways
- Oceanic waterways
Inland waterways
- The total length of navigable waterways in India comprising rivers, canals, backwaters, etc.
- India has 14,500 km of navigable waterways out of which 3700 km is navigable by mechanised boats.
- It contributes 1% of the country’s transportation.
Inland Waterways Authority
- For the development, maintenance and regulation of national waterways in the country, the Inland Waterways Authority was set up in 1986.
- The authority has declared 4 inland waterways as National Waterways
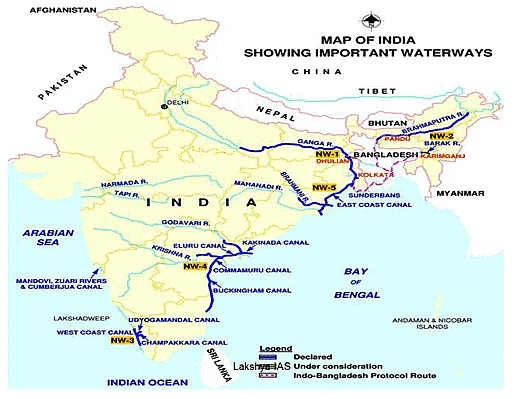
National Waterways of India
- NW 1: Allahabad to Haldia – 1,620 km
- NW 2: Sadia to Dhubari (on Brahmaputra river) – 891 km
- NW 3: Kottapuram-Kollam stretch of the West Coast Canal, Champakara Canal and Udyogmandal Canal – 205 km
NW 4: Kakinada to puducherry stretch of Canals and the Kaluvelly Tank, Bhadrachalam – Rajahmundry stretch of River Godavari and Wazirabad – Vijayawada stretch of River Krishna– 1,095 km
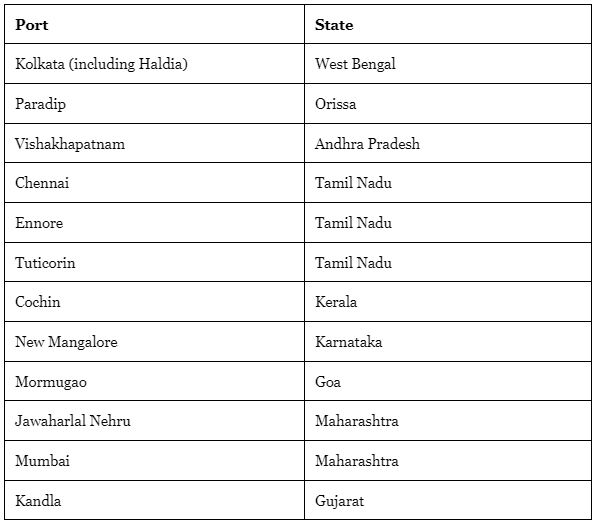
Ports in India
- The Waterways Authority in India divides Indian ports into three categories, major, minor and intermediate.
- India has about 190 ports in all, with 12 major and the rest intermediate and minor.
- All these ports are administered by the respective Port Trusts, except the newly constructed Ennore port which is under the Ennore Port Ltd. Company.
Salient Features
Kolkata Port (including Haldia) :
- Kolkata is a riverine port, located about 128 km from the Bay of Bengal on the banks of river Hooghly.
- Haldia was developed because excessive silting prevented the entry of large marine vessels in Kolkata.
Paradip Port :
- Located on the Orissa coast along the Bay of Bengal.
- India exports raw iron to Japan from here.
Vishakhapatnam Port
- The deepest port, located in Andhra Pradesh.
- It serves the Bhilai and Rourkela steel plants.
Tuticorin Port :
- It came into existence during the reign of Pandya kings.
- It has an artificial deep sea harbour.
Cochin Port :
- A fine natural harbour located on Kerala coast.
- Handles the export of tea, cofee and spices and import of petroleum and fertilisers.
New Mangalore Port :
- The ‘Gateway of Karnataka’.
- Handles the export of iron-ore of Kudremukh.
Marmugao Port :
- It has a naval base.
- India’s leading iron-ore port.
Mumbai Port :
- A natural port, India’s busiest.
- A new port, Nhava Sheva, developed near Mumbai port.
Jawaharlal Nehru Port :
- Occupies the 5th position in the world’s faster growing ports.
Kandla Port :
- Called the ‘offspring of partition’ as it was developed after the partition as a substitute of Karachi port.
- It is a tidal port and a free trade zone located in the Rann of Kachchh.
Air Transport
- It is the fastest means of movement
- Air transport made a beginning in 1911 when airmail operation commenced over a little distance of 10 km between Allahabad and Naini
- Its real development took place in post-independence period
Airport Authority of India
- Airport Authority of India is responsible for providing safe, efficient air traffic and aeronautical communication services in the Indian air space.
- The authority manages 126 airports including 12 International airports
- The air transport in India is managed by two corporations, Air India and Indian Airlines after nationalisation
- In 1953, all the private Airline companies were nationalised and Indian Airlines and Air India came into existence.
- Air India administers international flights while Indian Airlines caters to the domestic circuit.
- Indian Airlines is now known by the name of ‘Indian’.
- Vayudoot Limited started in 1981 as a private air carrier and later on it merged with Indian Airlines.
- Pawan Hans Limited operates helicopter support services to oil sector, hill stations and remote areas.
- Indian Airlines is now known by the name of ‘Indian’.
- Vayudoot Limited started in 1981 as a private air carrier and later on it merged with Indian Airlines.
- Pawan Hans Limited operates helicopter support services to oil sector, hill stations and remote areas.
- A number of private airlines also operates is India.
- They are Jet Airways, Sahara, etc.
- The Civil Aviation Centre in Fursatganj near Allahabad provided, among other things, ground training to the pilots.
There are 12 International Airports in India :
- Begumpet Airport, Hyderabad
- Calicut International Airport, Calicut
- Chatrapati Shivaji International Airport, Mumbai
- Chennai International Airport, Chennai
- HAL Airport, Bangalore
- Goa Airport in Vasco da Gama city, Goa
- Lokpriya Gopinath Bordolio International Airport, Guwahati
- Indira Gandhi International Airport, Delhi
- Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose International Airport, Kolkata
- Rja Sansi International Airport, Amritsar
- Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel International Airport, Ahmedabad
- Thiruvananathapuram International Airport, Thiruvananathapuram
Pipeline Transport
- Pipelines are the most convenient and efficient mode of transporting liquids, gases over long distances
- Even solids can be transported by pipelines after converting them into slurry
Merits
- Pipelines are laid through water as well difficult and different type of terrains.
- The operational and maintenance cost of pipelines is very less.
Demerits
- detection of leakage, repairing, safety and security of the pipelines.
Pipelines
- Asia’s first cross country pipeline covering a distance of 1157 km was constructed by Oil India limited from Naharkatiya oilfields in Assam to Barauni refinery in Bihar.
- It was further extended up to kanpur in 1966
Some other important pipelines are:
- Ankaleshwar- koyali
- Mumbai High- koyali
- Hajira- Vijaipur- Jagdishpur
- Salaya- Mathura
- Numaligarh – Siliguri
- Paradip-Haldia-Barauni
- Haldia - Barauni Pipeline
- Mathura-Delhi Pipeline
- Panipat-Ambala-Jalandhar Pipeline (PAJPL)
- Panipat-Delhi Pipeline (PDPL)
- Panipat-Bhatinda Pipeline
|
745 videos|1444 docs|633 tests
|





















