Class 7 Geography Chapter 5 Question Answers - Water
Q1. When you think of water, what images came to your mind?
Answer:
Three states of water: solid, liquid and gaseous.
- Water running in rivers, canals, streams etc.
- Frozen and moving like glaciers.
- In the form of steam (evaporation)
- In the form of droplets (condensation)
- Falling as rainfall (Rainfall)
- As ground water/Water in taps.
- In the wells, ponds, pools etc
Q2. Discuss the distribution of water bodies.
Answer:
- Nearly 75% of the earth’s surface is covered with water.
- There is more water than land on the earth, still so many countries face water scarcity due to the fact that most of this water is salty or it is polluted beyond use.
- Moreover all the water on the earth is not available to us.
- The following table gives the distribution of water in percentage.
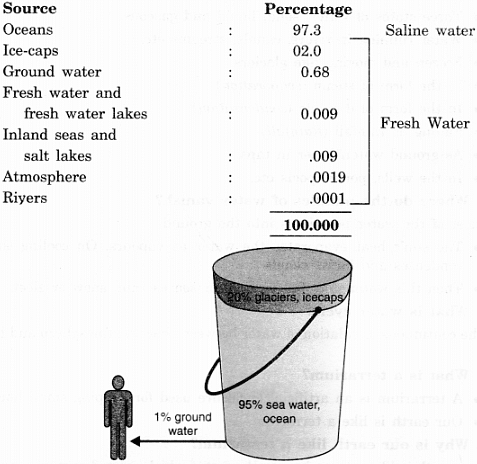
Q3. Why is water important to us? Suggest few ways to conserve water.
Answer:
- Water is very necessary for us. Water alone can quench the thirst thirsty.
- Water is needed for survival of plant and animal life.
Water is very essential and we should conserve it:
- By not wasting it during brushing, bathing, washing etc.
- By trapping the rain water by water shed development or rain water harvesting.
- By recycling water.
- By making check dams and bunds on the fields etc.
Q4. How are Tsunamis formed? How do they cause destruction?
Answer:
Tsunami is a Japanese word meaning harbour waves.
- Winds blowing at high speed during a storm form huge waves.
- An earthquake, volcanic eruption or underwater landslides can shift large amount of ocean water.
- These tidal waves called Tsunami may be as high as 15 m. It travels at a speed of more than 700 km/hr.
- The areas near the coasts get submerged and it leads to earthquakes also.
Q5. Briefly write about the sequence of events leading to Tsunami of 2004 in the Indian Ocean.
Answer:
Tsunami of 26 December 2004 was the result of the earthquake that had its epicentre close to western boundary of Sumatra. It caused havoc in the Indian Ocean.
- Due to the earthquake measuring 9.0 on Richter scale the Indian plate went under Burma plate.
- The ocean floor was displaced by about 10-20 m. Huge mass of ocean water flowed to fill the gap.
- After thrusting the Indian plate and Burma plate, this water rushed back towards the coastline.
- Tsunami at the speed of 800km /hr washed some of the islands in the Indian Ocean.
- As the wave moved away from the epicentre of earthquake the speed declined 700-900km/hr to 70-80km/hr.
- Waves travelled up to a depth of 3 km from the coast.
Q6. What were the effects of the Tsunami?
Answer:
Tsunami caused severe destruction.
- Some of the islands of Indian Ocean were completely washed away.
- Indira point in Andaman got completely submerged.
- More than 10,000 people were killed and more than a lakh of houses were affected.
- Coastal areas of Tamil Nadu. Kerala, Puducherry, Andhra Pradesh and the Andaman and Nicobar islands were worst affected.
Q7. Why was the Tsunami of December 26, 2004 very devastating?
Answer:
- The Tsunami that ravaged the South and South-east Asian coasts in December 2004 was the most devastating Tsunami in the last several hundred years.
- The large damage caused to life and property was primarily a result of the following:
- lack of monitoring,
- the early warning systems, and
- lack of knowledge among the coast dwellers of the Indian ocean.
- The first indication that Tsunami is approaching was the rapid withdrawal of water from the coastal region.
- It was followed by destructive wave.
- When this happened on the coast, instead of people going to high ground, they started assembling at the coast to view the miracle.
- It resulted in a large casualty of curious onlookers when the gigantic wave-tsunami struck.
Q8. Explain Spring and Neap Tides.
Answer:
During the full moon and new moon days, the sun, the moon and the earth are in the same liNe.
- On this day the tides are highest.
- These tides are called Spring Tides.
- But when the moon is in its first and last quarter, the ocean waters get drawn in diagonally opposite direction by the gravitational pull of the sun and the earth.
- It results in low tides.
- These tides are called Neap Tides.
Q9. Describe the importance of tides to man.
Answer:
- High tides help in navigation.
- They raise the water level close to the shores.
- This helps the ships to arrive at the harbour more easily.
- The high tides also help in fishing.
- Many more fish come closer to the shore during the high tides.
- This enables fishermen to get a plentiful catch.
- The rise and fall of water due to tides is used to generate electricity in some places like the gulf of Khambant.
Q10. Explain the advantages and disadvantages of ocean currents to man.
Answer:
The ocean currents influence the temperature conditions of the coastal areas.
- Warm currents increase the temperature over land surface.
- The areas where warm and cold currents meet, provide the best fishing grounds of the world.
- Seas Around Japan and the eastern coast of North America are such examples.
- The areas where a warm and cold current meet, also experience foggy weather making it difficult for navigation.
Q11. What are Ocean currents?
Answer:
Ocean currents are streams of water flowing constantly on the ocean surface in definite directions. They may be warm or cold currents:
- Warm currents originate near equator and move towards poles. They bring about warm temperatures over land surfaces, for example Gulf stream.
- Cold currents originate near poles and move towards tropical or lower latitudes. They bring about coolness over land surfaces, for example Labrador current.
Q12. Why are tides important to us?
Answer: Tides important to us because:
- High tides help in navigation.
- They raise the water level close to the shores. This helps the ships to arrive at the harbour more easily.
- The high tides also help in fishing. Many more fish come closer to the shore during the high tide. This enables fishermen to get a plentiful catch.
- The rise and fall of water due to tides is being used to generate electricity in some places.
Q13. Why the quality of water is deteriorating?
Answer: Quality of water is deteriorating because
- River water, which is our primary source of water, gets contaminated due to various reasons such as direct disposal of sewage by municipalities, excessive discharge of industrial pollutants, use for daily chores like washing, bathing, livestock bathing, garbage disposal, etc.
- Water sourced from groundwater too has deteriorated due to the excessive use of pesticides & insecticides in agriculture, which seep into the groundwater as well as get washed away into the rivers.
Q14. Write a short note on Tsunami?
Answer:
- Tsunami is a Japanese word that means “Harbour waves” as the harbours get destroyed whenever there is tsunami.
- An earthquake, a volcanic eruption or underwater landslides can shift large amounts of ocean water.
- As a result a huge tidal wave called tsunami, that may be as high as 15m., is formed. The largest tsunami ever measured was 150m. high. These waves travel at a speed of more than 700 km. per hour.
- The tsunami of 2004 caused wide spread damage in the coastal areas of India. The Indira point in the Andaman and Nicobar islands got submerged after the tsunami.
Q15. What are the major movements of ocean water?
Answer: The movements that occur in oceans can be broadly categorised as: waves, tides and currents.
- Waves: When the water on the surface of the ocean rises and falls alternately, they are called waves. Waves are formed when winds scrape across the ocean surface. The stronger the wind blows, the bigger the wave becomes.
- Tides: The rhythmic rise and fall of ocean water twice in a day is called a tide. It is high tide when water covers much of the shore by rising to its highest level. It is low tide when water falls to its lowest level and recedes from the shore. The strong gravitational pull exerted by the sun and the moon on the earth’s surface causes the tides.
- Ocean Currents: Ocean currents are streams of water flowing constantly on the ocean surface in definite directions. The ocean currents may be warm or cold. Generally, the warm ocean currents originate near the equator and move towards the poles. The cold currents carry water from polar or higher latitudes to tropical or lower latitudes. The Labrador Ocean current is cold current while the Gulf Stream is a warm current.
|
63 videos|371 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Geography Chapter 5 Question Answers - Water
| 1. What are the different states of water? |  |
| 2. How does water turn into ice? |  |
| 3. What is the boiling point of water? |  |
| 4. How does water evaporate? |  |
| 5. Why is water essential for life? |  |
















