Unit Test (Solutions): Chemical Reactions & Equations | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
M.M. 30
Attempt all questions.
- Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
- Question number 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
Q1: Which of the following reactions is an endothermic reaction? (1 Mark)
(a) Burning of coal.
(b) Decomposition of vegetable matter into compost.
(c) Process of respiration.
(d) Decomposition of calcium carbonate to form quicklime and carbon dioxide.
Ans: (d)
The reactions which require energy in the form of heat, light or electricity to break reactants are called endothermic reactions.
Q2: The following reaction is an example of a 4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) → 4NO(g) + 6H2O(g) (1 Mark)
(i) Displacement reaction
(ii) Combination reaction
(iii) Redox reaction
(iv) Neutralisation reaction
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Ans: (c)
The given reaction is a redox reaction because oxidation and reduction both take place simultaneously. Also, it is a displacement reaction because the hydrogen of NH3 has been displaced by oxygen.
Q3: Why is hydrogen peroxide kept in colored bottles? (1 Mark)
Ans: Hydrogen peroxide decomposes into H2O and O2 in the presence of sunlight, and hence to prevent decomposition, they are kept in colored bottles.
Q4: N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3, name the type of reaction. (1 Mark)
Ans: It is a combination reaction.
Q5: Why do silver articles become black after some time when exposed to air? (1 Mark)
Ans: They get tarnished by reacting with atmospheric air to form silver sulphide.
Q6: In the equations given below, state giving reasons, whether substances have been oxidised or reduced. (2 Mark)
(i) PbO + CO → Pb + CO2
(ii) H2S + Cl2 → 2HCl + S
Ans: (i) Carbon monoxide is oxidised as it gains oxygen.
(ii) Chlorine is reduced as it gains hydrogen.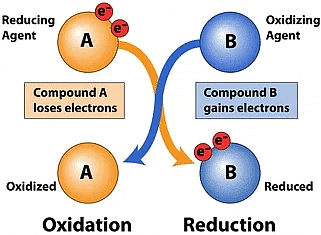
Q7: Can rancidity retard by storing foods away from the light? (2 Mark)
Ans: In the absence of light, the oxidation of fats and oils present in food is slowed down and hence the development of rancidity is retarded.
Q8: What are the different ways can make more informative about the chemical equation? (2 Mark)
Ans:
(i) By indicating the “physical states” of reactants and products.
(ii) By indicating the “heat changes” taking place in the reaction.
(iii) By indicating the “conditions” under which the reaction takes place.
Q9: The action of heat on ferrous sulphate is an example of a decomposition reaction. (3 Mark)
Ans: On heating, ferrous sulphate crystals lose water, and anhydrous ferrous sulphate (FeSO4) is formed. So, their colour changes from light green to white. On further heating, anhydrous ferrous sulphate decomposes to form ferric oxide (Fe2O3), sulphur dioxide (SO2) and sulphur trioxide (SO3).
2FeSO4 → ΔFe2O3 + SO2 + SO3
The reaction for the decomposition of ferrous sulphate is as above.
Q10: 2 g of ferrous sulphate crystals are heated in a dry boiling tube. Answer the following :
(i) List any two observations.
(ii) Name the type of chemical reaction taking place.
(iii) Write the chemical equation of the reaction. (3 Marks)
Ans. (i) Two observations are :
(a) Change in state and color.
(b) Evolution of gas
(ii) Decomposition reaction
(iii) 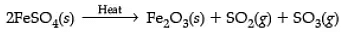 Q11: Write the balanced chemical equations for
Q11: Write the balanced chemical equations for
Q11: Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions (3 Marks)
(a) Sodium carbonate on reaction with hydrochloric acid in equal molar concentrations gives sodium chloride and sodium hydrogencarbonate.
(b) Sodium hydrogencarbonate on reaction with hydrochloric acid gives sodium chloride, water and liberates carbon dioxide.
(c) Copper sulphate on treatment with potassium iodide precipitates cuprous iodide (Cu2 I2 ), liberates iodine gas and also forms potassium sulphate.
Ans:
(a) Na2CO3 + HCl → NaCl + NaHCO3
(b) NaHCO3 + HCl → NaCl + H2O + CO2
(c) 2CuSO4 + 4Kl → 2K2SO4 + CU2l2 + I2
Q12: Identify the type of chemical reaction in the following statements and define each of them :
(i) Digestion of food in our body
(ii) Rusting of iron
(iii) Heating of manganese dioxide with aluminum powder.
(iv) Blue color of copper sulphate solution disappears when iron filings are added to it.
(v) Dilute hydrochloric acid is added to sodium hydroxide to form sodium chloride and water. (5 Marks)
Ans. (i) Decomposition Reaction: Carbohydrates are broken down to form glucose.
(ii) Oxidation Reaction: When an iron object is left in moist air for a considerable time, it gets covered with a red-brown flaky substance called rust.
(iii) Displacement reaction: More reactive metal displaces less reactive metal from its salt solution.
(iv) Displacement reaction: More reactive metal displaces less reactive metal from its salt solution.
(v) Double displacement reaction: Reaction in which two compounds react by exchanging ions to form two new compounds.
Q13: What happens when zinc granules are treated with dilute solution of H2SO4, HCl, HNO3, NaCl and NaOH, also write the chemical equations if reaction occurs. (5 Marks)
Ans: (i) Zinc reacts with dilute H2SO4 to form zinc sulphate and hydrogen gas.
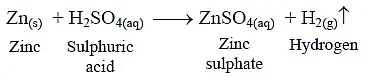
(ii) Zinc reacts with dilute HCl to form zinc chloride and hydrogen gas.
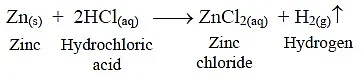
(iii) Zinc reacts with dilute HNO3 and forms zinc nitrate, nitrous oxide and water.
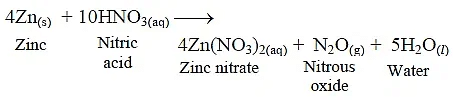
(iv) Zinc does not react with NaCl.
(v) Zinc reacts with sodium hydroxide to form sodium zincate and hydrogen gas.
|
80 videos|567 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions): Chemical Reactions & Equations - Science Class 10
| 1. What are chemical reactions? |  |
| 2. How are chemical reactions represented in equations? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of chemical reactions? |  |
| 4. How can you balance a chemical equation? |  |
| 5. Why is it important to study chemical reactions and equations? |  |






















