Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Question Answers - Control and Coordination
Q1: How do we detect smell of hot spicy food from a distance?
Ans: We have olfactory receptors in our nose which detect the smell of hot spicy food. This information is transmitted by nerve impulse to olfactory lobes of forebrain which interpret the information.
Q2: Why do tendrils coil around hard objects or support?
Ans: The tendrils coil around hard objects or support due to a stimulus of touch (thigmotropism) which causes less growth on the side in contact with support than the side which is away from it. This unequal growth of two sides of tendril makes it coil around the support.
Q3: Name the hormones reponsible for regulation.
(i) Metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins
(ii) Balance of calcium and phosphate
(iii) Blood pressure
(iv) Water and electrolyte balance.
Ans: (i) Thyroxin
(ii) Parathyroid hormone
(iii) Adrenaline
(iv) Vasopressin
Q4: What is an association neuron?
Ans: Association neurons are present in cortex part of spinal cord between the sensory neuron and motor neuron. It helps to interconnect the signals between the sensory neuron and motor neuron by forming synapse with axon of sensory neuron and dendrite of motor neuron.
Q5: How are the brain and spinal cord protected from mechanical shock?
Ans: Brain is present in a bony box called cranium (skull), spinal cord is protected by vertebral column. The cerebrospinal fluid present around the brain and spinal cord protect it from mechanical shock.
Q6: Which functions are regulated by the forebrain?
Ans: The thinking part of the brain is forebrain which controls:
- Movement of voluntary muscles.
- Hearing, smell, sight, hunger, thirst, pain, etc. by its association areas.
- It also stores information and controls intelligence.
Q7: Explain how a squirrel responds a dangerous situation with help of its hormonal system.
Ans: When a squirrel perceives a dangerous situation, adrenaline hormone is released in its blood which increases its heart beat and blood supply to tissues. This provides energy to its cells and tissues at a faster rate and enables it to run away from emergency situation.
Q8: How are sensory neurons different from motor neurons?
Ans: Sensory neuorons take information from receptors and transmit the impulses towards central nervous system. Motor neurons carry message from control nervous system to the muscle, gland or an organ to enable it to respond.
Q9: How are receptors different from effectors?
Ans: Receptors are cells, tissues or organs which receive the information in form of stimulus. For example, photoreception, gustatory receptors, etc. Effectors are muscles, glands tissues or cells which respond according to the information received through motor neuron from the central nervous system.
Q10: Define peripheral nervous system. What are its components?
Ans: The nerves that directly arise from the central nervous system and contact different parts of our body to help their involuntary controls. Spinal nerves and cranial nerves are components of peripheral nervous system.
Q11: What are nastic and curvature movements? Give one example of each.
Ans: The non-directional responses to stimuli are called nastic movements e.g., drooping of leaves of touch-me-not plant. Curvature movement are the movement of plant parts towards or away from stimulus e.g., bending of shoot towards light.
Q12: How does feedback mechanism regulate the hormone action? Explain with the help of an example.
Ans: The presence or absence of a particular hormone can regulate its further formation with the help of a regulatory mechanism called feedback mechanism.
Example: Hypothalamus regulates thyroxin levels in blood by secreting thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). If the thyroxine levels increases then hypothalamus stop secreting TSH in order to reduce the production of thyroxine from thyroid gland.
Low levels of thyroxin in blood again switches on the release of TSH from hypothalamus to increase levels of thyroxin in blood.
Q13: What are the different types of neurons and their functions in the human body?
Ans: There are mainly three types of neurons:
- Sensory neuron: They transmit information from receptors towards the central nervous system.
- Motor neuron: They transmit information from the central nervous system to effectors like muscles or glands.
- Relay neuron: It serves as a link between the sensory and the motor neurons in the brain or spinal cord.
Q14: What are the limitations to the use of electrical impulse?
Ans: The limitations to electrical impulse are:
- Only those cells used that are connected by nervous tissue, while other tissues do not receive the information directly.
- It takes some times to reset the mechanism of generation of new electrical impulse once an electrical impulse had been generated.
Q15: Depict the mechanism of Nervous tissue action.
Ans: The mechanism of nervous tissue action is: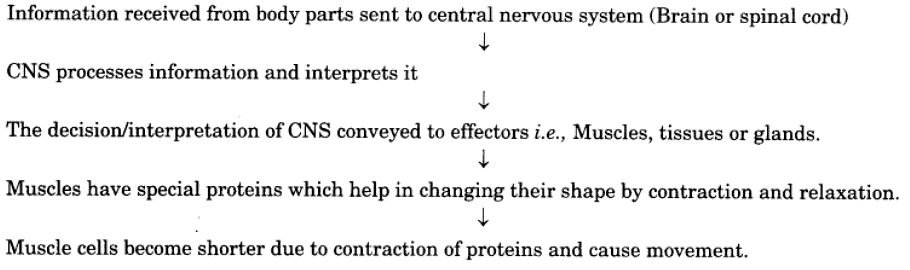
Q16: What is a tropic movement? Explain with an example.
Ans: The directional movements caused in plants due to an external stimuli are called tropic movements.
Example: During phototropism, the shoot bends towards light and show positive phototropism while the roots bend away from light to show negative phototropism.
Q17: What will happen if intake of iodine in our diet is low?
Ans: Iodine helps in the synthesis of thyroxin hormone from thyroid gland. Thyroxin hormone is necessary for carbohydrate, proteins and fat metabolism.
Deficiency caused due to low level of iodine in diet might result is a disease called goitre in the person.
Q18: Answer the following:
(a) Which hormone is responsible for the changes noticed in females at puberty?
(b) Dwarfism results due to deficiency of which hormone?
(c) Blood sugar level rises due to deficiency of which hormone?
(d) Iodine is necessary for the synthesis of which hormone?
Ans: (a) Oestrogen
(b) Growth hormone
(c) Insulin
(d) Thyroxin
Q19: Answer the following:
(a) Name the endocrine gland associated with brain.
(b) Which gland secretes digestive enzymes as well as hormones?
(c) Name the endocrine gland associated with kidneys.
(d) Which endocrine gland is present in males but not in females?
Ans: (a) Pituitary
(b) Pancreas
(c) Adrenal gland
(d) Testes
Q20: Label the parts of a neuron in figure given below.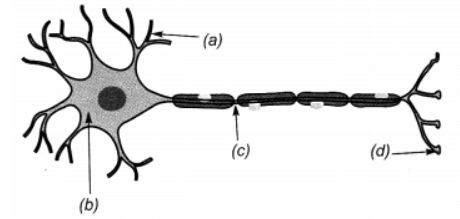
Ans:
(a) Dendrite
(b) Cell Body
(c) Axon
(d) Nerve ending
|
666 docs
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Question Answers - Control and Coordination
| 1. What is the role of the nervous system in control and coordination? |  |
| 2. How does the endocrine system contribute to control and coordination? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system? |  |
| 4. How do reflex actions work in the body? |  |
| 5. What are the major glands of the endocrine system and their functions? |  |
















