Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Question Answers - Motion
Q1: A person moves along the boundary of a square field of side 10 m in 20 s. What will be the magnitude of displacement of that person at the end of 2 minutes 20 seconds?
Ans: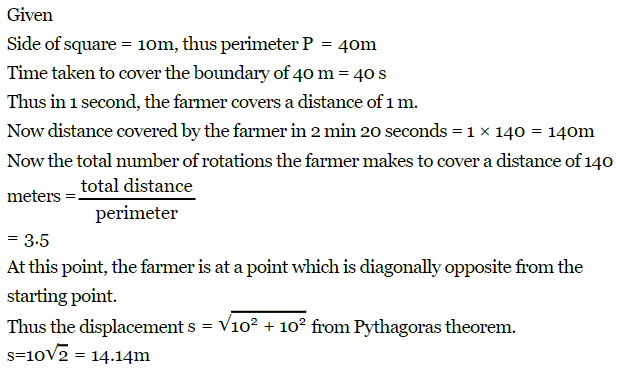
Q2: Neha swims in a 90 m long pool. She covers 180 m in one minute by swimming from one end to the other and back along the same straight path. Find the average speed and average velocity of Neha.
Ans:
Total distance = 180 m
Total displacement = 0
Time taken t = 1 min = 60 s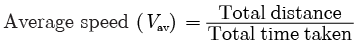
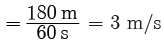
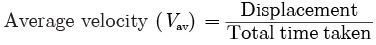
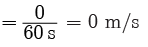
Q3: A car decreases its speed from 80 km/h to 60 km/h is 5 seconds. Find the acceleration of the car.
Ans: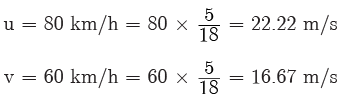
Time (t) = 5 s
Acceleration (a) = 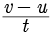
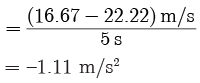
Q4: A train starting from a railway station and moving with uniform acceleration, attains a speed 40 km/h in 10 minutes. Find its acceleration.
Ans:
u = 0 (starting from rest)
v = 40 km/h= 11.11 m/s
Time t = 10 minutes = 600 s
Acceleration (a) = 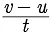
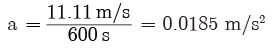
Q5: The average speed of a bicycle, an athlete and car are 18 km/h, 7 m/s and 2 km/min respectively. Which of the three is the fastest and which is the slowest
Ans: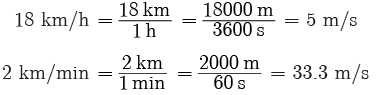
Thus, the average speeds of the bicycle, the athlete and the car are 5 m/s, 7 m/s and 33.3 m/s respectively. So, the car is the fastest and the bicycle is the slowest.
Q6: Figure shows distance-time graph of two objects A and B, which object is moving with greater speed when both are moving?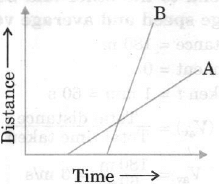
Ans: The line for object B makes a longer angle with the time-axis. Its slope is longer than the slope of the line for object A. Thus, the speed of B is greater than that of A.
Q7: Figure represents the speed time graph for a particle. Find the distance covered by the particle between t = 10 min and t = 30 min.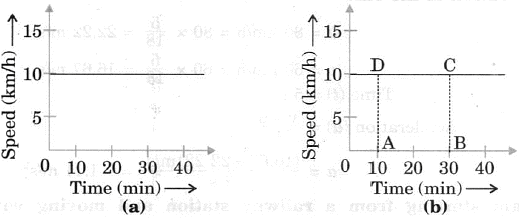
Ans:
We draw perpendicular lines from the 10-minute point and the 30-minute point to the time-axis (fig.). The distance covered is equal to the area of the rectangle ABCD, its value is
ABCD = (30 min - 10 min) x (10 km/h)
= 20 min × 10 km/h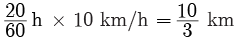
Q8: Find the distance covered by a particle during the time interval t = 0 to t = 20 s for which the speed time graph is shown in figure.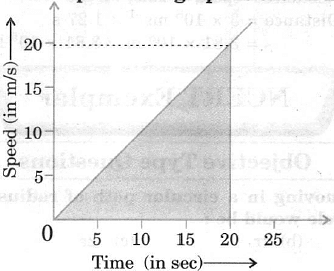 Ans:
Ans:
The distance covered in the time interval 0 to 20 s is equal to the area of the shaded triangle. So,
Distance = 1/2 x Base x Height
= 1/2 x (20 s) x (20 m/s)
= 200 m.
Q9: A bus moves 30 km in 30 min and the next 30 km. in 40 min. Calculate the average speed for the entire journey.
Ans: Given, the total time taken is 30 min + 40 min = 70 min and the total distance travelled is 30 km + 30 km = 60 km
The average speed is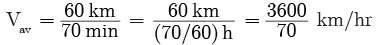
= 51.4 km/h
Q10: It is estimated that the radio signal takes 1.27 seconds to reach the Earth from the surface of the Moon. Calculate the distance of the Moon from the Earth. Speed of radio signal = 3 × 108 ms–1 (speed of light in air).
Ans:
Here,
time = 1.27 s
Speed = 3 × 108 ms–1
Distance = ?
Using distance = speed × time, we get
Distance = 3 × 108 ms–1 × 1.27 s
= 3.81 × 108 m
= 3.81 × 105 km
Q11: Divya walked 2 km on a straight road and then walked back 1 km. Which of the two quantities involved in her walking is greater- the scalar or vector?
Ans:
Distance travelled by Divya = 2 km + 1 km = 3 km
Displacement = 2 km – 1 km = 1 km
Hence, distance which is a scalar quantity is greater than the displacement which is a vector quantity.
Q12: Two satellites A and B revolve around a planet C. The time taken by satellite B to go around the planet is twice the time taken by A. Which of the two satellites will have a greater magnitude of velocity?
Ans:
Satellite A will have greater magnitude of velocity since velocity is inversely proportional to time. 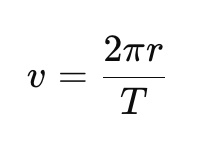
Q13: A child moving on a circular track of radius 40 m completes one revolution in 5 minutes. What is his (i) average speed (ii) average velocity in one full revolution?
Ans: Distance travelled in one revolution,
2p r =2p × 40m
Displacement in one revolution = 0
Time taken = 5 minutes = 5 × 60s
(i) Average speed = Distance / Time = 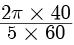
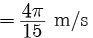
(ii) Average velocity = Displacement / Time = Zero
|
84 videos|478 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Question Answers - Motion
| 1. What is the definition of motion in physics? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of motion? |  |
| 3. How do you calculate speed and velocity? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between distance and displacement? |  |
| 5. What is Newton's first law of motion? |  |

















