Class 7 Science Chapter 3 Question Answers - Heat
Q1: Explain the structure and function of a clinical thermometer.
Ans: A clinical thermometer is designed to measure body temperature with precision. It consists of a long, narrow glass tube with a bulb at one end containing mercury. The thermometer is marked with a Celsius scale for temperature readings.
- The Celsius scale on the thermometer helps in reading the temperature, typically ranging from 35°C to 42°C for body temperature measurements.
- The clinical thermometer is a specialized tool for measuring human body temperature, providing reliable and consistent readings for health assessments.

Q2: Why is it important to state the unit when recording body temperature?
Ans: When recording body temperature, it is crucial to state the unit (°C) along with the numerical value. This practice ensures clarity, accuracy, and consistency in temperature measurements.
- Stating the unit (°C) clarifies the scale being used for temperature readings, preventing confusion or misinterpretation of the recorded value.
- Units provide a standard reference point, allowing healthcare professionals and individuals to understand temperature measurements universally.
Q3: Explain the precautions to be observed while using a clinical thermometer.
Ans: When using a clinical thermometer, certain precautions must be followed to ensure accurate temperature readings and maintain hygiene and safety standards.
- Thermometers should be washed before and after use, preferably with an antiseptic solution, to prevent contamination and ensure cleanliness.
- Prior to use, ensure that the mercury level in the thermometer is below 35°C to avoid inaccurate readings and potential breakage.
- When reading the thermometer, position it in such a way that the level of mercury aligns with the line of sight for accurate temperature assessment.
- Handle the thermometer with care to prevent breakage or damage, avoiding holding it by the bulb while reading the temperature to maintain accuracy.
Q4: How does a laboratory thermometer differ from a clinical thermometer?
Ans:
- A laboratory thermometer has a different temperature range compared to a clinical thermometer, typically measuring from -10°C to 110°C.
- Unlike a clinical thermometer, a laboratory thermometer should be kept upright and not tilted while in use.
- The bulb of a laboratory thermometer needs to be surrounded by the substance whose temperature is being measured, ensuring accurate readings.
- The divisions on a laboratory thermometer should be noted to read the temperature correctly.
- It is essential to handle a laboratory thermometer with care, ensuring accurate readings and longevity of the instrument.
Q5: Explain the differences between heat and temperature.
Ans: The differences between heat and temperature are given below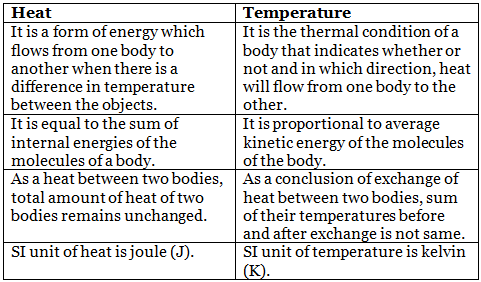 Q6: Explain the concept of heat transfer through conduction in solids.
Q6: Explain the concept of heat transfer through conduction in solids.
Ans:
- In solids, heat is primarily transferred through conduction, where vibrating particles transfer energy to neighbouring particles.
- Materials like aluminium, iron, and copper are good conductors as they allow heat to pass through them easily.
- In contrast, materials like plastic and wood are poor conductors, known as insulators, as they do not allow heat to pass through them easily.
- Conduction is the process where heat flows from a hotter object to a colder object through direct contact.
Q7: Describe the process of heat transfer through convection with examples.
Ans:
- In convection, heat transfer occurs through the movement of fluids like liquids or gases.
- When water is heated, hot water rises while colder water moves down, creating a convection current.
- The process of convection explains how heat is distributed within fluids, such as in the heating of water or air.
- Convection is responsible for phenomena like sea and land breezes, where air movement regulates temperature in coastal regions.
Q8: Explain the process of heat transfer through radiation and its significance.
Ans:
- Radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves without the need for a medium.
- Objects emit radiation based on their temperature, with hotter objects emitting more energy.
- Radiation plays a crucial role in how heat from the sun reaches the Earth and how objects exchange heat with their surroundings.
Q9: Why do we prefer different coloured clothes in summer and winter?
Ans:
- In summer, we prefer light-coloured clothes as they reflect most of the heat, keeping us cool.
- Dark-coloured clothes are preferred in winter as they absorb more heat, providing warmth.
- Woollen clothes are used in winter as wool is a poor conductor of heat, trapping air to insulate the body.
Q10: How is temperature measured, and what is the significance of a clinical thermometer?
Ans:
- Temperature is a measure of how hot or cold an object is and is typically measured using a device called a thermometer.
- A clinical thermometer is designed to measure human body temperature accurately.
- It consists of a long glass tube with a bulb containing mercury, and readings are usually in degrees Celsius.
- Reading a thermometer involves noting the temperature difference between two marks and counting the divisions between them.
- It is essential to handle and use a clinical thermometer carefully to ensure accurate readings.
Q11: The clinical thermometer is not used to measure high temperatures. Why? Also, state the limitations of clinical thermometers.
Ans:
- Clinical thermometer has the range 35°C to 42°C. If we use it to measure high temperatures, it may break, and the mercury present in the clinical thermometer is harmful. So, we cannot use a clinical thermometer to measure high temperatures.
- The clinical thermometer cannot be used to measure the temperature of any object more than 42°C (i.e., more than the body temperature). If it is kept in the sun or near a flame, then this clinical thermometer can be broken.
Q12: Differentiate between two modes of transfer of heat, i.e. convection and conduction.
Ans: Difference between convection and conduction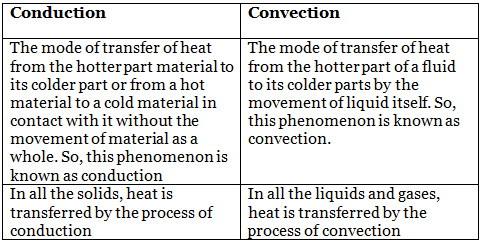 Q13: Can a clinical thermometer be used to measure the temperature of boiling water?
Q13: Can a clinical thermometer be used to measure the temperature of boiling water?
Ans: No, a clinical thermometer cannot be used to measure the temperature of boiling water because the temperature of boiling water is more than the fixed range of the clinical thermometer, i.e., 42°C. If we try to measure the temperature of boiling water, it will break down.
Q14: What is temperature? Describe two types of thermometers used to measure the temperature.
Ans: A reliable measure of the hotness of an object is called its temperature. It is measured by a device called a thermometer.
There are two types of thermometers:
(i) Clinical thermometer: The thermometer that measures the temperature of our body is called a clinical thermometer. It consists of a long, narrow, uniform glass tube. It has a bulb at one end which contains mercury. Outside the bulb, a small shining thread of mercury can be seen. There is also a scale on the thermometer. The scale used is the Celsius scale, indicated by °C. A clinical thermometer reads temperature from 35°C to 42°C.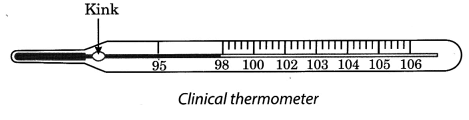 (ii) Laboratory thermometer: This type of thermometer is used to measure the temperature of different objects in laboratories. It is made of a thin glass tube sealed at one end and a bulb with mercury at the other end. The portion of the capillary tube above the bulb is graduated in degrees, usually from -10°C to 110°C.
(ii) Laboratory thermometer: This type of thermometer is used to measure the temperature of different objects in laboratories. It is made of a thin glass tube sealed at one end and a bulb with mercury at the other end. The portion of the capillary tube above the bulb is graduated in degrees, usually from -10°C to 110°C.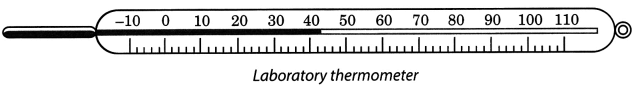
Q15: How does the heat travel in the air? Explain the sea breeze and land breeze in coastal areas in this reference.
Ans: Heat travels in the air through the process of convection. The air near the heat source gets hot and rises up. The cool air from the sides comes in to take its place. In this way, the air gets heated up.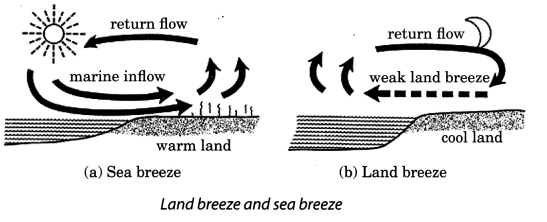
In the coastal areas, people experience an interesting phenomenon. The land gets heated faster than the water during the day. The air over the land becomes hotter and rises up. The cooler air from the sea rushes in towards the land to take its place. The warm air from the land moves towards the sea to complete the cycle.
The flow of cool air from the sea towards the land to replace the hot air on land is called sea breeze. At night, it is just the reverse: The water cools down more slowly than land. So the cool air from land moves toward the sea. This is called land breeze.
|
112 videos|286 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Science Chapter 3 Question Answers - Heat
| 1. What is heat? |  |
| 2. How is heat transferred? |  |
| 3. What are the units used to measure heat? |  |
| 4. How does heat affect different materials? |  |
| 5. What are some practical applications of heat in everyday life? |  |

















