Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Question Answers - How do Organisms Reproduce?
Q1: What is placenta? Mention its role during pregnancy.
Ans: A disc shaped special tissue connection between embryo and uterine wall is called placenta. It contains villi on the embryo’s side of the tissue which are surrounded by blood spaces on the mother’s side.
Roles of placenta are:
- It provides a large surface area for glucose and oxygen to pass from mother to the embryo.
- Removes waste substances produced by the developing embryo.
Q2: What are various ways to avoid pregnancy? Elaborate any one method.
Ans: (a) Contraceptive methods are used to avoid pregnancy which are of the following types:
- Mechanical
- Drugs (as pills)
- Loop or copper T and
- Surgical method.
(b) Surgical Methods:
- Vasectomy: The vas deferens of male is blocked to prevent sperm transfer.
- Tubectomy: The fallopian tube of female is blocked to prevent egg to reach uterus.
- Copper-T or loop is placed in uterus to prevent pregnancy.
Q3: How does fertilisation take place? Fertilisation occurs once in a month. Comment.
Ans:
- Sperm enters through the vaginal passage during sexual intercourse and moves upwards.
- Egg released from the ovary reaches the fallopian tube (oviduct).
- Sperm encounters egg in the oviduct and fertilisation takes place. Fallopian tube (oviduct) is the site of fertilisation.
- An egg is released once every month by the ovary as usually one ovum (egg) is released by an ovary during each cycle.
Q4: Reproduction is essentially a phenomenon that is not for survival of an individual but for the stability of a species. Justify.
Ans:
- The energy needed for survival of the organisms is obtained by them from life processes such as nutrition and respiration.
- Reproduction needs a lot of energy.
- Genetic material is transferred from one generation to the next as a result of reproduction through DNA copying.
- DNA copying takes place with high constancy and considerable variations, that is, advantages to the species for stability in the changing environment.
Q5: Describe sexually transmitted diseases and mention the ways to prevent them.
Ans: Sexually transmitted diseases are infectious diseases transmitted during sexual contact. Various agents like bacteria and virus cause these diseases. For example, Gonorrhoea, syphilis, genital herpes, chlamydiasis, genital warts, trichomoniasis, hepatitis-B and HIV-AIDS are sexually transmitted diseases.
Principles to follow to prevent such infections:
- Avoid sex with unknown partners/multiple partners,
- Always use condoms during coitus.
- Use of mechanical barrier like condom prevents transmission of infection
- In case of doubt, go to a qualified doctor for early detection and get complete treatment if diagnosed with disease.
Q6: Why are budding, fragmentation and regeneration all considered as asexual types of reproduction? With neat diagrams explain the process of regeneration in Planaria.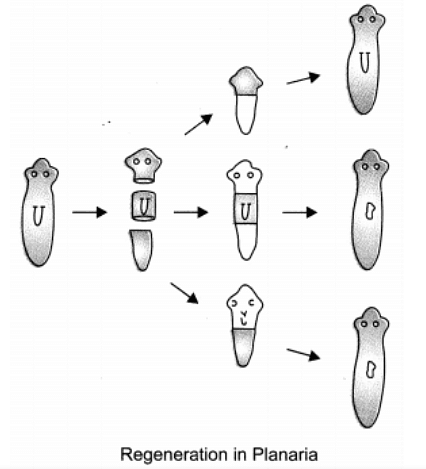 Ans: They are considered as asexual types of reproduction as all of them involve a single parent and no fusion of gametes take place in them.
Ans: They are considered as asexual types of reproduction as all of them involve a single parent and no fusion of gametes take place in them.
Q7: Write two points of difference between asexual and sexual types of reproduction. Describe why variations are observed in the offspring formed by sexual reproduction.
Ans: Asexual Reproduction:
- Single parent is involved.
- No fusion of gametes occur.
- Progeny is genetically identical to the parent.
- For example, Fission in Amoeba.
Sexual Reproduction:
- Two parents are involved.
- Fusion of gametes occurs.
- Variations occur in the progeny.
- For example, Human beings.
Fusion of gametes occurs during sexual reproduction. The gametes contain the same number of chromosomes but their DNA is not identical so variations arise among the offsprings.
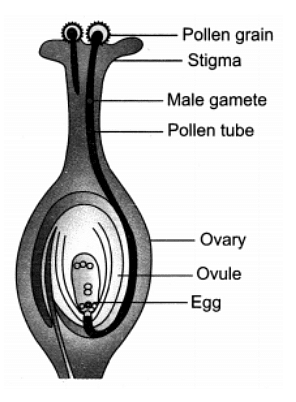
Q8: Distinguish between pollination and fertilisation. Mention the site and product of fertilisation in a flower. Draw a neat, labelled diagram of a pistil showing pollen tube growth and its entry into the ovule.
Ans:
- Pollination: The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of a flower is called pollination.
- Fertilisation: The process of fusion of male and female gametes to form a zygote is called fertilisation.
- The site of fertilisation is ovule. The product of fertilisation is zygote.
Q9: Distinguish between a gamete and zygote. Explain their roles in sexual reproduction.
Ans: The sex cell or germ cell in sexual reproduction is called gametes. There are two types of gametes, male and female. A male and a female gamete fuse with each other during fertilisation to form a zygote.
The gametes possess characters of their parents in their DNA and their fusion brings characters of both parents into one zygote cell. Zygote is the first cell of the next generation which divides to form an embryo which subsequently grows into a new individual.
Q10: Draw the diagram of a flower and label the four whorls. Write the names of gamete producing organs in the flower.
Ans: Male gamete forming part – anther/stamen
Female gamete forming part – pistil/ovary/ovule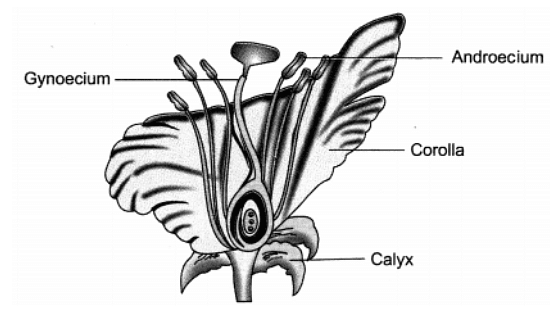
|
666 docs
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Question Answers - How do Organisms Reproduce?
| 1. How do organisms reproduce? |  |
| 2. What is the difference between sexual and asexual reproduction? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of sexual reproduction? |  |
| 4. What are the advantages of asexual reproduction? |  |
| 5. Can organisms switch between sexual and asexual reproduction? |  |





















