Life Processes- 1 Class 10 Worksheet Science
MCQ Questions
Q1: Pair of spongy organs lying in the chest cavity is called
(a) hearts
(b) kidneys
(c) lungs
(d) bronchioles
Ans: (c)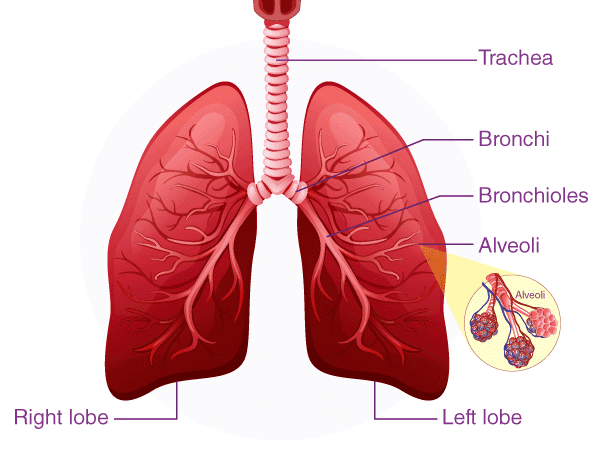 LungsThe lungs are a pair of spongy, air-filled organs located on either side of the chest (thorax). They play a crucial role in the respiratory system by taking in oxygen when we inhale and releasing carbon dioxide when we exhale.
LungsThe lungs are a pair of spongy, air-filled organs located on either side of the chest (thorax). They play a crucial role in the respiratory system by taking in oxygen when we inhale and releasing carbon dioxide when we exhale.
Q2: Which of the following structures increase the total surface area for the exchange of gases in the lungs?
(a) Bronchi
(b) Alveoli
(c) Bronchioles
(d) Trachea
Ans: (b)
These tiny, balloon-shaped air sacs located at the end of the bronchial tubes deep within the lungs provide a large surface area for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Q3: Bile is produced by
(a) pancreas
(b) liver
(c) small intestine
(d) stomach
Ans: (b)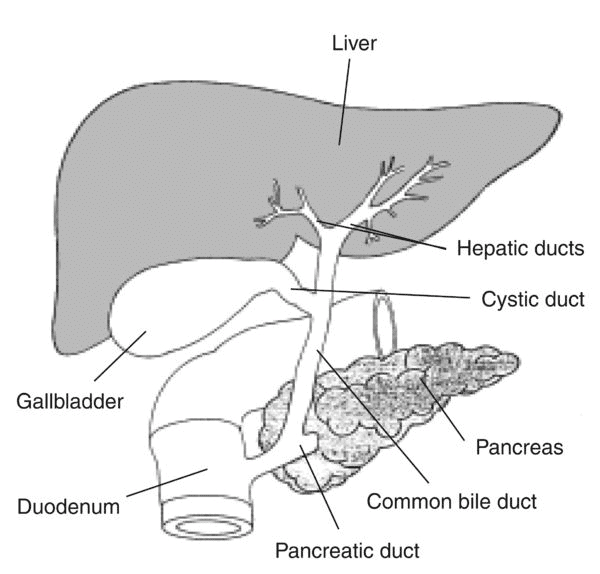 The liver produces bile, a digestive fluid that helps in the breakdown of fats during digestion.
The liver produces bile, a digestive fluid that helps in the breakdown of fats during digestion.
Q4: Which of the following represents the correct sequence of air passage during inhalation?
(a) Nostrils→ larynx → pharynx → alveoli → lungs
(b) Nostrils → trachea → pharynx → larynx → lungs
(c) Nostrils → pharynx → larynx → trachea → alveoli
(d) Nostrils → alveoli → pharynx → larynx → lungs
Ans: (c)
The sequence of air passage during inhalation starts from the nostrils, proceeds to the pharynx (throat), then to the larynx (voice box), followed by the trachea (windpipe), and finally reaches the alveoli in the lungs.
Q5: Balloon-like structures present inside the lungs are called
(a) alveoli
(b) bronchioles
(c) bronchi
(d) alveolar ducts
Ans: (a)
These are small, balloon-like structures present inside the lungs where the exchange of gases occurs.
Q6: Haemoglobin, the respiratory pigment is not found in
(a) WBC
(b) RBC
(c) platelets
(d) plasma
Ans: (a)
White blood cells (WBC) are part of the immune system and help the body fight infections. Unlike red blood cells (RBC), they do not contain the respiratory pigment haemoglobin.
Q7: Pacemaker is meant for:
(a) transporting liver.
(b) transplanting heart.
(c) initiation of heart beats.
(d) regulation of blood flow.
Ans: (c)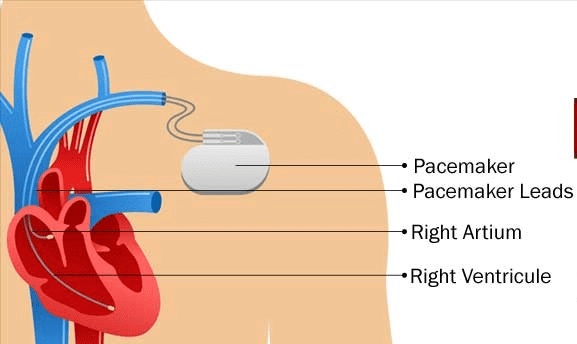 PacemakerA pacemaker is a small device that's placed in the chest to help control abnormal heart rhythms. It uses electrical pulses to prompt the heart to beat at a normal rate.
PacemakerA pacemaker is a small device that's placed in the chest to help control abnormal heart rhythms. It uses electrical pulses to prompt the heart to beat at a normal rate.
Q8: Veins can be differentiated from arteries because the veins
(a) have valves
(b) have hard walls.
(c) have pure blood in them.
(d) have thick walls.
Ans: (a)
Veins are blood vessels that carry blood towards the heart. They have valves that prevent the backflow of blood, which is a feature that differentiates them from arteries.
Q9: The rate at which oxygen moves from the alveoli of our lungs into our blood
(a) depends on the difference in oxygen concentration between the alveoli and the bloo(d)
(b) depends on the color of the alveoli.
(c) depends on the availability of energy to transport gases across the membrane.
(d) none of the above
Ans: (a)
The rate at which oxygen moves from the alveoli of our lungs into our blood depends on the difference in oxygen concentration between the alveoli and the blood.
Q10: Heart beat can be initiated by
(a) Sino-auricular node
(b) Sino-auricular node
(c) Sodium ion
(d) Purkinje’s fibres
Ans: (a)
This node is a group of cells situated in the wall of the right atrium of the heart. It has the capacity to initiate a heartbeat and is hence often referred to as the natural pacemaker.
Q11: Erythropoesis may be stimulated by the deficiency of
(a) Iron
(b) Oxygen
(c) Protein
(d) None of these
Ans: (b)
Erythropoiesis, the production of red blood cells, may be stimulated by a deficiency of oxygen in the body.
Q12: The chief function of lymph nodes in mammalian body is to
(a) produce RBCs
(b) collect and destroy pathogens
(c) produce a hormone
(d) destroy the old and worn out red blood cells
Ans: (b)
Lymph nodes play a crucial role in the body's immune system by trapping and destroying pathogens, such as bacteria and viruses.
Q13: Select the correct statement?
(a) Heterotrophs do not synthesise their own food
(b) Heterotrophs utilise solar energy for photosynthesis.
(c) Heterotrophs synthesise their own food
(d) Heterotrophs are capable of converting carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates.
Ans: (a)
They depend on other organisms for their food.
Q14: During deficiency of oxygen in tissues of human beings, pyruvic acid is converted into lactic acid in the
(a) cytoplasm
(b) chloroplast
(c) mitochondria
(d) golgi body
Ans: (a)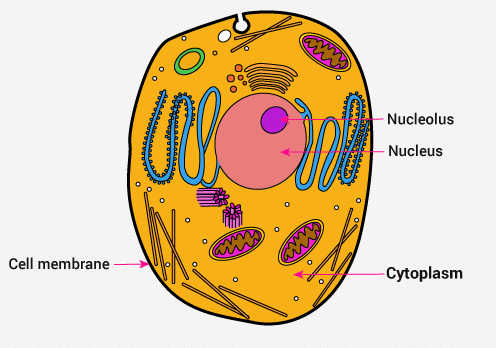 During deficiency of oxygen, pyruvic acid is converted into lactic acid in the cytoplasm of the cell.
During deficiency of oxygen, pyruvic acid is converted into lactic acid in the cytoplasm of the cell.
Q15: The phenomenon of normal breathing in a human being comprises.
(a) an active inspiratory and a passive expiratory phase.
(b) a passive inspiratory and an active expiratory phase.
(c) both active inspiratory and expiratory phases.
(d) both passive inspiratory and expiratory phases.
Ans: (a)
Normal breathing involves an active phase of inspiration, where muscles contract to pull air into the lungs, and a passive phase of expiration, where muscles relax to let air out.
Q16: Filteration unit of kidney is
(a) ureter
(b) urethra
(c) neuron
(d) nephron
Ans: (d)
Nephron is the basic structural and functional unit of the kidney. It is responsible for the filtration of blood and the removal of waste products.
Q17: Column of water within xylem vessels of tall trees does not break under its weight because of:
(a) Tensile strength of water
(b) Lignification of xylem vessels
(c) Positive root pressure
(d) Dissolved sugars in water
Ans: (a)
This refers to the ability of water to resist breaking under tension, which is why the column of water within xylem vessels of tall trees does not break under its weight.
Q18: Roots play insignificant role in absorption of water in:
(a) Pistia
(b) Pea
(c) Wheat
(d) Sunflower
Ans: (a)
In this water plant, the roots play an insignificant role in the absorption of water as it floats on the water surface and absorbs water directly from its surroundings.
Q19: Human urine is usually acidic because
(a) excreted plasma proteins are acidi(c)
(b) potassium and sodium exchange generates acidity.
(c) hydrogen ions are actively secreted into the filtrate.
(d) the sodium transporter exchanges one hydrogen ion for each sodium ion in peritubular capillaries.
Ans: (c)
This process contributes to the acidity of urine.
Q20: Which one of the following animals has two separate circulatory pathways?
(a) Lizard
(b) Whale
(c) Shark
(d) Frog
Ans: (b)
Whales, like all mammals, have a double circulatory system. This means they have two separate pathways for blood flow - one for oxygenated blood and one for deoxygenated blood.
Q21: Cow has a special stomach as compared to that of a lion in order to
(a) absorb food in better manner.
(b) digest cellulose present in the food.
(c) assimilate food in a better way.
(d) absorb large amount of water.
Ans: (b)
Cows have a complex digestive system with a special stomach to break down cellulose found in their plant-based diet.
Q22: Which of the following is not an enzyme?
(a) Lipase
(b) Amylase
(c) Trypsin
(d) Bilirubin
Ans: (d)
Bilirubin is not an enzyme but a yellowish substance produced by the breakdown of old red blood cells. High levels of bilirubin can lead to jaundice.
Fill in the blanks
Q1: The oxygen picked up by haemoglobin gets _________ with blood to various ________ .
Ans: transported, tissues
The oxygen picked up by haemoglobin gets 'transported' with blood to various 'tissues'. This means that oxygen, after being absorbed by haemoglobin present in the red blood cells, is carried or transferred through the bloodstream to different body tissues that require it for their metabolic activities.
Q2: Amoeba exhibits _______ nutrition.
Ans: holozoic
An amoeba exhibits 'holozoic' nutrition. This indicates that an amoeba feeds in a manner similar to humans, i.e., it ingests solid food particles, digests them internally, and throws out the waste. This type of nutrition is termed as holozoic nutrition.
Q3: Chlorophyll is mainly found in the__________.
Ans: leaves
Chlorophyll is mainly found in the 'leaves'. Chlorophyll is a green pigment that absorbs light energy for photosynthesis, and it's predominantly located in the chloroplasts of leaf cells, where the process of photosynthesis primarily takes place.
Q4: ATP is the ___________ for most cellular processes.
Ans: energy currency
ATP is the 'energy currency' for most cellular processes. This means that Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the primary energy carrier in all living organisms. The energy required for various biochemical reactions in the body is stored and transported by ATP.
Q5: The walls of the alveoli contain an extensive network of ____________ .
Ans: blood vessels
The walls of the alveoli contain an extensive network of 'blood vessels'. This network of blood vessels allows for the exchange of gases, with oxygen from the air in the alveoli diffusing into the blood, and carbon dioxide in the blood diffusing out into the alveoli to be exhaled.
Q6: The oral cavity opens into the ____________ .
Ans: pharynx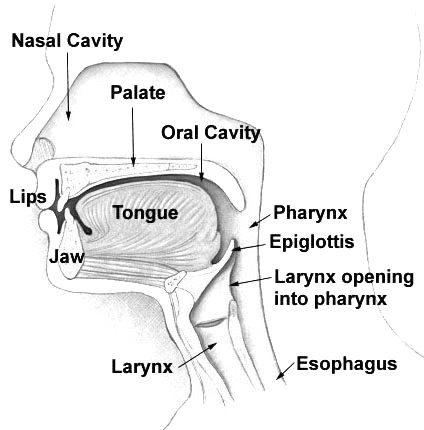 The oral cavity opens into the 'pharynx'. This means that the mouth or oral cavity leads to the pharynx, a part of the digestive and respiratory systems, which serves as a pathway for food to the esophagus and air to the larynx and trachea.
The oral cavity opens into the 'pharynx'. This means that the mouth or oral cavity leads to the pharynx, a part of the digestive and respiratory systems, which serves as a pathway for food to the esophagus and air to the larynx and trachea.
Q7: _____________ is the first part of small intestine.
Ans: Duodenum
'Duodenum' is the first part of the small intestine. This means that the first section of the small intestine that receives partially digested food from the stomach is called the duodenum. It plays a crucial role in the further digestion of food.
Mark the statements True (T) or False (F)
Q1: Anaerobic reactions after glycolysis produce lactic acid, or ethanol.
Ans: True
In the absence of oxygen, the process of glycolysis in anaerobic respiration is followed by fermentation. In human muscles, lactic acid fermentation happens which leads to the production of lactic acid. In yeast cells, alcoholic fermentation happens which leads to the production of ethanol. Therefore, the statement is true.
Q2: As compared to aerobic respiration, anaerobic respiration produces more energy.
Ans: False
Anaerobic respiration produces less energy compared to aerobic respiration. In aerobic respiration, glucose is completely broken down into carbon dioxide and water, releasing 38 ATP molecules which is a higher amount of energy. In anaerobic respiration, glucose is incompletely broken down and only 2 ATP molecules are generated, hence less energy is produced.
Q3: Stomach serves as a storehouse of food where complete digestion takes place.
Ans: False
The stomach does serve as a storehouse where food can be stored for 2-4 hours, but it is not the site for complete digestion. The process of digestion starts in the stomach with the action of gastric juices but it is completed in the small intestine with the help of various enzymes and intestinal juices.
Q4: Gastric glands are present in small intestine.
Ans: False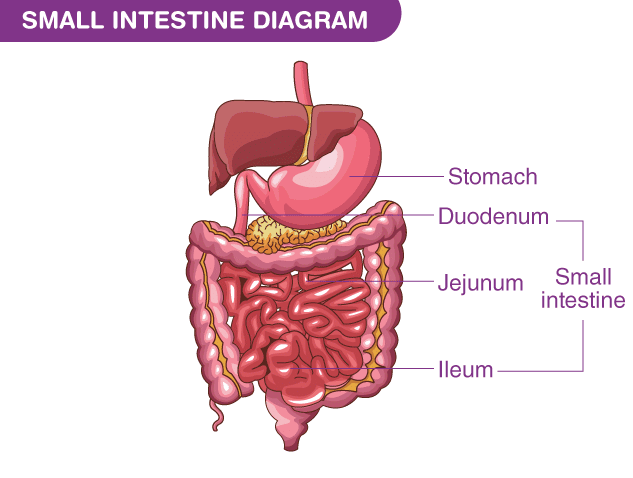 Gastric glands are not present in the small intestine. They are located in the stomach. They secrete gastric juice which contains enzymes like pepsin for the digestion of proteins. The small intestine has its own glands called intestinal glands which secrete intestinal juice.
Gastric glands are not present in the small intestine. They are located in the stomach. They secrete gastric juice which contains enzymes like pepsin for the digestion of proteins. The small intestine has its own glands called intestinal glands which secrete intestinal juice.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Life Processes- 1 Class 10 Worksheet Science
| 1. What are the different types of life processes in living organisms? |  |
| 2. How does nutrition play a crucial role in life processes? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of respiration in life processes? |  |
| 4. How does transportation help in life processes in living organisms? |  |
| 5. Why is excretion important for life processes in living organisms? |  |






















